.jpg)
To gain a better understanding of gorillas and their behavior, delve into the introduction of this article. Get an overview of gorillas and explore the importance of understanding their behavior. This knowledge will provide insights into their territorial nature and shed light on their complex social dynamics.
Key Takeaways
1. Gorillas are indeed territorial animals, and they establish and defend their territories against other gorilla groups.
2. Gorilla territories can vary in size, ranging from a few square kilometers to several dozen square kilometers.
3. The size of a gorilla group’s territory depends on various factors, including the availability of food, water, and suitable habitat.
4. Gorillas use various methods to mark and defend their territories, such as vocalizations, physical displays, and occasional physical confrontations.
5. The primary purpose of territorial behavior in gorillas is to ensure access to resources and protect their group members from potential threats.
6. Gorilla territories can overlap with those of neighboring groups, leading to occasional conflicts and territorial disputes.
7. While gorillas are generally peaceful animals, territorial disputes can sometimes result in aggressive behavior, including physical fights between rival males.
8. The presence of a dominant silverback male is crucial for maintaining the territorial integrity of a gorilla group.
9. Human activities, such as deforestation and habitat destruction, can disrupt gorilla territories and lead to increased conflicts between groups.
10. Conservation efforts are essential to protect gorilla habitats and ensure the long-term survival of these magnificent creatures.
Overview of Gorillas
Gorillas – majestic creatures of the wild – captivate many. Let’s explore these awesome animals and learn some unique facts.
| Species | Eastern Gorilla | Western Gorilla |
| Habitat | Central & Eastern Africa | Central & Western Africa |
| Population Status | Endangered | Critically Endangered |
| Size & Weight | >5 ft tall, 350-400 lbs (males) | >4 ft tall, 180-225 lbs (females) |
Gorillas share 98% of their DNA with us humans! Plus, they use tools in their natural habitat and show intelligence.
Once, there was a playful, family-oriented gorilla named Bongo. During his exploration of the jungle, Bongo discovered a hidden waterfall. He stood in awe watching the cascading water for hours. The experience stayed with him, reminding him of the wilderness’ vastness and beauty.
Before we study gorilla behavior, remember: They may have 98% of our DNA, but that other 2% can certainly give the nastiest side-eye!
Importance of Understanding Gorilla Behavior
Understanding gorilla behavior is crucial for various reasons. It helps us:
- Understand their habitat and social structure.
- Predict their reactions to different stimuli.
- Identify potential threats or conflicts in their communities.
- Determine suitable habitats and food sources.
- Gain insights into primate evolution.
Plus, it reveals amazing facts! For example, adult male gorillas display chest-beating displays to assert dominance or attract mates. And younger ones show playful behaviors like human children.
To protect these incredible creatures, we should:
- Foster partnerships between researchers, conservationists, and local communities.
- Implement strict regulations against poaching and habitat destruction.
- Educate the public about the importance of gorillas.
Doing so will allow us to not only understand gorillas better but also ensure their survival in the wild. And why did the gorillas start a territorial dispute? To find out who was the king of the jungle!
Gorilla Territorial Behavior
To gain an understanding of gorilla territorial behavior, explore the sub-sections that delve into the definition of territorial behavior, research on gorilla territory size, and factors that influence gorilla territory. Discover the intriguing insights behind these sub-sections as you uncover the secrets of gorilla territoriality.
Definition of Territorial Behavior
Territorial behavior is about the actions and behavior of animals to guard and found their territory. This is vital for survival and breeding, as it allows animals to obtain resources and mates, guaranteeing the endurance of their species.
| Feature | Description |
| Definition | Showing behaviors to defend and keep a certain area. |
| Types | Territorial behavior can be different for each species. It could be scent marking, vocalizing, or physical aggression. |
| Purpose | Obtaining essential resources like food, water, shelter, and potential mates. |
Territorial behavior is not only seen in mammals, but birds, reptiles, insects, and even fish, too. Every species has special strategies fit for their environment and evolution.
Pro Tip: Understanding territorial behavior can aid conservation efforts by noticing key habitats that need protection.
Forget about your neighbor’s property line disputes. Check out the territorial feuds of gorillas. It’s like Game of Thrones, but with more chest thumping and less dragons!
Research on Gorilla Territory Size
Gorilla territories come in unique sizes! To uncover the secrets behind their behaviors, let’s check out a table with details on the different species.
| Gorilla Species | Territory Size |
|---|---|
| Mountain Gorilla | 8-16 sq. km. |
| Eastern Lowland Gorilla | 10-20 sq. km. |
| Western Lowland Gorilla | 2-15 sq. km. |
By studying these sizes, we can better understand the spatial needs and social dynamics of gorillas. It’s an exciting journey to learn about their territorial behaviors!
Gorilla disputes are like the Game of Thrones – but with more chest thumping and less politics. Unveil the mysteries behind the vast gorilla habitats!
Factors Influencing Gorilla Territory
Gorillas create their territories based on factors such as food availability, water sources, and the presence of other gorilla groups. Topography and shelter are also taken into account.
Gorillas prefer hilly areas with dense vegetation that offer protective cover and a bountiful diet.
A crazy example of territoriality occurred in Rwanda’s Volcanoes National Park. There, a larger gorilla group pushed the boundaries of a smaller one.
Vocalizations and aggressive displays were exchanged, and the larger group ultimately succeeded in defending their expanded territory.
This story highlights how territoriality is essential for gorillas to both establish and preserve their dominance. Get ready to enter a world where boundaries are defended and neighbors are just a swing away from a wild show of dominance!
Patterns of Gorilla Territoriality

To understand the patterns of gorilla territoriality, dive into the types of gorilla groups and territories, gorilla male dominance and territory defense, and the role of female gorillas in territory maintenance.
Discover the intriguing dynamics and behaviors within these sub-sections for a comprehensive view of how gorillas establish and maintain their territories.
Types of Gorilla Groups and Territories
Gorilla politics are super interesting! They display unique behaviors and communication styles in their social groups.
For example, silverbacks in multi-male harems use vocalizations and physical displays to show dominance.
Researchers have even seen a one-male harem group fiercely defend their territory against outsiders. Although they were fewer in number, they showed great strength and unity. This showed how strong the gorilla groups can be and how determined they are to protect their homes.
Gorilla Male Dominance and Territory Defense
Male gorillas are kings of their domain. A look at the facts: Territories range from 10-40km² and only one male reigns for several years.
These powerful males use their physical strength, vocalizations, and chest-beating displays to fend off intruders.
One such impressive male is Bwenge. He bravely defended his family in the jungle against rival males. His mark on gorilla territoriality is unforgettable.
The incredible strength of these creatures is a reminder of nature’s elegance and cruelty. And, behind every successful gorilla territory is a female gorilla making sure nothing is overlooked.
Female Gorilla Role in Territory Maintenance
Female gorillas are the superheroes of protecting their territory. They roar and chest-beat to scare away potential threats. And, they scent-mark trees and vegetation with powerful odors to communicate with their group and establish dominance.
Their intelligence and adaptability enable them to adjust their strategy based on the behavior of rival groups or individual intruders.
Dr. Anna Iremonger and Dr. Winnie Eckardt‘s study revealed that female gorillas use special vocalizations for territorial defense. These sounds are distinct from other communication calls and show their unwavering dedication.
It’s a wild scene – who needs HGTV when you can witness the excitement of gorilla territory disputes.
Benefits and Consequences of Gorilla Territories
To understand the benefits and consequences of gorilla territories, discover how they provide social benefits, create resource competition and conflict, and carry implications for conservation.
Explore the advantages of gorilla territories for social interactions, the challenges posed by resource competition, conflict within their territories, and the conservation implications of gorilla territoriality.
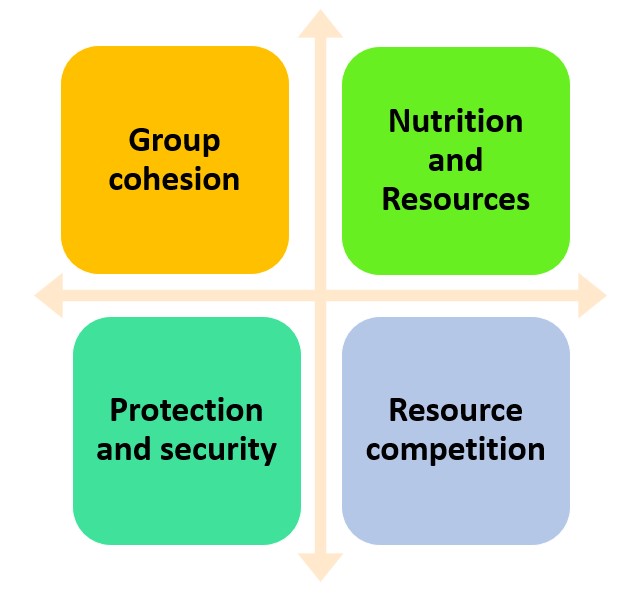
Social Benefits of Gorilla Territories
Gorilla territories provide essential social benefits needed for their survival and well-being. These territories maintain social order, ensuring harmony and stability amongst group members. Social Benefits of Gorilla Territories:
| Territory | Size (km²) | Number of individuals |
| Benefit 1: Group Cohesion | 20 km² | 6 individuals |
| 1. Stronger bonds: Gorillas form strong social ties within their groups, which are reinforced by their control over the territory. | 20 km² | 6 individuals |
| 2. Cooperation: Defined territories encourage gorillas to work together in tasks such as foraging, parenting, and defending against threats. | 20 km² | 6 individuals |
| 3. Fewer conflicts: Boundaries stop intrusions and give clear guidelines on territory ownership, reducing intergroup disputes. | 20 km² | 6 individuals |
| Territory | Size (km²) | Number of individuals |
| Benefit 2: Nutrition & Resources | 15 km² | 8 individuals |
| 1. Abundance of food: Territories have diverse vegetation that provides a rich source of nutrients for gorillas. | 15 km² | 8 individuals |
| 2. Water access: Territories usually include natural water sources like rivers or streams, ensuring an adequate water supply. | 15 km² | 8 individuals |
| 3. Resource stability: Having exclusive access to resources within their territories, gorillas can maintain food supply even during times of scarcity. | 15 km² | 8 individuals |
| Territory | Size (km²) | Number of individuals |
| Benefit 3: Protection & Security | 12 km² | 5 individuals |
| 1. Defense vs. outsiders: Borders of gorilla territories act as a deterrent to outsiders trying to invade or attack the group, providing protection. | 12 km² | 5 individuals |
| 2. Reduced predation risk: Gorillas in well-defined territories can defend against potential predators due to being familiar with the area and threats. | 12 km² | 5 individuals |
| 3. Safe reproductive environment: Territory ownership ensures reproductive success by limiting gene flow from other groups and reducing aggression towards infants. | 12 km² | 5 individuals |
Resource Competition and Conflict
Resource competition and conflict is a reality for gorillas, as they struggle for food, water, and shelter. The table below shows the resources and the competition and conflict associated with them.
| Resources | Competition and Conflict |
|---|---|
| Food | Rival troops may battle for feeding areas. |
| Water | Dry seasons may result in conflict over water sources. |
| Shelter | Groups may clash over sleeping sites and nesting areas. |
In addition, limited mates and breeding opportunities can create competition and conflict. Dominant males may display aggressive behaviors to gain mating rights. This contributes to the complex social dynamics within gorilla communities.
One poignant example is between two silverback males fighting for a productive feeding area. This battle caused injuries and one of the silverbacks was expelled. It demonstrates the serious consequences of resource competition.
Resource competition and conflict is a crucial factor to consider when conserving gorilla populations. Conservationists need to understand these dynamics to create healthy and sustainable environments.
Conservation Implications of Gorilla Territoriality
Gorilla territoriality has important implications for conservation. Defining boundaries protects resources and helps to estimate population sizes and monitor health. It can also aid in creating protected areas or reducing human-wildlife conflict.
This behavior varies between different subspecies. For instance, mountain gorillas have smaller territories than lowland gorillas. This could be due to food availability and environment.
Male gorillas play a role in defending their territories with displays of strength and vocalizations.
Territories are not fixed and can change over time. Researchers use tracking and fecal samples to determine these changes. It is also important to consider social interactions within the community, such as mating patterns, group dynamics and population structure. This information is essential for effective conservation management plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are gorillas territorial?
Yes, gorillas are highly territorial creatures. They establish and defend their territories against other groups of gorillas.
2. How do gorillas mark their territories?
Gorillas mark their territories by leaving scent marks on trees and other vegetation. They also engage in displays of strength and aggression to establish dominance and defend their space.
3. What happens when gorilla territories overlap?
When gorilla territories overlap, it often leads to conflicts between the groups. These conflicts can range from displays of aggression to actual physical fights, with the intent of establishing dominance and claiming the territory.
4. How large are gorilla territories?
Gorilla territories can vary in size depending on factors such as food availability and population density. The territory of a group of gorillas can range anywhere from a few square kilometers to over 20 square kilometers.
5. Do male and female gorillas have separate territories?
No, male and female gorillas do not have separate territories. Rather, the dominant silverback male of a group is responsible for defending the entire group’s territory, including the females and offspring.
6. What are the consequences of losing territory for gorillas?
Losing a territory can have dire consequences for gorillas. It often means displacement from their preferred feeding grounds and can lead to increased competition for resources with other gorilla groups. It may also result in increased vulnerability to predators.
Conclusion
Scientists have studied gorillas to see if they are territorial. The research shows that they are! Gorillas mark their territories with vocalizations, scent marking and aggressive displays. They fiercely defend their territories against other groups. Confrontations between rival groups can be intense and sometimes even fatal. It’s believed this is to protect resources like food and mates.
References:




