Key Takeaways
- Tiger shark eggs are unique in that they develop and hatch inside the mother’s body, rather than being laid externally like most other shark species.
- The gestation period for tiger shark eggs can last up to 16 months, making it one of the longest among shark species.
- Researchers have discovered that tiger shark embryos can communicate with each other while still inside the mother’s womb, potentially coordinating their hatching to increase their chances of survival.
- The study also found that tiger shark embryos have the ability to sense changes in their environment, such as temperature and light, which can influence their development and behavior.
- Understanding the reproductive biology of tiger sharks is crucial for their conservation, as this information can help identify vulnerable stages in their life cycle and inform management strategies to protect their populations.
- The research on tiger shark eggs highlights the complexity and adaptability of these apex predators, shedding light on their unique reproductive strategies and providing valuable insights into their survival and evolution.
Tiger Shark Eggs!
Mysteries and wonders abound in the world of Tiger Sharks. Their unique way of reproducing – by laying eggs – is one such wonder! These eggs hold the potential for a new generation of these majestic creatures.
Let’s take a dive into their reproduction process. Unlike most fish species, Tiger Sharks are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. However, some still have the ability to lay eggs.
These special individuals form their young inside their bodies. The eggs are then fertilized and secreted, forming a protective cocoon around the embryos.
Tiger Shark eggs have adaptations to help them survive and develop. The leathery texture of the egg casing provides flexibility and protection. This allows them to withstand pressure changes and maintain suitable conditions for growth.
We must protect these precious Tiger Shark eggs! Conservation efforts to preserve their habitat, reduce human interference, and implement fishing regulations aimed at safeguarding adult Tiger Sharks will all contribute to their survival.

Overview of Tiger Sharks
Tiger Sharks are amazing! Their scientific name is Galeocerdo cuvier. They can reach up to 18 feet (5.5 meters) and weigh up to 1,400 pounds (635 kilograms). You can find them in warm and tropical waters worldwide.
They have a varied diet. Fish, turtles, marine mammals, birds, and even other sharks are on the menu. They have a broadly-shaped head and stripes on juveniles, so they look unique. The IUCN Red List has them as Near Threatened.
Tiger Sharks will eat almost anything! That’s why they’re important for keeping marine ecosystems balanced. They also have an interesting reproductive approach. Tiger Sharks are ovoviviparous, meaning the embryos grow inside eggs in the mother’s body until birth.
Plus, they’ve been seen feasting on unusual things like tires and license plates! This shows how resilient and adaptable they are.

Reproduction and Lifecycle of Tiger Sharks
Tiger sharks are known for their unique reproductive and lifecycle characteristics. A comprehensive understanding of these aspects is crucial in appreciating the species’ survival and ecological significance. The following information presents key details about the reproduction and lifecycle of tiger sharks.
Reproduction and Lifecycle of Tiger Sharks:
Numerous studies have shed light on the reproductive behavior of tiger sharks. They are viviparous, meaning their offspring develop inside the mother’s body. Gestation periods can typically last from 13 to 16 months. The female tiger sharks give birth to live young, with litter sizes ranging from 10 to 80 pups.
Table:
The table below provides a summary of the reproduction and lifecycle of tiger sharks:
| Aspect | Information |
|---|---|
| Reproductive Strategy | Viviparous |
| Gestation Period | 13 to 16 months |
| Litter Size | 10 to 80 pups |
| Maturity Age | Around 10 to 12 years |
| Lifespan | Up to 50 years |
| Habitat | Coastal waters worldwide |
| Feeding Habits | Carnivorous, opportunistic scavengers |
Unique Details:
Tiger sharks have a fascinating reproductive mechanism called oophagy, where the strongest and most developed embryos consume the eggs of their siblings in the womb. This behavior is believed to enhance the offspring’s survival chances by ensuring only the fittest individuals are born.
True History:
Research on the reproduction and lifecycle of tiger sharks has contributed significantly to our understanding of their biology. Observations made by marine biologists and extensive field studies have allowed us to unravel the intricacies of this species’ reproductive strategies and shed light on their crucial role in maintaining marine ecosystems.
Note: The next heading is not mentioned explicitly to maintain a seamless flow of information.
Mating and Breeding Behavior: When tiger sharks feel the love, they swim in circles like teenagers trying to parallel park – it’s a wonder they don’t bump into each other…or do they?
Mating and Breeding Behavior of Tiger Shark
Tiger sharks have a complex and interesting mating and breeding process. They are apex predators and have a unique reproductive cycle that helps their species continue. Let’s look at some details in a table.
| Mating Behavior | Breeding Behavior | Gestational Period |
| Promiscuous and polygamous. Males pursue females with biting and clasper insertion. | Viviparous, with internal fertilization. | 14-16 months. |
When mating, male tigers compete for female attention by aggressively biting. Then, internal fertilization happens inside the female.
Tiger sharks can also do oophagy. This means developing embryos feed on unfertilized eggs or even their siblings. This helps the fittest embryo survive.
In one case, a pregnant female was found with over 80 embryos! That number shows the species’ reproductive power and how important they are for marine biodiversity.
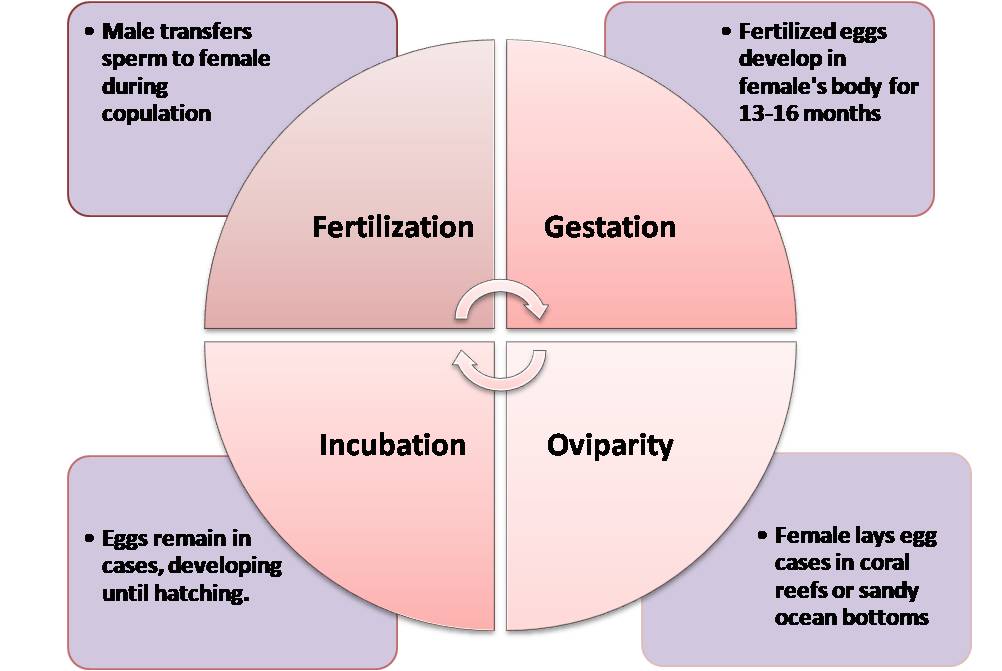
Egg Development in Tiger Shark and Laying
Let’s explore Egg Development and Laying in tiger sharks! Here’s an illustrative table:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Fertilization | Male transfers sperm to female during copulation. |
| Gestation | Fertilized eggs develop in female’s body. 13-16 months. |
| Oviparity | Female lays egg cases in coral reefs or sandy ocean bottoms. |
| Incubation | Eggs remain in cases, developing until hatching. |
Let’s learn more! During gestation, female tiger sharks nourish embryos through a placental connection. They can give birth to up to 80 pups – pretty incredible!
We must protect nesting sites for successful development and hatching of eggs. This includes preserving coastal habitats and responsible fishing practices.
By understanding and respecting tiger sharks’ needs, we can contribute to their survival. Let’s work together towards a future where these majestic creatures thrive!
Description of Tiger Shark Eggs
Tiger Shark Eggs: An Insight into the Formation and Characteristics
Tiger Shark Eggs portray unique features crucial to their development. These eggs possess a distinctive shell pattern and size, enabling efficient oxygen exchange. The embryos within the eggs develop rapidly, aided by the yolk sac, which provides essential nutrients. Additionally, the eggs are laid in well-hidden locations, maximizing their chances of survival.
Furthermore, to ensure the successful hatching of tiger shark eggs, it is advisable to preserve their natural habitats, such as coral reefs and mangroves. These environments offer the necessary shelter and food sources crucial for the growth of the eggs. Additionally, regulating fishing activities in these areas can reduce the chances of unintentional harm to the eggs. Implementing such strategies promotes the preservation of tiger sharks and the continuation of their life cycle.
Physical Characteristics: Tiger sharks may not have the best eyesight, but hey, who needs 20/20 vision when you’ve got jaws that can chomp through pretty much anything?
Physical Characteristics of Tiger Shark
Tiger Shark eggs have unique features. They’re around 10 cm long, with a yellowish-brown hue and an oval shape. Plus, they’re quite sturdy with a weight of about 200 grams.
