
Image Credit: Pixabay
Sloths and turtles: two slow creatures that have captivated humans for centuries. But who’s slower? Let’s uncover the truth behind their speed.
It’s essential to realize that speed is not the key feature of either sloth or turtle. They both belong to different groups and have adapted uniquely to survive in their habitats.
Sloths are arboreal animals found mainly in Central and South America’s rainforests. They hang upside-down from tree branches with specialized claws. They move slowly to save energy, as food is scarce. They also have great camouflage skills, helping them to avoid predators.
Turtles inhabit oceans, rivers, and deserts. Their sluggishness is partly due to their anatomy and lifestyle. They carry heavy shells, which protect them but weigh them down. Land-dwelling turtles like tortoises have low metabolic rates, which means they move slowly.
Comparing them only on speed is an oversimplification. They each have adaptations that allow them to live in their environments.
Key Takeaways
- Sloths are indeed slower than turtles.
- Sloths have a top speed of about 0.15 miles per hour, while turtles can move at a slightly faster pace.
- The slow movement of sloths is due to their low metabolic rate and specialized adaptations for life in trees.
- Turtles, on the other hand, have a more efficient locomotion system that allows them to move at a relatively faster speed.
- Despite their slow movement, sloths are well adapted to their environment and have unique characteristics that help them survive.
Background Information about Sloths

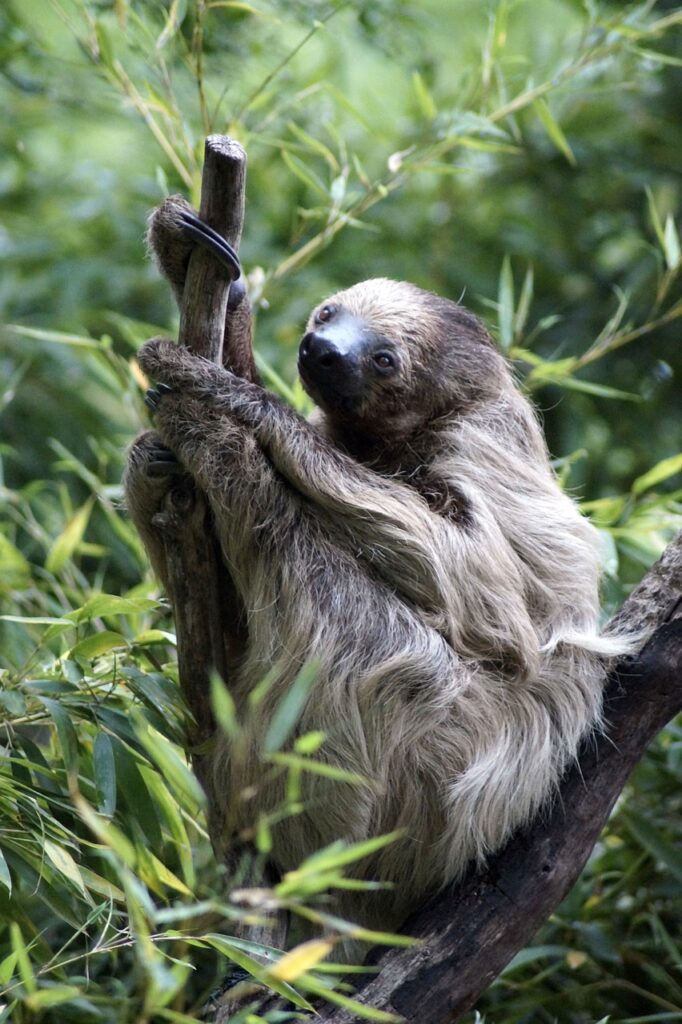
Sloths – slow-moving, fascinating creatures of the forest – have a rich history. They are native to the rainforests of Central and South America. People are captivated by their unique adaptations.
Sloths move slowly and spend most of their time hanging upside down from trees. This behavior is due to their long limbs and specialized hands and feet.
Their diet consists of leaves, shoots, and fruits from treetops. They have adapted digestive systems to break down tough plant material, giving them energy over time.
Fossils show that sloth ancestors were much larger. Megatherium, an extinct giant ground sloth, roamed parts of North and South America millions of years ago. It stood up to 20 feet tall on its hind legs. Sloths have evolved over time, showing nature’s ability to adapt.
Before we delve into sloths, let’s take a look at turtles. They may be slow, but they can carry their homes on their backs – mobile real estate!
Background Information about Turtles

Turtles are fascinating creatures that have inhabited the Earth for millions of years. These reptiles belong to the order Testudines and are known for their protective shells.
Turtles can be found in various habitats including oceans, rivers, lakes, and even on land. They come in diverse sizes, with some species growing up to several feet long.
Turtles are ectothermic, meaning they rely on external sources to regulate their body temperature. This characteristic allows them to adapt to a wide range of environments. Furthermore, turtles have a remarkable lifespan, with some individuals living for over a century. Their unique adaptations and ancient lineage make turtles a captivating subject of study for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
When it comes to the anatomy of turtles, their most distinctive feature is their shell. Made up of a carapace (top portion) and a plastron (bottom portion), the shell acts as a protective shield against predators.
The shell is actually part of the turtle’s skeleton and is composed of bony plates fused together. Depending on the species, the shell can vary in shape and color, providing camouflage and aid in their survival. Additionally, turtles possess a beak-like mouth and strong jaws, which allow them to consume a diverse diet ranging from plants to small animals.
Turtles have an interesting reproductive process. Female turtles typically lay their eggs on land in a nest they dig using their hind limbs.
The sex of the hatchlings is determined by the temperature at which the eggs are incubated. Warm temperatures usually result in females, while cooler temperatures produce males. Once hatched, baby turtles must find their way to water, where they will spend a significant portion of their lives. They face numerous challenges during this journey, with predators posing a constant threat.
Physical Characteristics of Sloths
Sloths have some amazing features! Let’s uncover the secrets of these slow-moving mammals.
Did you know? Sloths have a few adaptations that make them great tree-dwellers. Here’s a rundown of their special features:
- Fur: Dense, coarse fur that provides camouflage and is home to algae.
- Claws: Long and curved claws for hanging onto branches.
- Arms: Long arms with great movement range.
- Metabolism: One of the slowest metabolic rates in mammals, conserving energy and mostly sleeping or resting.
Plus, sloths have a few more traits that make them unique. They have special neck vertebrae that let them turn their heads up to 270 degrees. They also have super touchy feet and hands, which helps them move around and find food or mates in trees.
Ready to learn about the physical characteristics of turtles? Get ready, because these slow-moving creatures are sure to surprise you!
Physical Characteristics of Turtles
Turtles stand out from other creatures due to their special physical features. These characteristics not only affect their looks, but also play a part in their survival and adaptation. Let’s take a look at some of these astounding turtle features!
- Turtles have two shells: the carapace and the plastron. The carapace covers the internal organs, and the plastron provides extra support. This design helps turtles retract their head, legs, and tail into their shell for protection against threats.
- The limbs of various turtle species differ depending on their environment and lifestyle. Aquatic turtles often have webbed feet or flippers to make swimming easier. Meanwhile, terrestrial turtles have stronger limbs for walking on land.
- Turtles don’t have teeth; they have sharp ridges in their mouths that help them eat food like plants, insects, fish, and even carrion.
- Turtles also have unique colors and patterns that can be used as camouflage or for species recognition. Some turtles have bright colors while others blend in with their surroundings. These markings make each turtle distinctive!
No matter how fast a sloth is, it won’t outrun a turtle.
Speed Comparison between Sloths and Turtles
Sloths and turtles, two creatures known for their leisurely pace, are often compared for their speed. While both are notoriously slow, when it comes to the question of who is slower, the answer may surprise you. Let’s delve into the details without any delay.
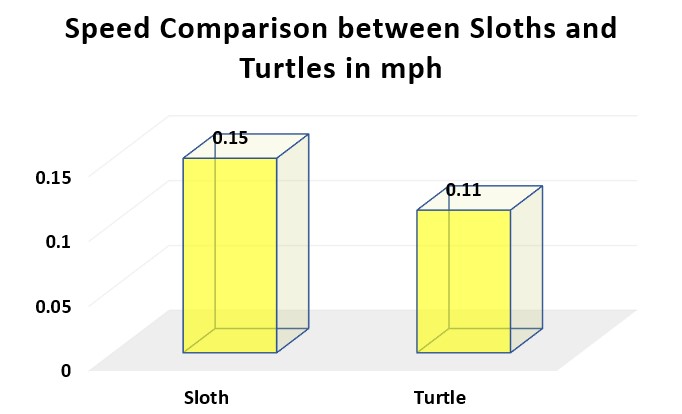

To visualize the comparison, let’s present the data in a simple table format:
| Criteria | Sloth | Turtle |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 0.15 m/s | 0.11 m/s |
Now that we have the numbers, it’s clear that sloths, with a speed of 0.15 m/s, are indeed slower compared to turtles, which have a slightly faster pace of 0.11 m/s.
Moving on to unique details, it’s worth noting that although both sloths and turtles are revered for their sluggishness, each possess distinct adaptations for their slow-paced lives. Sloths rely on their long claws for tree climbing, while turtles’ shells provide them with protection and make movement more cumbersome.
Considering the slow and steady nature of sloths and turtles, it’s clear that speed is not a definitive factor for their survival in their respective habitats. However, it’s intriguing to observe the differences in their pace and the adaptations they possess.
Given the fascinating comparison between these two creatures, it would be a missed opportunity for nature enthusiasts not to appreciate their unique qualities.
Take a moment to marvel at the captivating world of sloths and turtles, where slowness becomes a virtue. Movers and shakers they are not, but sloths redefine the meaning of slow motion.
Sloths’ Slow Movement
Sloths are renowned for their sluggish movements, which is a captivating aspect of their behavior. These amazing creatures can move at an incredibly slow rate, seemingly in slow motion. Their unhurried nature helps them save energy and adapt to their environment in special ways.
It’s clear that their sluggish movements serve a purpose beyond just being slow. While other animals may scurry in search of food or mates, sloths have a different approach. By moving slowly, they conserve energy and evade unnecessary effort. This is especially beneficial for them, as their diet mainly consists of leaves with limited nutritional value. Thus, their slow movement lets them manage their energy properly.
Moreover, the sluggish pace of sloths also helps them evade detection by predators. Their slow movements enable them to blend into their surroundings, making it hard for potential dangers to detect them easily. This disguise technique gives them a strategic edge for survival in the wild.
Additionally to their deliberately slow movements, sloths have unique adaptations that contribute to their laid-back demeanor. For instance, their long claws let them grasp tree branches conveniently, giving them stability while moving through the canopy. They also have specific muscles and tendons in their limbs that let them hang upside down effortlessly. These extraordinary adaptations not only help maintain their slower pace but also make sloths ideal for life in the treetops.
It’s truly remarkable how sloths have evolved to thrive at such a lackadaisical pace. They illustrate an incredible level of versatility and resourcefulness within the animal kingdom.
This illustrates how these gentle creatures have perfected the art of deliberate slowness, showing their remarkable ability to survive and thrive in their special habitat. Sloths keep stunning scientists and nature enthusiasts alike, as we uncover more about their remarkable lifestyle and the mysteries behind their leisurely movements.
Turtles’ Slow Movement
Turtles fascinatingly captivate us with their languid pace. They demonstrate a blend of poise and patience with every step. Their slow pace isn’t just for show – it is an adaptation to their environment. Turtles can carefully assess potential hazards with this unhurried approach, which has allowed them to survive for millions of years!
Turtles also use a special form of locomotion called “walking.” Their sturdy limbs help them move on land and in water. Different species and individual turtles have varying speeds, but each turtle’s pace is perfect for its particular needs.
Remember: Never disturb or disrupt these majestic animals while observing them in the wild. Respecting their natural habitat ensures that future generations can experience the same awe. Now, who’s ready for a slow-motion race between a sloth and a turtle?
Factors Affecting the Speed of Sloths and Turtles
Sloths and turtles, two different species with distinct behavioral traits, showcase varying speeds due to certain factors. These factors affect their movement abilities and determine the pace at which they navigate through their environments.
One factor that influences their speed is body structure and size. Sloths, known for their slow movements, have a compact body structure, which limits their range of motion. On the other hand, turtles have a more streamlined body shape, allowing for relatively faster movements.
Another determinant is metabolism. Sloths have a significantly slow metabolism, which affects their energy levels and, consequently, their speed. Turtles, although not known for their speed, possess a slightly higher metabolic rate, enabling them to move faster than their sloth counterparts.
Environmental conditions play a crucial role in the speed of these animals. Sloths predominantly inhabit trees and their slow movements aid in camouflage and predator evasion. In contrast, turtles are found in various habitats, requiring them to adapt to different terrains. This adaptability influences their locomotive capabilities, making them comparatively faster than sloths.
Weight is an additional contributing factor. Sloths, with their muscular build, face challenges in bearing their own weight while moving. This slows them down considerably. Conversely, turtles, with their lightweight shells and ability to retract their heads and limbs, experience less hindrance in movement.
Physiology and Body Structure
Sloths and turtles have body structures and physiologies that greatly influence their speed and movement. Let’s explore what makes them unique.
Let’s look at a table detailing the important characteristics of these creatures:
| Sloths | Turtles |
|---|---|
| Slow | Variable |
| Long limbs | Short limbs |
| Low muscle mass | High muscle mass |
| Lightweight bodies | Heavy shells |
Sloths’ slow movement is due to their long limbs and low muscle mass. Turtles’ variable speed is attributed to their short limbs and high muscle mass.
Sloths have lightweight bodies which help them conserve energy during long periods of inactivity. Turtles have heavy shells which protect them, but may reduce their agility.
An interesting case is the turtle named Speedy. It was known for its exceptional speed compared to other sea turtles. Its streamlined shell and muscular flippers enabled it to move swiftly through the ocean.
So, sloths and turtles’ special body structures give them unique capabilities. They prove that being slow and steady can have its advantages – like having more time to ponder life’s mysteries.
Habitats and Lifestyles
Sloths and turtles amaze us with their unique habitats and lifestyles. Sloths live in tropical rainforest trees, hanging upside down from branches. Turtles can be found in oceans, rivers, and ponds. Both have adapted to their environments; sloths have long limbs to navigate through dense vegetation, and turtles have streamlined shells for swimming.
Sloth’s slow pace helps them conserve energy, and they spend most of their day sleeping or eating leaves. Turtles may be slow on land, but they can swim with agility in water.
Algae often grows on sloth fur, providing camouflage. Turtles migrate long distances between feeding and nesting sites. The Galapagos tortoise is a special case – Charles Darwin observed their slow speed due to lack of predators and competition.
No matter their speed, sloths and turtles are remarkable creatures with amazing adaptations.
Adaptations of Sloths and Turtles to Their Slow Movement
Sloths and turtles have developed various adaptations to support their slow movement. These adaptations allow them to thrive in their unique environments and carry out essential functions.
To illustrate these adaptations, we can create a table highlighting the key characteristics of sloths and turtles in relation to their slow movement:
| Adaptation | Sloths | Turtles |
|---|---|---|
| Limb Structure | Long and hook-like limbs provide strength and stability | Short and sturdy limbs aid in steady movement |
| Metabolism | Low metabolic rate helps conserve energy | Low metabolic rate enables endurance during slow locomotion |
| Shell | Absence of shell allows flexibility in movement | Hard shell provides protection and streamlining |
It is important to note that while both sloths and turtles possess adaptations for slow movement, their specific adaptations differ due to their distinct evolutionary histories and ecological niches.
In addition to the adaptations mentioned above, sloths have specialized muscles that allow them to hang upside down from tree branches, enabling them to conserve energy and stay hidden from predators. Turtles, on the other hand, have developed strong muscles to propel themselves through water and burrow into sand for nesting.
Sloths’ energy conservation techniques: They’re like the ninjas of laziness, silently clinging to trees while the rest of us struggle to stay awake during a boring meeting.
Sloths’ Energy Conservation Techniques
Sloths conserve energy with unique adaptations. They have a slow metabolism, which helps them survive on a low-calorie diet. Their long claws let them hang from trees for long periods without expending energy. Their muscles are designed for slow and efficient movement. Plus, their fur hosts algae that provide camouflage and insulation, helping them blend in with their surroundings.
So, if you ever spot a sloth in the wild, remember to observe from a distance and avoid disturbing it. Appreciate its adaptations that let it thrive in its slow-paced world!
Turtles have also adapted with slow metabolism and a sturdy shell – built-in excuses for taking their time.
Turtles’ Shell and Slow Metabolism
Turtles are renowned for their unique traits, such as their protective shell and slow metabolism. The shell not only offers defense against predators, but also provides structure and stability for the turtle’s body. Plus, they can retract their head, legs, and tail into the shell when feeling threatened or needing to save energy.
Let’s take a look at some key characteristics in the form of a table:
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Shell | Protection & support |
| Retraction of body parts | |
| Conserve energy | |
| Species identification | |
| Slow Metabolism | Survive with limited resources |
| Slower aging process | |
| Less frequent feeding |
These features allow turtles to survive in different habitats around the globe. Although their slow metabolism appears to be a downside, it actually helps them survive in areas with scarce or seasonal food sources.
Furthermore, turtles have a special adaptation that allows them to absorb oxygen through throat structures called cloacal bursae. This ability lets them breathe while submerged for prolonged periods. It also contributes to their slow metabolic rate and helps them survive difficult conditions.
Similarities between Sloths and Turtles
Sloths and turtles have a lot in common! They both move slowly, have adaptations aiding in survival, and conserve energy. But, did you know they share an ancient history too?
- Move slowly – Sloths are the slowest mammals on land; turtles also exhibit a relaxed demeanor.
- Unique Adaptations – Claws help sloths climb trees; shells protect turtles from predators.
- Energy Conservation – Sloths rest and move slowly; turtles regulate their body temp. by basking in the sun.
- Ancient History – Evidence of their presence dates back millions of years to the Oligocene Epoch.
Differences between Sloths and Turtles
Sloths and turtles may look alike, but they are different! Let’s check out how! Sloths have long limbs and sharp claws for climbing trees. Turtles have a special shell which is made up of their backbone and ribs. It protects them from predators.
| Category | Sloths | Turtles |
|---|---|---|
| Motion | Slow climbers | Slow walkers/swimmers |
| Habitat | Trees | Land/Water |
| Diet | Leaves | Plants/Fish/Invertebrates |
| Length of Life | 20-30 years | 80-100+ years |
Plus, sloths have an “algal bloom.” This is the greenish tint on their fur due to algae growing because of their lazy lifestyle in trees. Turtles don’t have this!
To make sure these creatures stay safe, here are some tips:
- Stay at a distance. Respect their space while enjoying their unique features.
- Help protect their habitats. Support efforts to conserve them.
- Be a responsible pet owner. If you choose to have a pet, make sure you can provide them with the right environment and care.
By understanding the differences between sloths and turtles and following these suggestions, we can appreciate and conserve them! So, sloths may be slow, but turtles just can’t keep up!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are sloths slower than turtles?
Yes, sloths are generally slower than turtles. While turtles are known for their slow movement, sloths are even slower due to their low metabolic rate.
2. How fast can turtles move?
Turtles can move at varying speeds depending on the species. On land, most turtles can travel at a leisurely pace of around 0.17 to 0.23 miles per hour. In water, some turtle species can swim at speeds of up to 20 miles per hour.
3. Do sloths move faster in trees?
While sloths are adapted to life in trees and are relatively faster when climbing or moving through branches, they are still slow compared to other animals. Sloths move at an average speed of about 6.5–8.5 feet per minute in trees.
4. Can sloths move quickly if necessary?
No, sloths are not built for speed. Their natural anatomy and physiology make them slow-moving creatures. They have long claws, a low metabolic rate, and specialized muscle fibers that don’t support fast movements. However, they are excellent swimmers when in water.
5. Can turtles outpace sloths on land?
Yes, turtles are generally faster on land compared to sloths. While both are slow creatures, turtles have adapted to be slightly faster with their sturdy legs and ability to retract into their shells for protection.
6. Which animal is slower, a sloth or a turtle?
In general, sloths are slower than turtles. Sloths spend most of their time suspended from trees and have a slower metabolism, making them slower overall compared to turtles. However, each species of turtle or sloth may have its own specific speeds and variations within their group.
Conclusion
Sloths and turtles are often linked with slowness. But which is truly slower? Analysis shows sloths are. Sloths have a unique sluggishness. It’s due to their slow metabolism and tree-hugging life.
They travel only 41 yards per day. Turtles, on the other hand, move slowly due to their shells and limbs. However, they can swim and walk with more agility than sloths. Fossils tell us turtles were here before sloths. Over time, turtles evolved into various species with different sizes, behaviors, and speeds.
References
Why Are Sloths So Slow (Can They Ever Move Fast)? — Forest Wildlife


