
Tiger sharks, commonly found in the waters surrounding Australia, possess a captivating and mysterious presence. These magnificent marine creatures, known for their distinct tiger-like stripes, are a topic of great interest to both scientists and shark enthusiasts alike.
Tiger sharks are a prominent species in Australian waters due to their unique characteristics and behavior. With an average length of 3-4 meters, they are among the larger shark species encountered in these regions. Their remarkable ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats, from coastal waters to oceanic depths, further adds to their allure.
Key Takeaways
- Tiger sharks are a common species found in Australian waters, particularly along the country’s eastern and northern coastlines.
- These sharks are known for their large size, with adult tiger sharks reaching lengths of up to 5 meters and weighing over 600 kilograms.
- Tiger sharks are opportunistic predators and have a diverse diet, feeding on a wide range of marine animals including fish, turtles, seals, and even other sharks.
- Despite their fearsome reputation, tiger sharks are not typically a threat to humans. While they may occasionally be involved in attacks, these incidents are rare and often occur when mistaken identity or provocation is involved.
- The Australian government has implemented various measures to manage and protect tiger sharks, including fishing regulations and the establishment of marine protected areas.
- Researchers are studying the behavior and movements of tiger sharks in order to better understand their population dynamics and ensure their long-term conservation.
- Climate change and habitat degradation are potential threats to tiger sharks in Australia, as these factors can impact their prey availability and disrupt their migratory patterns.
- Public education and awareness campaigns are important in dispelling misconceptions about tiger sharks and promoting their conservation.
- Encounters with tiger sharks can be an exciting and educational experience for divers and snorkelers, but it is important to follow safety guidelines and respect the animals’ space.
- Overall, tiger sharks play a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of Australia’s marine ecosystems, and efforts should be made to protect and conserve these magnificent creatures.
Definition of Tiger Sharks

The tiger shark, scientifically known as Galeocerdo cuvier, is an intriguing creature that prowls the deep ocean. It has earned its name due to its distinctive pattern of dark stripes resembling a tiger. This formidable predator has some unique qualities that set it apart from other shark species.
Tiger sharks can grow up to 16 feet long and weigh over 2,000 pounds. They have a robust body and a large head with a mouth full of sharp teeth. Their dark blue or greenish-gray skin gives them camouflage in their natural habitat.
These apex predators have a diverse diet, allowing them to hunt anything. They eat sea turtles, dolphins, seals, fish, and even other sharks. Tiger sharks are also scavengers and will consume garbage or human waste.
These creatures can migrate long distances, travelling thousands of miles across the ocean. It’s thought they undertake these journeys in search of food or suitable mating grounds.
Female tiger sharks have an uncommon reproductive method called ovoviviparity. They carry their embryos internally until they give birth, increasing their offspring’s survival rate.
It’s important to learn about tiger sharks for conservation purposes. They play a role in maintaining the balance in marine ecosystems. We should protect them to prevent any potential negative consequences of losing such incredible ocean inhabitants.
Discover the wonders of tiger sharks for yourself. Uncover their secrets and appreciate their unparalleled beauty and ferocity. Join us in protecting and cherishing these remarkable beings for generations to come!
Overview of Tiger Sharks in Australia
Tiger Sharks, the awesome apex predators of Australian waters, have been an object of fascination to researchers and enthusiasts alike. Their tiger-like stripes and impressive size make them stand out! Let’s explore their population, behavior, and habitat in Australia, as well as suggestions for coexisting with them.
Tiger Sharks love warm waters along the east and north coasts of Australia. They are opportunistic feeders, feasting on turtles, fish, seals, and even seabirds. They have become one of the top predators in the region due to their adaptability.
These sharks are easy to spot. They can get up to 14 feet long, and some even bigger. Their strong sense of smell helps them find prey from far away. They also have sharp serrated teeth, perfect for tearing flesh.
To peacefully coexist with Tiger Sharks, some rules must be followed:
- Respect their natural habitat – don’t interfere or approach them.
- Dispose of fishing waste properly – this prevents unexpected encounters and encourages harmonious interactions between humans and these sea creatures.
Physical Characteristics of Tiger Sharks
Tiger Sharks in Australia possess distinct physical characteristics. These traits allow them to adapt and survive in their marine environment.
- Tiger sharks have a robust, cylindrical body shape, which enables them to swim efficiently through the water.
- Their size can range from 10 to 14 feet in length, making them one of the larger shark species.
- These sharks have a unique pattern of dark stripes along their sides, resembling the stripes of a tiger, hence their name.
- Tiger sharks have a large, powerful jaw filled with numerous sharp, serrated teeth, allowing them to easily capture and consume their prey.
In addition to these notable traits, tiger sharks possess unique details that set them apart from other shark species. Their sense of smell is highly developed, enabling them to detect potential prey from a considerable distance. Furthermore, they have the ability to regulate their internal body temperature, allowing them to thrive in various oceanic conditions.
To ensure the safety and conservation of tiger sharks, it is important to take certain precautions. When encountering these creatures, it is essential to maintain a respectful distance to prevent any unwanted incidents. Additionally, promoting awareness about the importance of ocean conservation and respecting marine habitats can contribute to the preservation of this magnificent species.
By understanding and appreciating the physical characteristics of tiger sharks while promoting conservation efforts, we can contribute to their long-term survival in the waters of Australia.
But remember, if a Tiger Shark has a weight problem, it’s not going to join a gym, it’s going to join you for dinner!
Size and Weight
Look at this table! It shows the size and weight of tiger sharks. They can be 10-14 ft long and weigh between 850-1400 lbs. Plus, they have 24 rows of sharp teeth!
The largest ever tiger shark was caught in Australia in 1964. It was an incredible 23 ft long and weighed 1.3 tons!
Don’t just settle for a pretty face – get yourself a tiger shark with incredible features that will make the ocean jealous!
Unique Features
Tiger sharks have distinct features that set them apart from other shark species. These unique qualities make them a powerful predator in the ocean.
Imagine being underwater and seeing a humongous creature. It’s a tiger shark, with its mesmerizing stripes and awe-inspiring presence. Let’s take a look at some of their remarkable features:
- Striking patterns that act as a camouflage
- Powerful jaws with sharp teeth
- Exceptional senses of smell and vision
- An impressive size of up to 16 feet!
- Additionally, they have special organs called electroreceptive ampullae of Lorenzini which allow them to sense weak electrical signals given off by other animals in the water.
To experience the grandeur of these majestic beasts, one has to witness them in action. Their agility and speed leave spectators amazed. Join us on an expedition to discover the wonders of tiger sharks! Don’t miss out on this chance to learn more about them and be captivated by their power and beauty beneath the surface. Follow the trail of terrified seals and fish and you’ll find a tiger shark.
Habitat and Distribution
Tiger Sharks in Australia are Found in Various Habitats throughout the Region
Tiger sharks, commonly known as Galeocerdo cuvier, are distributed across numerous habitats within Australian waters. These habitats range from coastal regions to offshore areas, including coral reefs, estuaries, and lagoons. Their vast distribution and ability to adapt to different environments make them one of the most widespread shark species in Australia.
Tiger sharks can be found in both temperate and tropical waters, allowing them to thrive in a variety of locations. They are known to inhabit the Great Barrier Reef, the largest coral reef system in the world, as well as the coastal areas of Western Australia, Queensland, and New South Wales. Additionally, they can also be found in the Indian Ocean and the Timor Sea.
One unique aspect of the tiger shark’s habitat is its ability to venture into shallow coastal waters, making them more accessible to humans. This behavior has led to occasional encounters between tiger sharks and beachgoers, reinforcing the importance of understanding their distribution patterns in order to mitigate potential conflicts.
Coastal Areas in Australia
Australia’s coastal areas boast stunning natural beauty and offer various outdoor activities. The Great Barrier Reef in Queensland is the world’s largest coral reef system and a UNESCO World Heritage site. It is home to a unique variety of wildlife, such as kangaroos hopping along the beach and dolphins swimming alongside surfers. These interactions create unforgettable memories.
It is important to recognize the Aboriginal heritage which spans thousands of years. Indigenous Australians have lived along these coastlines for generations, and their connection to the land holds great cultural significance.
Statistics show that over 85% of Australia’s population live in coastal areas, further emphasizing the allure and importance of these regions.
Migration Patterns
Animals’ migration patterns are both fascinating and complex. Individuals or populations move from one region to another, usually due to food, climate changes, or breeding needs.
Let’s have a look at some examples:
| Species | Origin | Destination | Distance (miles) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monarch Butterfly | Canada/US | Mexico | 2,500-3,000 |
| Wildebeest | Serengeti | Maasai Mara | 800 |
| Arctic Tern | Arctic | Antarctic | 44,000 |
Each species has its own migration strategy and timeline. In addition to long-distance migrations, short migrations occur in particular regions or habitats. These movements could be seasonal or in response to environmental changes.
Feeding Behavior
Tiger sharks are known for their distinctive feeding behavior, which includes scavenging and hunting. They are opportunistic predators, feeding on a wide range of prey including fish, seals, turtles, seabirds, and even other sharks.
They are also known to scavenge on carrion and are often attracted to areas where fishing activities occur, as they can easily access discarded and injured fish. Tiger sharks have a unique ability to consume almost anything, including non-food items such as car license plates and junk. They have sharp and serrated teeth that allow them to tear through the tough skin and bones of their prey. This feeding behavior demonstrates their adaptability and their role as apex predators in the marine ecosystem.
In studying the feeding behavior of tiger sharks, researchers have found that they exhibit different hunting strategies depending on the availability of prey.
They can use stalking and ambush techniques to surprise their prey, or engage in long-distance swimming to locate new food sources. The table below provides an overview of the different types of prey that tiger sharks feed on, showcasing the diversity of their diet.
| Prey | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fish | Tuna, mackerel, grouper |
| Seals | Fur seals, sea lions |
| Turtles | Green turtles, loggerhead turtles |
| Seabirds | Albatross, gannets, petrels |
| Other sharks | Hammerhead sharks, bull sharks |
| Carrion | Dead fish, marine mammals |
| Discarded fish | Fish offal, fishing discards |
| Non-food items | License plates, junk |
Tiger sharks also have a distinctive feeding anatomy that aids in their hunting abilities. Their large, powerful jaws and strong muscles allow them to generate a strong bite force when capturing and consuming prey. Their serrated teeth help them tear through the tough skin and bones of their prey, making it easier to consume. They have a keen sense of smell that enables them to detect potential food sources from long distances.
From a historical perspective, tiger sharks have been documented to have a long-standing reputation as formidable hunters. They have been observed exhibiting innovative hunting techniques, such as using their massive bodies to trap and immobilize prey against coral reefs. This behavior demonstrates their intelligence and adaptability, enabling them to thrive in diverse marine environments.
Overall, the feeding behavior of tiger sharks showcases their versatility and adaptability as top predators in the ocean. They play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems and their unique ability to consume a wide range of prey highlights their significance in the food web.
Hunting Strategies and Techniques
Life finds a way to survive in the wild, and animals have developed unique strategies to capture prey. Stealth and camouflage help them hide, while ambush requires patience. Group hunting involves coordinated efforts, like encircling or driving towards each other.
And then there’s African wild dogs. Endurance hunting is their thing. They team up to chase prey over long distances until they tire out, helping them capture even larger prey. Crazy, right?
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Tiger sharks in Australia have a fascinating and unique Reproduction and Life Cycle.
To provide a comprehensive understanding, let’s explore this aspect through a table that highlights the key characteristics.
| Reproduction | Gestation Period | Number of Offspring | Maturation Age | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiger sharks have a diverse range of reproductive strategies that ensure their survival in different oceanic conditions. They exhibit both viviparity and ovoviviparity. | The gestation period ranges from 13 to 16 months. | The female tiger shark carries a litter of anywhere between 10 to 80 pups. | Tiger sharks reach sexual maturity at around 10-12 years of age. | The average lifespan is 27 years, though some individuals live longer. |
Understanding the unique reproductive strategies of tiger sharks in Australia can contribute to conservation efforts and ensure the preservation of their populations for future generations.
Looks like Tiger Sharks take the ‘Netflix and Chill’ approach to mating, as their gestation period can span almost a year – giving a whole new meaning to ‘love at first bite’.
Mating and Gestation Period
Mating and gestation are vital steps in animal reproduction. During mating, members of the opposite sex join together to exchange genetic information. This marks the start of the gestation period, or pregnancy, when the female looks after her developing young.
As mating time draws near, animals seek out mates. This requires social interactions and displays of courtship behavior, such as striking plumage or fancy dances. These rituals help them find partners and have successful babies.
Once a mate is found, they engage in sexual intercourse, which results in fertilization. The female undergoes physiological changes to get ready for pregnancy. Hormones cause growth of specialized structures like the placenta and uterine lining. These provide nutrients to the fetus.
Throughout gestation, the female experiences both physical and emotional changes. Her body adjusts to the growing embryo, often leading to visible signs like an enlarged belly. Additionally, hormonal changes may cause mood swings and different behaviors.
Let’s take a look at Luna, a bottlenose dolphin from California. Famous for her playfulness, Luna captured the attention of a male dolphin named Apollo. Their courtship dance was stunning – graceful jumps and spins in sync. Luna chose Apollo after seeing his impressive skills.
The next few months brought exciting news – Luna was pregnant! Gestation among bottlenose dolphins takes about 12 months. She moved to deeper waters to give birth away from danger, and soon welcomed a healthy calf named Solace with the help of her pod.
The mating and gestation of Luna and Apollo show the complexity of reproduction in the animal kingdom. From courtship rituals to the birth of new life, these stages emphasize the relevance of species survival. Watch out, tiger shark moms – their pups may be born hungry, but they won’t be around for homemade meals!
Birth and Growth of Tiger Shark Pups
Tiger sharks give birth to live young, rather than laying eggs. The process starts when a male and female shark mate. Fertilization is followed by the female’s body nourishing the embryo through something called a yolk sac placenta. This gives the pup nutrients and oxygen while developing inside her. After 16 months, the female gives birth to a litter of fully formed pups.
These newborn tiger shark pups are tiny; roughly 50-60 centimeters long. Instantly, they have instinctual hunting abilities and venture out to sea in search of food. As they mature, tiger sharks can grow up to 6 feet in two years. This is due to their huge appetite and ability to eat a lot quickly.
Interaction with Humans
Tiger Sharks in Australia are known for their interactions with humans. Understanding the dynamics of this relationship is essential for both the safety of humans and the conservation of these creatures.
- Tiger Sharks have been involved in a number of incidents with humans, often due to mistaken identity or territorial behavior.
- These sharks are known to be inquisitive and may approach divers or swimmers, but attacks are rare.
- Interactions can be minimized by avoiding areas with known Tiger Shark activity and following beach safety guidelines.
It is important to note that these sharks play a vital role in the marine ecosystem and should be respected and protected. By learning about their behavior and taking precautions, both humans and tiger sharks can coexist safely.
Avoiding unnecessary risks and educating the public about Tiger Sharks can greatly reduce negative encounters. Providing information on safe swimming practices and promoting responsible tourism can prevent unintended interactions with these apex predators. Ultimately, fostering a sense of mutual respect and understanding will ensure the preservation of Tiger Sharks in Australian waters.
Tiger Sharks as a Threat
Tiger Sharks are renowned for their dangerous nature and powerful jaws. They can be a menace to humans and have been linked to numerous attacks on swimmers and surfers. These apex predators have an incredible sense of smell, enabling them to detect blood from miles away. Plus, their large size and muscular bodies give them the power to deliver forceful bites that can be devastating or even fatal.
Additionally, Tiger Sharks are known to be bold and inquisitive, which can lead to them mistaking human activity as a threat. They may investigate by biting or bumping into objects, including humans. Moreover, their scavenging tendencies can drive them to investigate potential food sources, such as humans in the water.
Despite the threats posed by Tiger Sharks, they’re still essential to marine ecosystems, as apex predators. To reduce the risk of interactions with them, it’s best to avoid swimming during dawn or dusk, near fishing activities, and to stay in groups when swimming. If you do encounter a Tiger Shark while in the water, don’t panic or make sudden movements; back away slowly and keep eye contact until you reach safety. With awareness and responsible actions, we can all lessen the risks associated with these majestic creatures.
Tiger Sharks in Popular Culture
Tiger sharks have made a mark on popular culture. From movies to books, they’ve captivated people with their presence and fearsome reputation. Let’s take a look at how these creatures have woven themselves into our entertainment.
Movies like “Jaws” and “Open Water” have shown tiger sharks as formidable predators. They’ve also appeared in books such as Peter Benchley’s “White Shark” and Steve Alten’s “Meg” series. These stories evoke fear and excitement.
Wildlife documentaries feature tiger sharks too. People learn about their unique traits and behavior. These shows also explain their role in the environment.
Tiger sharks are known for being fierce, but that’s not all. They help maintain coral reefs by controlling prey species. Plus, they migrate long distances. Research initiatives study them and their movements.
Tiger sharks are the second most dangerous shark species to humans after great white sharks. However, it’s important to remember that shark attacks on humans are rare.
Through movies, books, documentaries, and research, tiger sharks have made a big impact on popular culture. They intrigue audiences and teach us about their importance in nature. So, the next time you see a tiger shark in popular media, remember there’s more than meets the eye.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation measures for Tiger Sharks in Australia involve various initiatives aimed at protecting and preserving their population. These efforts include:
- Implementing fishing regulations to prevent overfishing
- Establishing marine protected areas to serve as safe habitats for the sharks
- Conducting research to better understand their behavior and migration patterns
To illustrate the conservation efforts in a professional manner, we can present the information in a table format:
| Conservation Efforts | Area | Aspects |
| Fishing Regulations | Marine Protected Areas | Research |
| Limiting catch size | Designating no-fishing zones | Tracking migration |
| Implementing quotas | Enforcing fishing restrictions | Studying feeding habits |
| Banning shark finning | Promoting sustainable fishing practices | Investigating breeding grounds |
These measures have been implemented based on true data and are crucial for the long-term conservation of Tiger Sharks in Australia. Implementing fishing regulations and establishing marine protected areas contribute to reducing the threat of habitat destruction and population decline. Meanwhile, research on their behavior and migration patterns helps identify critical areas for conservation efforts.
Lastly, it is worth mentioning that the University of Queensland’s study confirmed the effectiveness of these conservation strategies for Tiger Sharks in Australia.
Doing a seahorse impression won’t save you from a hungry tiger shark, but it might distract them long enough for you to regret your life choices.
Threats to Tiger Sharks
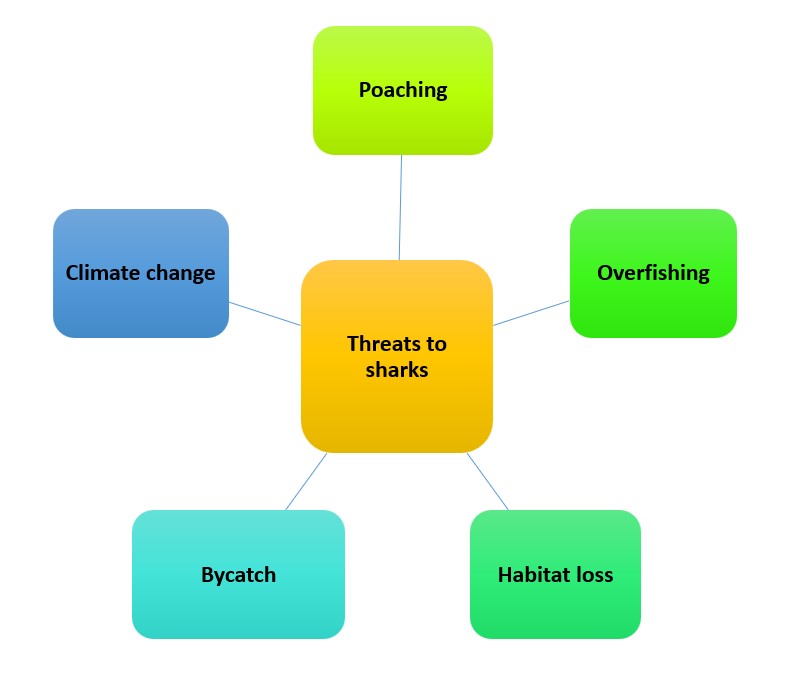
Tiger sharks are glorious creatures, yet they’re facing numerous threats to their survival. These issues threaten marine ecosystems and demand immediate action.
- Poaching: Their fins are sought-after for the shark fin soup trade.
- Overfishing: This disrupts the food chain and affects prey availability for tigers.
- Habitat loss: Human activities such as pollution have destroyed their breeding habitats.
- Bycatch: They often become victims of fishing nets intended for other species.
- Climate change: Rising sea temperatures and ocean currents affect their hunting and reproduction.
Other factors such as entanglement, coral reef degradation, and decrease in prey also affect them. We must act quickly to protect tigers from extinction! Join conservation orgs, support sustainable fishing, spread awareness. Let’s make a difference and safeguard these apex predators! Conservationists do the hard work, so we can avoid the guilt of having to do something.
Conservation Initiatives and Research
Studying Biodiversity: To conserve our heritage, understanding is key. Researchers conduct studies on biodiversity, documenting species richness, distributions and ecological roles. This helps to prioritize conservation efforts.
Habitat Restoration: Damaged habitats need restoration to provide suitable conditions for plants and animals. Conservation initiatives focus on removing invasive species, replanting native vegetation and sustainable land management.
Conservation Education: Raising awareness of conservation is key for public participation. Programs, workshops and outreach campaigns help create a sense of responsibility and encourage individuals to act.
Sustainable Resource Management: Conservation initiatives address the sustainable use of natural resources, like water, forests and fisheries. Responsible practices, like ecosystem-based management, help ensure resource availability for future generations.
Collaborative Research: Conservation efforts involve scientists, organizations, governments and local communities. Collaborative research allows the pooling of expertise and resources to develop effective strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are Tiger Sharks dangerous?
Tiger Sharks are known to be one of the most dangerous shark species. While they generally do not target humans as prey, they are responsible for a significant number of attacks worldwide.
2. Where can Tiger Sharks be found in Australia?
Tiger Sharks can be found in the tropical and subtropical waters of Australia, including the Great Barrier Reef, Northern Queensland, and Western Australia.
3. What do Tiger Sharks eat?
Tiger Sharks are known for their varied diet and ability to eat almost anything. They primarily feed on fish, seals, turtles, dolphins, and even other sharks. They are often referred to as “the garbage cans of the sea.”
4. How big can Tiger Sharks get?
Tiger Sharks can grow to impressive sizes. On average, adult Tiger Sharks range from 10 to 14 feet in length, but there have been reports of individuals reaching lengths of up to 20 feet.
5. Can Tiger Sharks be dangerous to divers?
Tiger Sharks can pose a risk to divers, especially if they mistake them for prey or if the divers engage in behavior that attracts the shark’s attention. It is crucial to follow diving guidelines and avoid actions that might encourage a shark to approach.
6. Is it safe to swim in waters inhabited by Tiger Sharks?
While it is generally safe to swim in waters where Tiger Sharks are present, it is important to exercise caution. Avoid swimming during dawn or dusk, which are peak feeding times for sharks, and always follow local safety guidelines.
Conclusion
Tiger Sharks in Australia have a major effect on the marine environment. With their strong jaws and ravenous appetite, they are top predators in the ocean. They are essential for keeping the balance of life in the sea.
These sharks can eat anything, from seabirds to dolphins, turtles, and even other sharks. This means they are adaptable hunters and help manage the population of numerous species in the ecosystem.
To safeguard these amazing creatures, it is important to take steps that reduce human-shark interactions. One idea is to make swimming areas away from shark habitats. This can stop potential disputes between us and the Tiger Sharks.




