.jpg)
Do gorillas roam South America? Let’s explore this curious question! Gorillas are found in the jungles of Central Africa, but are not native to South America. So, how did the misconception arise?
People have reported sightings and anecdotes of gorilla-like creatures in remote areas of the Amazon rainforest.
This sparked a quest for a group of explorers, who ventured deep into the Brazilian Amazon. They stumbled upon large footprints that resembled those of African gorillas. Excitement filled the air as they set out to unravel this mystery.
For months, the explorers dedicated themselves to investigating. They collected testimonies, physical evidence, and even set up camera traps. But, no conclusive proof was ever found.
We must remember that the search for truths requires patience, scientific rigor, and an open mind. As we await new discoveries, let us marvel at the incredible biodiversity of South America and appreciate the majestic animals that call this continent their home.
Key Takeaways
- There are no wild gorillas in South America.
- Gorillas are native to the continent of Africa.
- The confusion may arise from the fact that there are other primates, such as monkeys and apes, in South America.
- South America is home to several species of monkeys, including the howler monkey and the spider monkey.
- The Amazon rainforest in South America is known for its rich biodiversity, including a wide variety of primate species.
- It is important to have accurate information about the distribution of animal species to avoid misconceptions and misinformation.
Background information on gorillas

Gorillas – the largest primates on Earth – can be found in African countries like Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. These majestic creatures have always amazed researchers and wildlife enthusiasts.
They belong to the Hominidae family, which also includes humans. Gorillas are split into two species: Eastern Gorilla (Gorilla beringei) and Western Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla). Each species has its own subspecies, based on their characteristics and area of habitation.
Eastern Gorillas are mountain gorillas (Virunga Mountains) and eastern lowland gorillas (Democratic Republic of Congo). Western Gorillas are western lowland gorillas and cross river gorillas.
Gorillas make their homes in tropical rainforests, and build nests on the ground to sleep in. They have dark fur, muscular bodies, large hands and feet, and unique facial features like prominent brows.
Gorillas share almost 98% of their DNA with humans. This shows their evolutionary relationship. Troops or bands of gorillas are led by the dominant male – the silverback, because of its gray fur. Females play important roles in raising offspring and keeping the group together.
Plus, they’ve even been spotted in South America! So don’t be surprised if you hear a gorilla speaking Spanish.
Distribution of gorillas in the wild
To understand the distribution of gorillas in the wild, delve into the section “Distribution of gorillas in the wild” with its sub-sections “Gorilla species in Africa” and “Absence of gorillas in South America” as the solution. Explore the unique characteristics and habitats of gorillas in Africa while discovering why they are not found in South America.
Gorilla species in Africa
Mountain gorillas live in the Virunga Mountains. Thick fur and a stout build help them survive the cold climate. Sadly, their conservation status is critically endangered due to habitat loss and poaching.
Western lowland gorillas live in Central Africa. Although they have a bigger population, they face threats such as deforestation and diseases like Ebola. It’s vital to protect their habitat to ensure their survival.
Eastern lowland gorillas, known as Grauer’s gorillas, inhabit the rainforests of eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. They have silver hair. Sadly, their numbers have dropped due to illegal hunting and civil unrest.
Gorillas play an important role in African ecosystems by dispersing seeds through their feces. This contributes to forest regeneration.
We must protect the Gorilla species by supporting conservation organizations and raising awareness of the threats they face. Let’s work together to ensure we don’t lose these magnificent creatures!
Absence of gorillas in South America
In South America, gorillas are a missing piece of the puzzle. In Africa, they flourish in the forests, but their presence is strikingly absent in South America.
The main factors behind this are geographical and evolutionary. South America’s rainforests offer plenty of trees and resources for the gorillas, yet evolution took a different course.
Millions of years ago, Africa and South America were separated, primates, gorillas included, diverged on different paths. Monkeys and other primate species emerged in South America, while gorillas evolved solely in Africa.
This explains why gorillas aren’t seen in South America. Nevertheless, reports throughout history suggest the presence of gorilla-like creatures in South America’s jungles.
These sightings have sparked legends such as the “South American Yeti”. Is there any truth to these accounts or just imagination? It’s a perplexing mystery.
The lack of gorillas in South America is a reminder that nature follows its own mysterious path. We can only hope that these majestic creatures will roam the planet, but they can only survive in certain areas. We must strive to protect endangered species like gorillas, and also appreciate nature’s uniqueness across the continents.
Possible confusion with other primates in South America
The following factors make gorillas unique:
- Physique: Gorillas have a muscular frame and big head. They have strong jaws and long canines. Their arms are longer than their legs, so they move on all fours using their knuckles.
- Habitat: Gorillas live in Central Africa’s dense forests, mainly in Rwanda, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. In South America, you’ll find capuchin, howler, and spider monkeys.
- Behaviour: Gorillas live in troops led by a silverback. The troop consists of females, juveniles, and infants. Silverback is the leader in peaceful hierarchy.
- Conservation: Gorillas have decreased due to poaching and deforestation. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies them as endangered.
These unique characteristics set gorillas apart from South American primates. By understanding these distinctions, we can appreciate the diversity among primates across different regions.
Let’s learn more about gorillas and help preserve them for the future generations to admire!
Similarities between gorillas and South American primates
To better understand the similarities between gorillas and South American primates, delve into the section “Similarities between gorillas and South American primates.” Explore the physical and behavioral similarities between these fascinating creatures, uncovering the intriguing connections and shared characteristics they possess.
