
Image Credit: Pixabay
Sloths – curious creatures with a slow-paced lifestyle. But are they nocturnal? Let’s explore the world of sloths and find out!
Sloths, renowned for their sluggish movements and long claws, are sighted mostly at night. They leave their homes in search of food and socialization during the darkness. However, not all sloths are nocturnal.
Two types of sloths exist – two-toed and three-toed. While both usually display nocturnal behavior, some individuals can be active during the day. This contradicts the idea that all sloths are nocturnal.
Some sloths break the norm and enjoy daytime activities. So if you spot a sleeping sloth, remember that they might just be saving energy for a fun night ahead!
Key Takeaways
- Sloths are not strictly nocturnal animals, but they are known to be more active at night.
- They have a slow metabolism and spend most of their time sleeping or resting.
- Sloths have adapted to their environment by developing a slow-paced lifestyle, which helps them conserve energy.
- They are primarily herbivores and feed on leaves, which provide them with a low-energy diet.
- Sloths have a unique ability to hang upside down from trees, thanks to their long claws and specialized muscles.
- While they may be active at night, sloths can also be seen moving during the day, especially when searching for food or changing trees.
- Their slow movements and camouflage help them avoid predators, such as eagles and jaguars.
- Sloths have a symbiotic relationship with algae and moths, which live in their fur and provide them with additional camouflage and nutrients.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect sloth populations, as they are threatened by habitat loss and illegal wildlife trade.
Definition of Nocturnal
Nocturnal creatures are active during the night and rest during the day. This applies to many species across the animal kingdom, with adaptations to help them navigate in the dark. It doesn’t mean these animals live in total darkness, but they mainly move around at night.
Sloths are unique. They spend about 15-20 hours a day sleeping or resting. However, they are sometimes active at dawn or dusk, so experts say they are crepuscular, not nocturnal.
One rainforest researcher noticed something special one night. A sloth descended from its tree slowly – so slowly it almost seemed motionless. It was a rare chance to see these mysterious creatures up close.
Background on Sloths

To better understand the background on sloths, delve into their behavior and lifestyle. Explore the sub-section that focuses on the description of sloths’ behavior and lifestyle, outlining key aspects of their unique traits and habits. This will shed light on the fascinating world of these slow-moving creatures.
Description of Sloths’ Behavior and Lifestyle
Sloths are known for their slow-motion moves – they hang upside-down from trees, adapted to life in the treetops. Their low body temperature and metabolic rate help them conserve energy.
Specialized adaptations like long claws help them grip branches securely. Plus, their fur is home to algae, giving it a greenish tint and providing camouflage to hide from predators.
This is a symbiotic relationship between sloths and algae. The algae benefits from shelter and sunlight, while the sloth gets nutrients from the algae’s diet.
Pro Tip: When you encounter a sloth in the wild, maintain your distance and observe quietly from afar. Even though they seem docile, sloths are still wild animals. So, remember to respect them!
Do Sloths Sleep During the Day?
To better understand whether sloths sleep during the day, delve into the section that explores the sleep patterns of these fascinating creatures. The sub-sections on the horizon provide an explanation of sloths’ sleep patterns, shedding light on their unique habits and behaviors.
Explanation of Sloths’ Sleep Patterns
Sloths have unique sleep patterns that are interesting to study. At night they are active, but during the day they retreat high up in trees and sleep for long stretches. The reason for this behavior is complex.
One factor is their diet. Leaves are low in nutrients and energy, so sloths’ digestion is slow. This means they need to save energy by sleeping longer. Plus, their metabolism is slow, helping them survive on a limited food supply.
Plus, they sleep during the day as it is harder for predators to spot them due to their camouflage. They sleep in short naps of 10-20 minutes, and they hang upside down from tree branches too. This helps protect them from threats.
To help these creatures, it is important to create an environment like their natural habitat. Provide elevated structures for them to sleep in, and give them chances to mimic their tree-dwelling behaviors.
Evidence of Sloths Being Nocturnal
To understand the evidence of sloths being nocturnal, delve into studies and research on sloths’ activity at night. Explore the sub-sections: the behavioral patterns of sloths in darkness, their adaptation to the nighttime environment, and the factors that contribute to their nighttime activity.
Studies and Research on Sloths’ Activity at Night
Studies and research show sloths are nocturnal. Scientists are intrigued by their unique habits. At night, they become more active with activities such as feeding and socializing. This behavior helps them take advantage of cooler temperatures and resources.
A detail about their night activity is they rely on touch, rather than sight. Limited vision means they navigate their environment by feeling around. This adaptation helps them locate food and move around in the dark.