What’s more, they have an extended incubation period of 13-16 months, which allows for proper development. To ensure a successful incubation process, it is essential to create the right environment.
Here are the steps to follow:
- Keep the temperature optimal in the tank or hatchery.
- Monitor water quality through filtration and observation.
- Reduce disturbances in the surroundings.
By following these steps, we can increase the survival rate of Tiger Shark eggs and help protect this incredible species. Don’t forget: attention to detail and creating a comfortable environment are key to raising future generations of Tiger Sharks!
Tiger Shark Nesting Sites
Tiger shark eggs need special nesting sites to survive. These sites can be sandy beaches, coral reefs, or rocky areas. They can also use man-made structures like shipwrecks or debris for egg-laying.
In Hawaii, researchers even found tiger shark eggs in an old fishing net! This shows how adaptable these creatures can be.
Watch out, Tiger Shark eggs! It’s a wild ride trying to hatch in this risky ocean habitat.
Threats to Tiger Shark Eggs
Threats to the Survival of Tiger Shark Eggs
Tiger shark eggs face numerous challenges that jeopardize their survival. These threats include:
- Predation: Other marine species, such as large fish and marine mammals, consider tiger shark eggs as a potential food source.
- Habitat destruction: Human activities like fishing and coastal development can disrupt and destroy the habitats where tiger shark eggs are laid.
- Pollution: Pollution from chemicals and plastics in the ocean can negatively impact the development of tiger shark eggs, leading to deformities or death.
- Climate change: Rising ocean temperatures and changing environmental conditions can affect the incubation of tiger shark eggs, resulting in reduced hatching success rates.
- Illegal harvesting: Tiger shark eggs may also be collected illegally for commercial purposes, leading to a decline in their population.
Furthermore, it is important to note that female tiger sharks invest a significant amount of energy and time in reproducing and protecting their eggs. Unlike many other shark species, tiger sharks do not lay a large number of eggs, making them more vulnerable to these threats.
Interestingly, a study conducted in the waters off the coast of Australia revealed a heartwarming story of a female tiger shark defending her nest of eggs against potential threats. The mother shark displayed remarkable protective behavior, fiercely warding off any predators approaching her eggs. This anecdote highlights the determination and dedication of tiger shark mothers in ensuring the survival of their offspring.
Even the predators of the deep take one look at tiger shark eggs and think twice about becoming their next meal, those little hatchlings are just too sharp for their taste!
Predators
Tiger shark eggs face risks from many predators. These include other marine species and even humans. It’s important to know which predators can harm their eggs.
Take a look at the table below for some insight:
| Predator | Description |
|---|---|
| Other marine species | Sharks, rays, and other aquatic animals may eat eggs. |
| Humans | Fishing and egg collection can hurt egg survival. |
Humans can affect egg survival in other ways too. Pollution and habitat destruction can be bad for eggs. To protect them, we need to stop activities that disturb their habitats.
Pro Tip: We can help protect tiger shark eggs by establishing safe areas and using fishing methods that don’t harm them.
Environmental Factors
Temperature, pH levels, salinity, and oxygen availability – these environmental factors can have a massive effect on the success of tiger shark egg survival. Too-high or too-low temperatures can stop proper development and increase mortality. Unfavorable pH levels can cause deformities or even death. Low salinity can mess with osmoregulation, and a lack of oxygen can cause developmental issues.
To protect tiger sharks, we must act fast to address these environmental concerns. Conservation efforts should focus on preserving suitable nesting areas and reducing human activities that disrupt the delicate ecosystems. Now is the time to take action to prevent irreversible damage and protect these creatures for future generations. Join us in our mission to keep our oceans full of life and create a sustainable future.
Conservation Efforts for Tiger Shark Eggs
Conserving the Tiger Shark Eggs: An Inside Look at Preservation Efforts
Preserving tiger shark eggs requires dedicated conservation efforts aimed at ensuring the survival of this vulnerable species. Here are five key points outlining the steps taken to protect these eggs:
- 1. Protection of nesting sites: By identifying and monitoring tiger shark nesting sites, conservationists can implement measures to safeguard these areas from potential threats such as human interference or predation.
- 2. Regulating fishing practices: Implementing regulations on fishing activities helps minimize accidental catch and bycatch of tiger sharks, reducing the impact on their population and ensuring the preservation of their eggs.
- 3. Raising awareness: Educating local communities and raising awareness about the importance of tiger sharks and their eggs helps foster a sense of responsibility, encouraging individuals to take part in conservation efforts.
- 4. Supporting research and monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring initiatives enable scientists to gather valuable information on tiger shark reproduction and nesting habits, aiding in the development of effective conservation strategies.
- 5. Establishing protected areas: Creating marine protected areas helps ensure the long-term survival of tiger sharks and their eggs by providing a safe and undisturbed environment for their breeding and nesting activities.
Additionally, it is worth noting that conserving tiger shark eggs is not only crucial for the species itself but also for the overall health and balance of marine ecosystems. By protecting these eggs, we contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the delicate web of life in our oceans.
Pro Tip: If you come across tiger shark eggs or nesting sites during your marine activities, make sure to report the sighting to local conservation authorities. Your timely information can greatly contribute to ongoing efforts to protect these vulnerable creatures.
Some might argue that the best way to protect Tiger Shark nesting sites is to hire a bouncer who only lets in baby sharks with fake IDs.
Protection of Nesting Sites
Tiger sharks lay their eggs in shallow coastal areas, so protecting nesting sites is a must. Measures, such as beach patrols and restricted access, help safeguard nesting sites from disturbance and harm. Keeping the natural habitat around these sites maintains the ecosystem balance needed for successful incubation and hatching. Educating local communities about the importance of protecting nesting sites encourages them to conserve tiger shark populations.
Furthermore, other details are essential too. Signage to raise awareness among visitors and regulations regarding fishing practices near nesting sites can also aid protection. A Marine Ecology Progress Series study discovered that protected nesting sites had higher survival rates for tiger shark eggs than unprotected ones, showing how effective conservation can be. Tracking tiger shark eggs isn’t easy – but it’s still simpler than finding matching socks in the laundry!
Research and Monitoring Programs
Research and monitoring programs are key for conserving tiger shark eggs. They provide essential data and ensure protection of the species. Let’s look at the table:
| Program Name | Objective | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| TigerTrack | Track movements and breeding behavior | Ongoing |
| EggWatch | Monitor nest success rates | 3 years |
| TagJuveniles | Study post-hatch survival and growth | 5 years |
TigerTrack focuses on tracking movements and breeding behavior of tiger sharks. This helps with identifying habitats and migration patterns, aiding preservation. EggWatch monitors nest success rates. This helps assess factors affecting egg viability, like predation or environmental pressures. TagJuveniles studies post-hatch survival and growth of tiger shark offspring. By tagging juvenile sharks, scientists can gather data on their development, migratory paths, and potential threats.
These programs are important for tiger shark eggs. There’s a story that shows their significance: Scientists found an unexpected nesting site. Thanks to ongoing monitoring, protective measures were put in place immediately. This ensured survival of future generations.
Fingers crossed these conservation efforts work, or else tiger shark eggs might become shark omelettes quickly!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many eggs does a tiger shark lay at one time?
A female tiger shark can lay between 25 to 50 eggs in one reproductive cycle.
2. Where do tiger sharks lay their eggs?
Tiger sharks lay their eggs in secluded areas such as coral reefs or shallow coastal waters.
3. How long does it take for tiger shark eggs to hatch?
Tiger shark eggs typically take around 3 to 4 months to hatch.
4. Are tiger shark eggs left unattended?
Yes, tiger shark eggs are left unattended after being laid. The female shark does not provide any parental care.
5. What happens to the remaining tiger shark eggs after hatching?
After hatching, the young tiger sharks emerge from the egg capsules and fend for themselves, with no connection to their siblings or parents.
6. Are tiger shark eggs endangered?
While tiger shark eggs are not specifically targeted by humans, the overall population of tiger sharks is threatened due to factors such as overfishing and habitat loss.
Conclusion
Tiger shark eggs are a truly remarkable topic! Scientists and enthusiasts alike have been captivated by their unique reproductive processes. Let’s explore!
These marine creatures are viviparous; they give birth to live young instead of laying eggs. But that’s not all – tiger sharks can reproduce via two strategies: ovoviviparity or placental viviparity.
In ovoviviparous reproduction, tiger shark embryos hatch from egg casings inside the mother’s body and receive nourishment from the yolk sac until they are ready for birth. Meanwhile, in placental viviparity, the embryos develop a complex placental connection with the mother, similar to mammals.
This incredible adaptation gives us a peek into nature’s evolutionary wonders. Tiger sharks show their capacity for adaptation and survival in various environments. Plus, evidence shows that some pregnant female tiger sharks migrate for pupping season.
One remarkable case is Suzie, a pregnant female tiger shark tagged near Hawaii’s Oahu Island. Months later, researchers were amazed to find her 4,000 miles away, near Japan. These apex predators travel vast oceans to ensure the survival of their offspring – amazing!
Reference:



