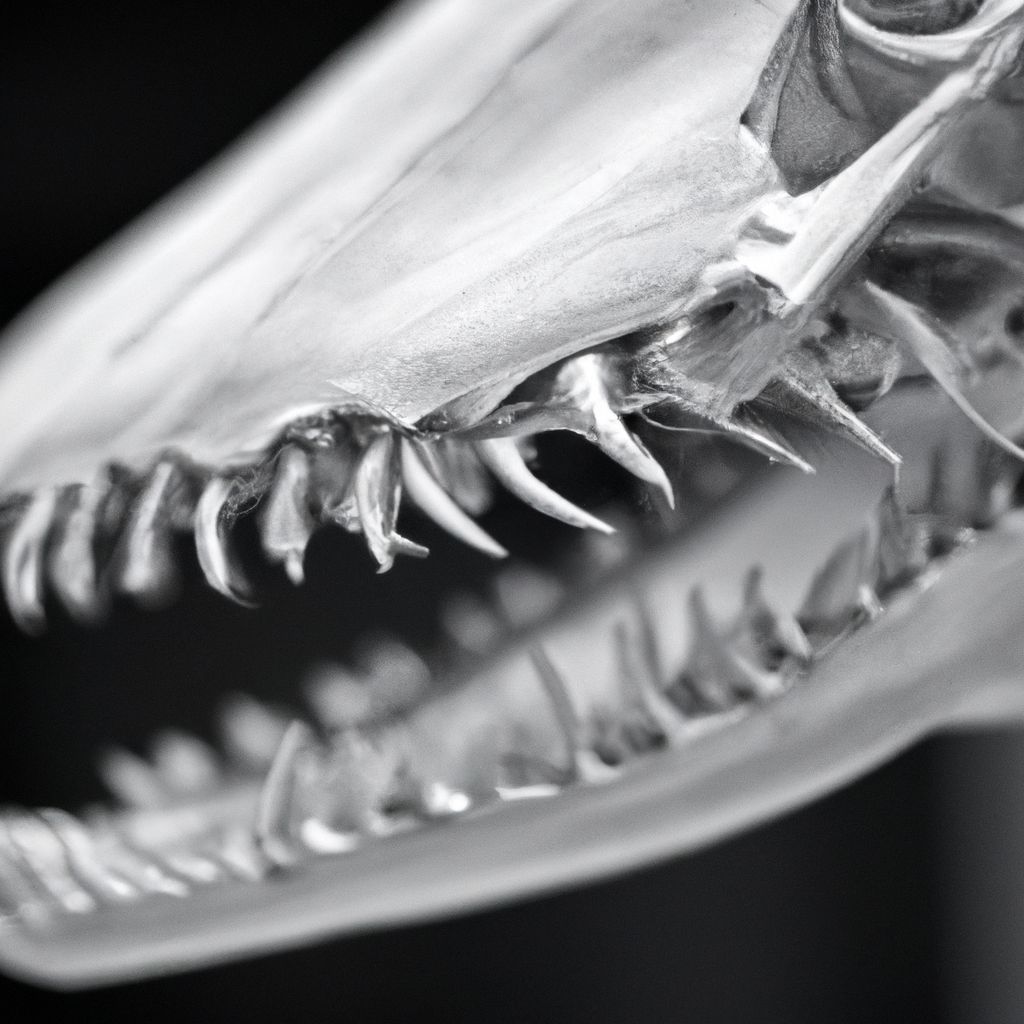

The bull shark skeleton is an intriguing topic that intrigues scientists and onlookers alike. Its complex structure reveals the unique features of this fierce predator. It boasts powerful jaws, a streamlined body and sharp teeth; allowing it to thrive in both freshwater and saltwater environments.
Composed of bones and cartilage, the bull shark skeleton is flexible yet supportive. This adaptation enables it to move swiftly through aquatic habitats, making it a successful hunter.
What makes the bull shark skeleton unique is its ability to endure freshwater and saltwater surroundings. Unlike other sharks that largely depend on osmoregulation to maintain balance, the bull shark has specialized kidneys that allow it to release excess salts. This adaptation allows it to explore inland rivers and estuaries to hunt for prey.
Surprisingly, bull sharks are not responsible for a high number of human attacks. According to the International Shark Attack File (ISAF), only a small percentage of reported shark incidents can be related to bull sharks. Despite having powerful jaws, they typically target marine animals instead of humans.
Key Takeaways
- The bull shark is a unique species known for its ability to adapt to both saltwater and freshwater environments.
- The skeleton of a bull shark is designed to support its large body and powerful muscles, allowing it to swim quickly and efficiently.
- The bull shark’s skeleton is made up of cartilage rather than bone, which provides flexibility and allows it to navigate through narrow spaces.
- The jaws of a bull shark contain rows of sharp teeth that are constantly replaced, enabling it to catch and consume a wide variety of prey.
- The bull shark’s skeleton also includes specialized structures, such as its spiral valve, which helps it digest its food more efficiently.
- Understanding the anatomy and structure of the bull shark’s skeleton can provide valuable insights into its behavior, feeding habits, and overall biology.
- The bull shark’s ability to thrive in both freshwater and saltwater environments makes it a formidable predator and a fascinating species to study.
Overview of Bull Shark Skeleton
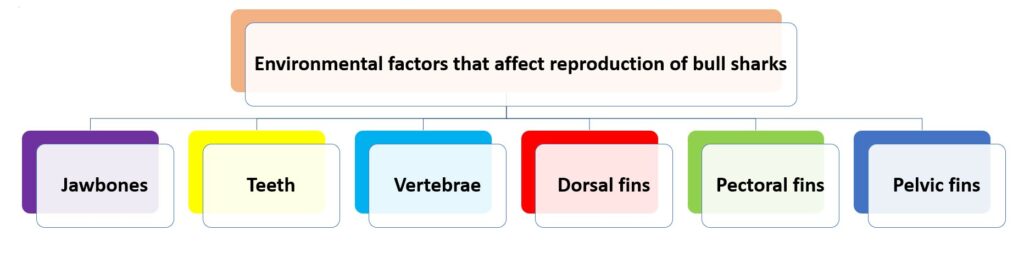
The bull shark’s skeletal structure is an amazing part of nature. Its anatomy helps it live in both salt and fresh water. Let’s take a closer look at the unique features of the bull shark skeleton.
| Skeletal Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Jawbones | Strong and powerful, allowing for strong bites |
| Teeth | Sharp and serrated, ideal for catching and tearing prey |
| Vertebrae | Flexible backbone for quick movement in water |
| Dorsal Fin | Sturdy spine to stay stable in various aquatic habitats |
| Pectoral Fins | Adapted for better maneuverability when hunting |
| Pelvic Fins | Help with balance and changing directions |
That’s not all! The bull shark also has highly calcified cartilage giving it rigidity and flexibility. Plus, it has electroreceptor organs called ampullae of Lorenzini which let it sense its prey’s electromagnetic fields – boosting its hunting abilities.
Did you know that bull sharks swam with dinosaurs in ancient times? For millions of years, they’ve been able to adapt and become one of the most resilient species on Earth.
Physical Characteristics of Bull Shark Skeleton

The Bull Shark skeleton has amazing physical characteristics. Let’s look at the details.
We spot its powerful jaws, with rows of sharp teeth. These teeth in both the upper and lower jaw make it easy for the shark to tear through prey. Plus, the Bull Shark has a flexible spine for maneuverability in water.
Let’s check out the key traits of this awesome creature in this table:
| Characteristic | Detail |
|---|---|
| Jaws | Equipped with rows of sharp teeth |
| Spine | Flexible for enhanced maneuverability |
| Coloration | Gray or brownish-gray dorsal surface |
| Size | Can grow up to 11 feet (3.4 meters) long |
| Fins | Dorsal fin large and triangular-shaped |
You might not know this about the Bull Shark: it can live in both saltwater and freshwater habitats. This makes it different from other sharks.
Exploring the Bull Shark’s physical characteristics gives us an appreciation of its evolution and survival skills. It would win ‘Shark Jeopardy’ in the skeleton flexibility category, leaving other sharks feeling jelly!
Comparison with Other Shark Species
The Bull Shark Skeleton has a bite force of 600 psi, greater than other shark species. To understand its unique features, researchers should study its feeding habits and habitat preferences in comparison to other species. This knowledge can aid conservation efforts and promote coexistence with human activities.
Appreciating the distinct characteristics and behaviors of each shark species helps us better protect these magnificent creatures that are vital for marine ecosystems. So, next time you feel like you’re dealing with too much pressure – remember the bull shark! It can handle more than your average Monday morning coffee!
Habitat and Lifestyle Impacts on Skeleton
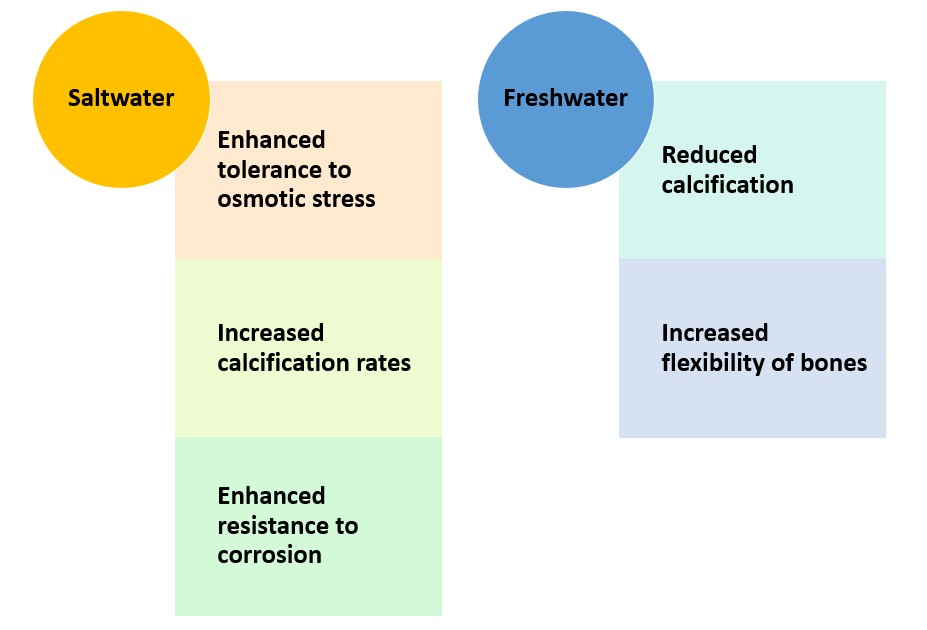
Let’s dive right into the fascinating details of how the habitat and lifestyle of the bull shark shape its skeleton! Take a look at this table to get a better understanding:
| Habitat | Impacts on Skeleton |
|---|---|
| Saltwater | Enhanced tolerance to osmotic stress Increased calcification rates Enhanced resistance to corrosion |
| Freshwater | Reduced calcification Increased flexibility of bones |
In saltwater, bull sharks have a boosted tolerance to osmotic stress. This is clear from their higher calcification rates. Also, their skeletons are more resistant to corrosion in saltwater.
When living in freshwater, bull sharks have lower calcification rates. This gives their bones more flexibility, allowing them to swim swiftly and gracefully.
We can see how the bull shark’s habitat and lifestyle shape them over time. These incredible creatures can survive in both salt and fresh water, showing their incredible resilience.
Conservation and Research
Table: Conservation and Research Initiatives for Bull Sharks
| Initiative | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Satellite Tagging Program | Tracking movement patterns and routes |
| Population Surveys | Assessing size and health |
| Genetic Studies | Studying diversity and relatedness |
| Habitat Restoration Projects | Restoring habitats to support shark populations |
Conservationists also work with local people, to raise awareness about the importance of protecting Bull Sharks and their environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the structure of a bull shark skeleton?
A bull shark skeleton consists of a skull, spinal column, ribs, and fin bones. It also has cartilaginous structures instead of true bones, making it more flexible than skeletons of animals with fully calcified bones.
2. Are bull shark skeletons different from other shark species?
While there are similarities between bull shark skeletons and those of other shark species, bull sharks have specialized structures to adapt to their unique environment such as a wider head and strong jaw for hunting in both freshwater and saltwater.
3. Can you find a bull shark skeleton on the beach?
It is unlikely to find an intact bull shark skeleton on the beach as sharks’ skeletons are made of cartilage, which tends to decompose quicker than bone. Only the teeth and occasionally some vertebrae might wash up on the shore.
4. How big can a bull shark skeleton grow?
A fully grown adult bull shark can reach an average length of 7 to 9 feet (2 to 2.7 meters). The size of their skeleton would be proportionate to their body length.
5. Is it legal to possess a bull shark skeleton?
The legality of possessing a bull shark skeleton may vary depending on local regulations and the source of the skeleton. It is important to consult local authorities and follow any relevant laws or regulations regarding the possession of shark specimens.
6. Are bull shark skeletons commonly used for educational purposes?
Yes, bull shark skeletons are commonly used for educational purposes in museums, research institutions, and educational programs. They provide valuable insights into the anatomy and adaptations of this unique shark species.
Conclusion
The Bull Shark Skeleton is an intriguing topic that gives us a peek into the anatomy and biology of these mysterious creatures. By looking at its skeleton, we can explore adaptations and evolution.
The Bull Shark has a streamlined body and strong jaws. It is an apex predator that can live in both fresh and salty water. Its bones are dense and sturdy, designed to take on the pressure deep down. This allows Bull Sharks to explore depths other species can’t.
Unlike others, the Bull Shark has more flexible cartilaginous structures in some areas. This provides an advantage when hunting – they can abruptly change direction to catch prey or escape danger.