To observe sloths at night, be patient and keep quiet. They need a calm atmosphere for their slow movements. Who knew sloths could teach us to pull an all-nighter?
Factors That Influence Sloths’ Nocturnal Behavior
To understand what influences sloths’ nocturnal behavior, delve into the factors of climate and habitat, as well as predation and protection. Climate and habitat play a significant role in determining when sloths are most active, while predation and protection impact their behavior patterns. Explore these sub-sections to gain insights into sloths’ nocturnal tendencies.
Climate and Habitat
Climate and habitat impact sloth behavior. Let’s dig deeper into why they are so important.
Tropical temperatures and humidity suit slow-paced sloths. They mainly live in rainforests and cloud forests. Trees are important to them for nutrition and shelter.
Historically, it was thought that sloths had special powers due to their rainforest adaptations.
But really, even at night, sloths have better relationships than I do!
Predation and Protection
Sloths have low predation rates as a result of their camouflage, arboreal lifestyle, and slow movement. They have unique fur that harbors algae, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings for extra protection. They also live high up in trees, with flexible limbs and long claws to keep them safe from predators on the ground.
An amazing story illustrates their survival strategies. Once upon a moonlit night, a jaguar went to catch a sloth in the leaves. However, its cryptic coat blended perfectly, so the jaguar left empty-handed. The sloth’s incredible camouflage saved it.
Sloths are like superheroes, reaping the benefits of nocturnal life.
Benefits of Sloths Being Nocturnal
To understand the benefits of sloths being nocturnal, delve into the section ‘Benefits of Sloths Being Nocturnal’ with a focus on the sub-sections ‘Adaptations and Survival Strategies’ and ‘Food Availability and Diet’.
Adaptations and Survival Strategies
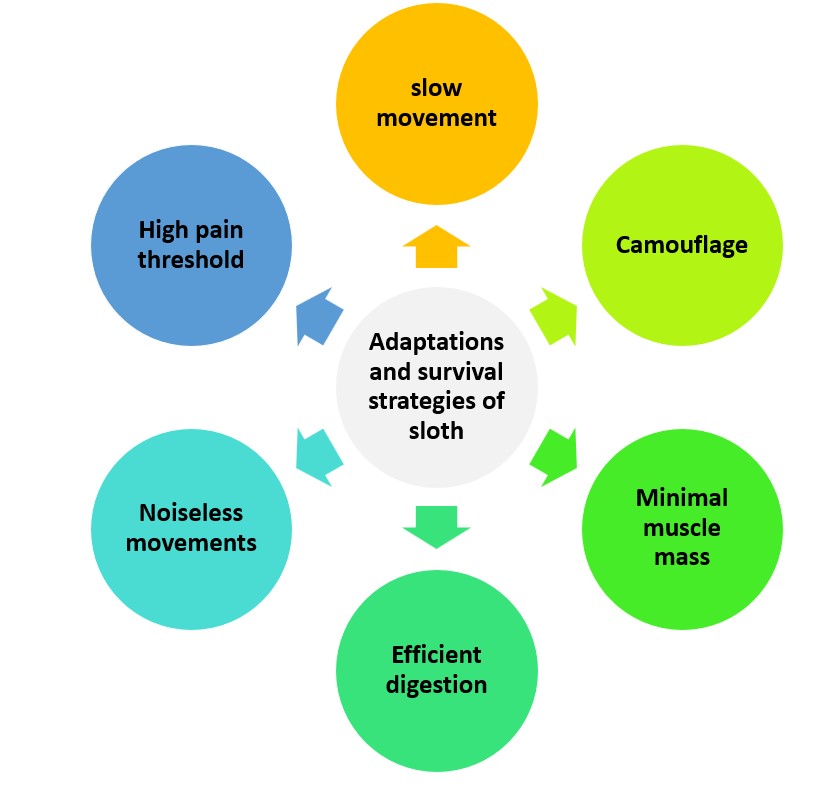
Sloths have unique adaptations that enable them to survive and thrive in their nocturnal lifestyle. These strategies are essential for their survival. Such as:
- Slow movements: Sloths are able to move at a slow pace, conserving energy during the night when they’re active. This also helps them blend into their surroundings, making it harder for predators to detect them.
- Camouflage: Their fur is covered in algae, which provides a greenish tint that helps them blend in with trees, and act as natural camouflage.
- Minimal muscle mass: Sloths have evolved with minimal muscle mass, allowing them to conserve energy and reduce metabolic needs.
- Efficient digestion: Sloths have specialized digestive systems that allow them to efficiently process leaves. They possess a multi-chambered stomach and microorganisms in their gut, which help extract nutrients.
- Noiseless movements: Sloths are able to move silently through the trees, using their long arms and strong claws to grip branches without making any noise.
- High pain threshold: Sloths have a high pain threshold, and can withstand injuries that would incapacitate other animals due to their slow metabolism and low activity levels.
Plus, sloths can regulate body temperature, huddling together for warmth during cooler nights. An amazing true story highlights sloths’ adaptive qualities – where a sloth was attacked by an eagle, but swiftly grabbed onto a branch and evaded its predator. This quick response showcases the incredible reflexes and agility that sloths possess.
Food Availability and Diet
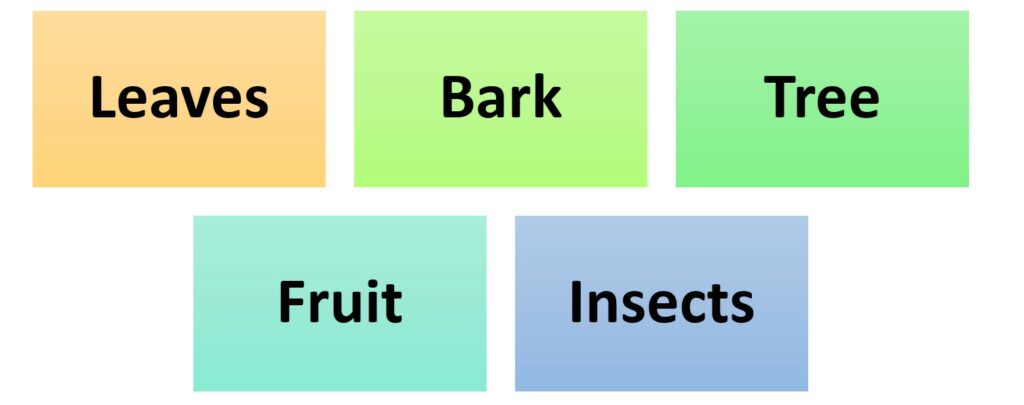
Food availability and the diet of sloths are very much connected. It’s key to their survival. To understand what they eat, let’s look at the components of their diet:
| Dietary Component | Food Source |
|---|---|
| Leaves | Trees |
| Bark | Tree trunks |
| Fruits | Select tree species |
| Insects | Occasionally |
Leaves are sloths’ main food source. Bark and fruits are supplementary. They rarely eat insects but do so to get more nutrition.
They have special stomachs with multiple compartments for digesting vegetation properly. This means they get the most out of their leafy meals.
On a moonlit night, a nocturnal sloth searches for food. It moves slowly and uses its senses and claws to navigate the treetops. It grabs leaves and strips them for nutrition. Its digestive system helps it get the energy it needs during the night.
We can understand how sloths have adapted to live in the dark. The night brings advantages greater than just food. It shows how resilient and clever these creatures are. Though we may not become nocturnal, we can still appreciate their skill for relaxing all night long.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are sloths nocturnal?
Yes, sloths are nocturnal animals, meaning they are most active during the night.
2. What do sloths do during the day?
Sloths sleep during the day, typically for around 15 to 20 hours. They spend the remaining hours eating, moving slowly, or grooming themselves.
3. How do sloths adapt to their nocturnal lifestyle?
Sloths have highly specialized adaptations to thrive in the darkness. They possess large, round eyes that are excellent in low light, and their slow metabolism helps conserve energy during periods of rest.
4. Can sloths see well in the dark?
While sloths have good night vision, they do not possess exceptional visual capabilities in complete darkness. Their eyes are designed to function best in dim lighting conditions.
5. Do sloths make any sounds at night?
Although sloths are generally quiet animals, some species can produce low-pitched vocalizations during the night. These sounds can include soft clicks, whistles, and occasional vocal calls.
6. Are there any sloth species that are diurnal?
Yes, while most sloths are nocturnal, there is one species known as the “pygmy three-toed sloth” that is primarily active during the day. However, this species is critically endangered and found only in a specific region of Panama.
Conclusion
Sloths are mainly nocturnal. This is proven through several clues.
First, they come down from trees to scavenge for food in the night, their slow metabolism and low body temperature help them conserve energy during the day, they have sharp claws and strong grip to help them move around in the dark. Lastly, sloth behavior studies prove increased activity at night.
Moreover, their limited range of motion makes them well-suited for night-time activities. This helps them blend into the darkness.
To observe these creatures better, researchers should use infrared cameras or other technologies for nighttime monitoring. This way, they can watch without disrupting the sloths.