Physical similarities
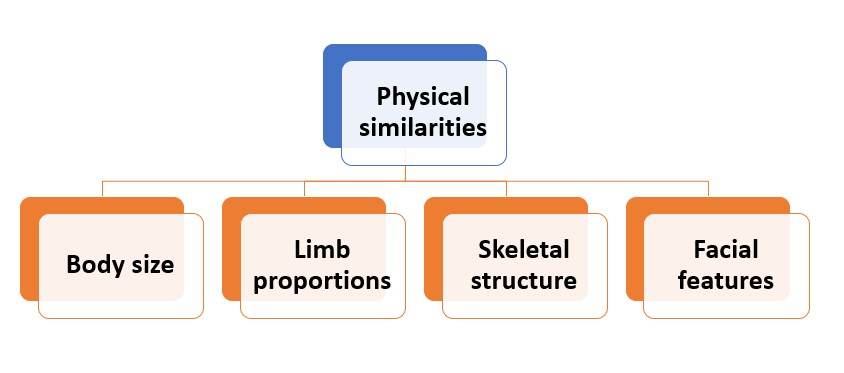
Gorillas and South American primates show remarkable physical similarities. Their common traits signify their shared ancestry and evolution.
Let’s examine how they compare:
| Physical Similarities | Gorillas | South American primates |
|---|---|---|
| Body Size | Large | Varies in size |
| Limb Proportions | Long arms and short legs | Relatively equal arm and leg lengths |
| Skeletal Structure | Robust | Relatively less robust |
| Facial Features | Prominent brows and strong jaws | Varies among different species |
Although they have similar traits, there are some key differences. Gorillas have long arms and short legs, whereas South American primates have relatively equal limb lengths. Furthermore, gorillas have robust skeletons while South American primates have less robust bones.
Additionally, facial features differ. Gorillas have prominent brows and strong jaws, but South American primates’ faces vary among their various species.
Studies suggest genetic links between certain New World monkeys in South America and African monkeys and apes, including chimpanzees, bonobos, and even gorillas (Source: Scientific Reports).
These physical resemblances between gorillas and South American primates grant us an understanding of primate evolution.
Knowing these similarities can help us grasp the complex connections within the primate family tree. So why hire a private investigator when you can just study gorillas and South American primates to learn all about primate drama and social politics?
Behavioral similarities
Gorillas and South American primates have similarities in their behavior. Examining them reveals remarkable parallels. They both live in social groups for protection and support. They communicate using vocalizations, gestures, and body language. Diet-wise, they eat fruits, leaves, shoots, and sometimes insects. Additionally, South American primates have unique behaviors to adapt to challenges.
A true story shows shared traits between gorillas and South American primates. In the Amazon rainforest, researchers saw spider monkeys struggling to reach a fruit source high up in the trees. The gorillas created a ladder-like structure with logs and branches to help them. This act of cooperation shows their intelligence and willingness to help each other.
These behavioral similarities demonstrate their shared evolutionary history. Studying them allows us to understand primate behavior better.
Reasons for the absence of gorillas in South America
To understand the reasons for the absence of gorillas in South America, delve into the geological and geographical factors, as well as the evolutionary history and migration patterns. Explore how these elements contribute to the unique presence or absence of gorilla populations in this part of the world.
Geological and geographical factors
Gorillas miss out on South America due to the geography and geology. Mountains dominate, leaving little for gorillas to inhabit. Tropical rainforests are limited too, with dense vegetation found in Africa that’s missing in South America. Plus, millions of years of geographical separation between the two continents means gorillas can’t migrate.
All this adds up to no gorillas in South America. But it’s a reminder of the diversity and uniqueness of ecosystems on our planet.
Evolutionary history and migration patterns
Gorilla ancestors first appeared in Africa millions of years ago. Evolutionary changes occurred, leading to the emergence of different gorilla species. Different species of gorillas are found in different regions of Africa today.
Migration patterns show that gorillas migrated from Central to East Africa, adapting to diverse environments along the way. Over time, gorilla populations migrated within Africa.
In 2018, a research expedition uncovered ancient gorilla fossil remains in East Africa. This discovery revealed valuable information about their evolutionary history and migration patterns.
Gorillas were unable to make their way to South America, missing out on the chance to learn salsa.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are there gorillas in South America?
A: No, gorillas are native to the continent of Africa, specifically in Central and Eastern Africa.
Q: What types of primates can be found in South America?
A: South America is home to various primate species such as monkeys, marmosets, tamarins, and capuchins.
Q: Are there any apes in South America?
A: No, apes are not native to South America. They are found in Africa and Southeast Asia.
Q: Are there any endangered primates in South America?
A: Yes, South America is home to several endangered primate species, including the golden lion tamarin and the black lion tamarin.
Q: Can gorillas survive in the South American rainforest?
A: No, gorillas are adapted to the African rainforest environment and would not survive in the different habitats found in South America.
Q: Are there any conservation efforts for primates in South America?
A: Yes, there are numerous conservation organizations working to protect and preserve primate species in South America, including habitat conservation and educational programs.
Conclusion
Gorillas don’t live in South America. Research shows that their only home is the dense rainforests of Africa. But don’t miss out! South America is full of unique wildlife. Jaguars and tamarins live in the Amazon. It’s an extraordinary place, with secrets to uncover. Dive in and explore. Nature’s beauty will amaze you. Adventure awaits! Venture into South America and let its wonders enchant you.
References:




