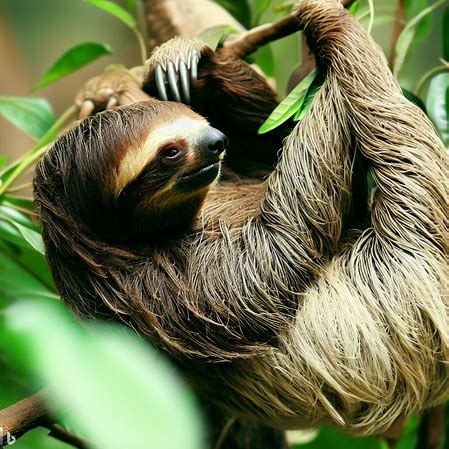

Sloths are intriguing creatures, possessing amazing adaptations that help them thrive. Scientists and nature enthusiasts alike are captivated by their unique attributes.
Their specialized claws enable them to effortlessly cling to trees and blend in with their surroundings, making them invisible to predators.
Sloths have a slow metabolism, which helps them conserve energy. This low metabolic rate gives them a calm demeanor and lack of aggression.
The evolutionary history of sloths dates back millions of years. Fossils show that their ancestors adapted and migrated to tree-dwelling habitats as new ecological niches opened up. Sloths may be slow, but their long claws are nature’s way of saying ‘I make up for it in high-five precision!‘
Physical Adaptations of Sloths
Sloths are the masters of adaptation, with remarkable physical traits that help them thrive in their treetop homes. They’ve evolved to move at a leisurely pace, conserving energy and navigating with ease. Their limbs are strong and their claws are sharp, providing a secure grip on branches. To cope with their plant-based diet, they have a specialized multi-chambered stomach. Plus, their fur coat contains grooves that harbor algae, creating a greenish camouflage.
These adaptations work together brilliantly to provide the sloth with protection. Slowness reduces visibility to predators, limbs and claws grant stability, and digestion maximizes nutrient absorption. It goes to show that even unconventional qualities can be key for survival and prosperity.
Behavioral Adaptations of Sloths

Sloths: amazing creatures with marvelous adaptations. Let’s explore their behavioral adaptations!
They have slow metabolisms, which helps them conserve energy and eat low-calorie diets.
Plus, their strong grip and elongated limbs let them hang upside-down from trees all day.
They also camouflage perfectly into the forest, and can remain motionless for long periods.
Did you know they even have specialized neck vertebrae that let them rotate their heads up to 270°?
This lets them scan their surroundings without moving their bodies!
As an example, there’s a sloth called Velcro in Costa Rica.
She managed to cross a busy highway unscathed by using her slow movements and camouflaged fur.
Sloths show us how adaptation can help us survive tough situations.
From chillin’ like ninjas to growing algae in their fur, they’ve mastered the evolutionary game!
Evolutionary Adaptations of Sloths
Sloths, known for their slow-moving nature, have developed many unique adaptations to survive in their environment. Let’s explore some of these fascinating features.
| Adaption | Description |
|---|---|
| Slow metabolism | Sloths have a low metabolic rate to save energy and move slowly. |
| Long claws | Their long, curved claws help them grip onto tree branches and hang upside down. |
| Camouflaged fur | Their fur is covered with algae, giving them a greenish tint and helping them blend in. |
| Flexible neck | Sloths can rotate their neck up to 270 degrees, giving them a wide field of vision. |
| Gripping tail | A prehensile tail lets them anchor to branches and aid their movement. |
Plus, sloths have a special digestive system with bacteria that break down tough fibers in their plant-based diet. Surprisingly, they are also great swimmers. This adaptation helps them navigate flooded areas or rivers when needed.
Fun Fact: National Geographic reports that sloths can live up to 20 years in the wild and 50 years in captivity.
These evolutionary adaptations show the amazing ways sloths have adapted to their natural habitat. Survival of the slowest: sloth adaptations will make you reevaluate your life choices – or lack thereof!
The Importance of Sloth Adaptations
Sloths have adapted in some incredible ways. They have a low metabolic rate, allowing them to conserve energy and get the most out of their low-nutrition leaf diet. Plus, their long claws help them grip branches for stability and even reach leaves that would otherwise be out of reach. The algae-covered fur coat helps them blend into the foliage, keeping predators at bay. And, their muscle arrangement lets them hang upside down without expending much energy. Truly amazing! When observing them in the wild, remember to respect their natural behaviors and habitats so we can keep these creatures around. Sloths are on the fast track to survival!
Human Interactions and Conservation Efforts
Interactions with sloths and conservation efforts are very important for their survival. Initiatives such as protecting their habitats, raising awareness, and promoting responsible tourism help this cause.
Organizations work hard to preserve and restore sloths’ natural habitats as deforestation puts them in danger. They also try to reduce human-wildlife conflicts by teaching locals how to coexist peacefully.
Research is done to understand sloths’ behavior, reproductive patterns, and ecology. This helps inform conservation strategies and create effective measures for protecting these special animals.
For example, wildlife corridors are built to connect fragmented habitats, making it easier for sloths to move and find food. These corridors are beneficial for other endangered species too, showing the importance of protecting these gentle creatures.
Remember: if you see a sloth in its habitat, keep your distance and observe from afar. This way, you avoid stressing or harming them.
Love ’em or hate ’em, sloths may be slow, but their adaptability is no joke!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do sloths adapt to their environment?
A: Sloths have several adaptations to survive in their environment. They have long claws that allow them to hang upside down from trees for long periods of time, which helps conserve energy. Sloths also have a slow metabolism to reduce the need for food, and their fur provides camouflage.
Q: How do sloths move in trees?
A: Sloths are well adapted for moving in trees. They use their long arms and claws to grip the branches, allowing them to hang or climb with ease. Sloths move slowly and deliberately to conserve energy, using a hand-over-hand motion to navigate through the trees.
Q: Why are sloths so slow?
A: Sloths have a slow metabolic rate, which means they process food very slowly. This slow digestion helps them extract maximum nutrients from their low-energy diet. Additionally, their slow movement helps them avoid predators in the trees, where they spend most of their time.
Q: How do sloths survive in the rainforest?
A: Sloths have several adaptations that help them survive in the rainforest. Their fur is home to symbiotic algae, which provides camouflage and helps them blend in with their surroundings. They also have a special grip that allows them to hang from branches even when they are asleep.
Q: Do sloths have predators?
A: While sloths are relatively slow-moving and spend most of their time in trees, they do have predators. Jaguars and large birds of prey such as harpy eagles are known to feed on sloths. However, sloths have evolved to blend in with their surroundings and may go unnoticed by predators.
Q: How do sloths protect themselves?
A: In addition to their camouflage, sloths have a unique defense mechanism. When threatened, they may bite or swipe at predators with their long claws. They can also emit a loud, hissing sound to scare away potential threats. However, their best defense is often their ability to remain still and go unnoticed.
Conclusion
Sloths’ adaptations make them fascinating! Their slow metabolism and tree-dwelling lifestyles conserve energy and help them blend in. Special claws for gripping branches, plus their slothful nature, keep them safe from predators. Algae on their fur provides camouflage and natural sunscreen. Sloths are amazing climbers, swinging effortlessly among trees with strong limbs. Plus, their heads can rotate 270 degrees, giving them a wide field of vision to spot danger. Pro Tip: Go to a tropical rainforest to see these incredible creatures!

