
Key Takeaways
- Gorillas have excellent night vision and can see in the dark.
- Their eyes have a larger pupil and more rods, which are specialized cells for low-light vision.
- Gorillas also have a reflective layer behind their retina called the tapetum lucidum, which enhances their night vision.
- This adaptation allows gorillas to navigate and forage for food during the night, giving them a competitive advantage over other animals.
- Gorillas’ night vision is particularly useful in their natural habitat, where they live in dense forests with limited sunlight.
- Understanding the unique visual abilities of gorillas can help researchers and conservationists develop strategies to protect their habitats and ensure their survival.
To understand “Can Gorillas See in the Dark,” delve into the importance of understanding gorilla vision. Exploring this topic sheds light on their ability to navigate in low-light conditions. Understanding their vision is crucial in deciphering how gorillas adapt to their natural habitats and enhances our comprehension of their unique visual capabilities.
Can Gorillas See in the Dark?
Do gorillas have the ability to see in the dark? Let us discover the vision capabilities of these remarkable creatures.
Gorillas have a diurnal lifestyle, so their eyes are not adapted for the dark like nocturnal animals. However, they have features that help them navigate low-light environments.
For instance, their large eyes with pronounced brow ridges let more light in. Additionally, they have rod cells in their retinas which detect motion and light intensity. Finally, their tapetum lucidum boosts their vision even in dimly lit areas.
Importance of understanding gorilla vision
Gorillas rely on their sight to make sense of the world. To understand them better, we need to delve into their vision. Different aspects of their visual perception, like depth perception, color vision, and object recognition, are important for their daily lives.
Did you know gorillas have dichromatic vision? This means they can only see blue and green. This unique adaptation affects how they interact with their environment and other gorillas.
To gain more insight into gorilla vision, we need to employ specific methods. We can provide enrichment activities to stimulate their visual senses. Showing them diverse objects in different colors can boost their engagement and mental stimulation. Also, natural light sources in their environment can help them develop healthy eyes.
Gorilla Visual Abilities
To understand Gorilla Visual Abilities, explore how gorillas perceive their surroundings by examining an overview of their eyesight and comparing it to human vision. Delve into the fascinating aspects of their visual capabilities and gain insights into the unique ways gorillas experience the world around them.
Overview of gorilla eyesight
Gorillas are magnificent creatures of the animal kingdom, possessing visual prowess that rivals our own. Their strong retinas allow them to see colors and details that we cannot. Plus, their close-range vision is incredible! They can inspect objects with precision and accuracy.
Gorillas have an amazing ability to adapt to low light conditions. While humans struggle in the dark, gorillas can maneuver effortlessly through shadowy landscapes. This adaptation gives them an advantage in their habitat, letting them explore during dusk or dawn.
Comparison with human vision
Gorillas have amazing visual talents compared to humans! They can pick up colors and sense depth. Studies even show that they can recognize themselves in mirrors – a sign of self-awareness! Plus, their vision is specially made for living in the forest, helping them to find food and spot danger.
To learn more about gorillas’ visual abilities, researchers should explore their visual cortex and neural pathways. It could uncover great secrets about how their brains process visuals, differently from us.
It’s also recommended to make educational programs or exhibits that bring out the uniqueness of gorilla vision. This would help people to feel closer to these incredible creatures and understand why they need to be conserved.
Diving into the world of gorilla vision leads to knowledge about their evolution, and an appreciation of the variety of nature. Night vision goggles got nothin’ on these guys!
Adaptations for Low Light Conditions
To better understand how gorillas adapt to low light conditions, let’s delve into their specialized abilities and adaptations. Explore the details of their impressive vision in the dark and learn about their unique bodily adaptations that help them navigate and survive in dimly lit environments.
Details on gorilla’s ability to see in the dark
Gorillas have amazing vision in low-light conditions. Large pupils and a high density of rods in the retina help them gather dim light. Plus, their tapetum lucidum amplifies their sensitivity. This gives them an advantage when foraging for food at night.
Depth perception is another skill that helps gorillas move through dense vegetation and climb trees. Their visual acuity and depth perception let them move through their habitat easily.
In dark environments, gorillas don’t just rely on sight. They use touch and hearing too. These senses help them locate food and threats in limited visibility. It’s amazing how these creatures adapt to survive.
Observing gorillas in low light? Use night vision technology or infrared photography. That way, you can experience their world without disturbing them. Even in the darkest of shadows, these adaptations show how they survive.
Description of specialized adaptations
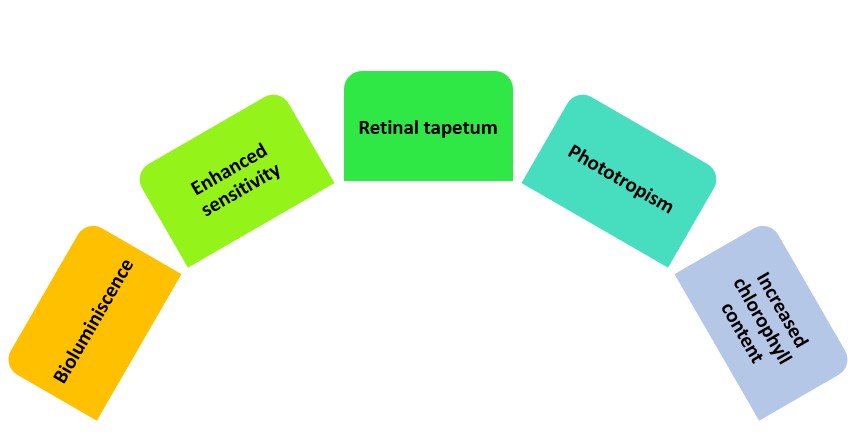
Specialized adaptations are unique traits that help organisms survive in low light. It enables them to flourish where others struggle. Let’s look at some of these remarkable features!
The table below shows the diverse range of specialized adaptations that let creatures thrive in dim conditions:
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Bioluminescence | Living organisms give off light, like fireflies and deep-sea fish. |
| Enhanced sensitivity | Eyes or other senses become more sensitive to capture even faint light. |
| Retinal tapetum | A reflective layer behind the retina, improving night vision in animals, like cats and owls. |
| Phototropism | Plants grow towards sources of light for photosynthesis. |
| Increased chlorophyll content | Plants produce more chlorophyll to absorb energy in dim light. |
Some deep-sea creatures have bioluminescent organs called photophores, emitting light through chemical reactions. This lets them blend in or draw prey in the dark ocean depths.
Nocturnal animals, such as bats, use echolocation to “see” their environment in complete darkness. They make high-frequency sounds and interpret the echoes to hunt food accurately.
These specialized adaptations show nature’s capacity to overcome dim conditions. Now, let’s admire these wonders and appreciate life’s forms.
Factors Affecting Gorilla Vision
To understand the factors affecting gorilla vision, delve into the influence of habitat and lifestyle, as well as the impact of their nocturnal activities. Explore how these elements play a role in shaping the visual capabilities of gorillas and their ability to navigate and thrive in their surroundings.
Influence of habitat and lifestyle
Gorillas are highly adapted creatures. Their habitat and lifestyle affect how they see and interact with their environment.
Diet plays a big role in their visual abilities. As herbivores, gorillas use their eyes to find edible plants in dense foliage. This has sharpened their color perception and depth perception.
Living in groups also shapes their vision. Gorillas communicate visually with facial expressions and body postures. They must interpret subtle visual signals for group cohesion.
Activity level impacts vision too. Gorillas spend a lot of time resting. However, they can climb trees and defend their territory which demands good coordination between vision and movement.
Impact of nocturnal activities

Gorillas are diurnal animals, so the impact of their nocturnal activities on their sight is intriguing. Their eyes are adapted to darkness, with large forward-facing eyes and specialized cells called rod photoreceptors. These adaptations give them better vision in low-light conditions and help them hunt.
Nocturnal activities are also important for gorillas socially, helping them form bonds and establish dominance. They also help regulate body temperature and optimize energy.
The darkness brings risks, like decreased depth perception and increased susceptibility to predators. Gorillas have strategies to mitigate these risks, including heightened auditory senses and relying on tactile methods like grooming.
To observe gorilla behavior at night without disturbing them, researchers can use infrared camera equipment. This lets them gather insights into the complex world of gorilla social dynamics without human interference.
Research and Studies
To understand the research and studies on gorilla vision, delve into the mention of scientific studies conducted on gorilla vision and discover the compelling findings and insights from the research. Explore the fascinating world of gorilla vision and unravel the mysteries of their ability to see in the dark.
Mention of scientific studies conducted on gorilla vision
Scientists have been studying gorilla vision for a while. They’ve found that gorillas have acute eyesight and can spot small details and colors in their surroundings. This helps them find food and navigate.
Recent research has also revealed that gorillas have a great sense of depth perception, which makes them incredibly agile.
Dr. Jane Goodall wrote about an amazing incident she watched between two young gorillas. One found an insect hidden in a tree stump. This shows how important vision is to gorillas – and how scientific studies help us understand their amazing vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can gorillas see in the dark?
A: Yes, gorillas have excellent night vision which allows them to see in the dark.
Q: How do gorillas see at night?
A: Gorillas have large eyes and a high number of rod cells in their retina, which enables them to gather more light and see well in low-light conditions.
Q: Do gorillas have better night vision than humans?
A: Yes, gorillas have better night vision than humans. Their eyes are adapted to low-light environments, giving them a clear advantage in the dark.
Q: Why do gorillas need good night vision?
A: Gorillas are primarily active during the day but having good night vision is important for their safety and survival. It helps them navigate through their habitat and detect potential threats or predators in the dark.
Q: Can gorillas see color at night?
A: No, like most mammals, gorillas have reduced color perception in low-light conditions. Their vision is primarily black and white at night.
Q: Are gorillas completely nocturnal?
A: No, gorillas are not completely nocturnal. While they have good night vision, they are primarily diurnal, meaning they are most active during the day.
Conclusion
To conclude, gain a clear understanding of gorilla vision in the dark through the following: a summary of key points discussed in the article and final thoughts on gorilla vision in low-light conditions.
Refrences
https://www.britannica.com/animal/Gorilla-primate-genus
https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/facts/mountain-gorilla




