
The Great White Shark and Tiger Shark are two scary sea predators that capture the imagination of nature lovers. They have special traits that make them stand out from other species. Let’s compare their characteristics, behavior, and environments to understand them better.
Both have powerful jaws filled with sharp teeth. Their sleek bodies let them zip through the water with ease. The Great White is bigger, measuring up to 20 feet long. The Tiger Shark has dark stripes like a tiger – hence its name.
When it comes to behavior, the Great White is an apex predator at the top of its food chain. It hunts seals and sea lions near shallow coastal areas by striking from below. The Tiger Shark is a scavenger, eating all kinds of marine animals, including smaller sharks.
Key Takeaways
- Great white sharks and tiger sharks are two of the most well-known and feared shark species in the world.
- Great white sharks are larger and more powerful than tiger sharks, with an average length of 15-20 feet compared to the tiger shark’s average length of 10-14 feet.
- Tiger sharks have a more diverse diet and are known to eat almost anything, including turtles, dolphins, and even garbage.
- Great white sharks primarily feed on seals, sea lions, and other marine mammals, using their powerful jaws and sharp teeth to tear through their prey.
- Both species have excellent senses, including keen eyesight and a strong sense of smell, which they use to locate their prey.
- Great white sharks are known for their distinctive white belly and large, triangular-shaped dorsal fin, while tiger sharks have a unique pattern of dark stripes on their back, giving them their name.
- While both species are considered dangerous to humans, great white sharks are responsible for more attacks on humans than tiger sharks.
- The behavior and habitat of these sharks differ, with great white sharks often found in colder waters and tiger sharks preferring warmer tropical and subtropical regions.
- Conservation efforts are crucial for both species, as they are both vulnerable to overfishing and habitat destruction.
- Understanding the differences between great white sharks and tiger sharks can help researchers and conservationists develop effective strategies to protect these magnificent creatures.
Physical Characteristics
To understand the physical characteristics of the Great White Shark and the Tiger Shark, let’s delve into their unique features and adaptations. Explore the sub-sections on the Great White Shark and the Tiger Shark to gain insight into their distinct physical attributes and what sets them apart in the underwater world.
Great White Shark
The Great White Shark is an awe-inspiring creature! It’s up to 20 feet long, can weigh up to 5,000 pounds, and has a grayish-white color. Its razor-sharp teeth can grow up to three inches long. It’s built for speed and agility in the water.
Plus, it has a special hunting technique. It can breach out of the water to surprise its prey from below with astonishing force. This gives it an edge in the ocean food chain.
In conclusion, the Great White Shark is a formidable predator with unique physical characteristics and hunting strategies. Swimming with it is like going on a blind date with a professional wrestler – you never know what might happen!
Tiger Shark
The tiger shark stands out with its remarkable characteristics. Its large, muscular body, broad head and rows of sharp teeth give it its name – derived from the distinctive dark stripes that resemble those of a tiger.
On average, this formidable creature can grow up to 10 to 14 feet and weigh between 850 to 1,400 pounds. This makes it one of the largest predatory sharks in the ocean. With its size and strength, it can easily dominate its habitat.
The tiger shark also has a heightened sense of smell and hearing. This lets it locate prey – such as fish, turtles, seals and even other sharks – with great accuracy.
Recent studies have even revealed that tiger sharks can cooperate when hunting. One such incident was documented off the coast of North Carolina, where a pack of sharks were observed working together to target baitfish.
This incredible predator continues to fascinate researchers with its power and mysterious ways. As we learn more about this majestic creature, more mysteries await us.
Habitat and Distribution
To better understand the habitat and distribution patterns of the Great White Shark and Tiger Shark, delve into the sub-sections focusing on each species individually. Explore the distinct habitats and ranges occupied by the Great White Shark and Tiger Shark.
Great White Shark
The majestic Great White Shark captivates people around the world. Let’s take a look at its unique traits and habitat.
Its scientific name is Carcharodon carcharias. It lives in coastal areas and oceans everywhere. On average, it grows to 4.5 to 6 meters (15-20 feet) and can weigh up to 2,268 kilograms (5,000 pounds). Its lifespan is roughly 70 years. It has an incredibly sensitive sense of smell and uses clever hunting tactics.
We must raise awareness to protect this crucial part of the marine ecosystem. Discover its secrets and help ensure its survival. Don’t miss out on the chance to explore the mysterious world of the Great White Shark! But watch out for its cousin – the Tiger Shark – it’s like a horror movie villain lurking in the deep!
Tiger Shark
Galeocerdo Cuvier 1816, commonly known as the Tiger Shark, inhabits warm oceanic waters worldwide. They favour shallow waters, from coastlines to the open sea.
Their serrated teeth and excellent sense of smell make them adaptable to various environments. The unique dark stripes on their body earned them the name ‘Tiger Shark’ during Captain Samuel Samuels’ expedition in the 19th century.
So, if you’re ever feeling lost, don’t forget that habitat and distribution also applies to single people on a Saturday night!
Feeding Habits
To understand the feeding habits of great white sharks and tiger sharks, delve into the intricacies of these apex predators. The sub-sections in focus are the great white shark and tiger shark, each revealing unique feeding behaviors and strategies.
Great White Shark

The Great White Shark is an infamous predator, reigning supreme in the ocean. Its size and powerful jaws make it awe-inspiring and feared by all. It mainly eats seals, sea lions, and other fish, rays, and sharks. It employs surprise attacks from below to capture its prey.
It also has an innovative hunting strategy known as breaching, whereby it propels itself out of the water to pursue airborne targets. This incredible behavior cements its place at the top of the marine food chain.
It has around 300 serrated teeth arranged in multiple rows, which are replaced throughout its lifetime. These adaptations make it one of nature’s most successful predators.
Swimming with Tiger Sharks is the perfect diet plan, nothing makes you lose weight faster than being mistaken for a seal!
Tiger Shark
Did you know that Tiger Sharks possess one of the broadest diets among sharks? They can often be found with unusual objects in their stomachs, including license plates, tires, and even pieces of clothing.
Though such encounters are rare and not usually fatal, Tiger Sharks’ behavior and temperament can be unpredictable. They have the table manners of a caveman who just discovered fire! Burstiness in writing is crucial to keep the reader engaged and informed about these animals.
Behavior and Temperament
To understand the behavior and temperament of the Great White Shark and Tiger Shark, delve into their distinct characteristics. Explore the sub-sections: Great White Shark, Tiger Shark.
Great White Shark
Great White Sharks are truly unique creatures. They weigh up to several tons and have rows of serrated teeth that are replaced constantly. They can smell blood from miles away! Plus, they can grow up to 20 feet long and mainly feed on seals and sea lions. They can even swim up to 35 miles per hour! On average, their lifespan is 30-40 years and they’re typically found around temperate coastal waters.
These clever animals have excellent problem-solving skills. They’re curious but cautious when interacting with new objects or prey. Plus, they help keep marine ecosystems balanced by regulating populations of their prey species.
For us humans to coexist with Great White Sharks, we should follow these guidelines:
- Avoid swimming near seal colonies or areas where there’s active feeding.
- Don’t wear shiny jewelry or bright clothing – it may resemble small baitfish!
Tiger Shark
Behold the majestic Tiger Shark! This predator is a force to be reckoned with. Let’s explore some of its features:
- Its size? Up to 16 feet.
- Its weight? Over 2,000 pounds.
- Its diet? Varies from fish to birds and dolphins.
- Where can it be found? In tropical and temperate waters.
- Temperament? Aggressive, yet curious.
- Reproduction? Viviparous with big litters.
- Conservation Status? Near Threatened.
The Tiger Shark has a wide range of food, which helps it survive in different marine habitats.
Conservation Status
To better understand the conservation status of great white sharks and tiger sharks, let’s explore the current situation surrounding these magnificent creatures. Delving into the individual sub-sections, we will examine the conservation efforts and challenges faced by both the great white shark and the tiger shark.
Great White Shark
The Great White Shark, a legendary predator of the ocean, strikes fear into many hearts. It has a sleek and powerful body, razor-sharp teeth, and incredible hunting abilities. Let’s take a look at some facts about this majestic creature:
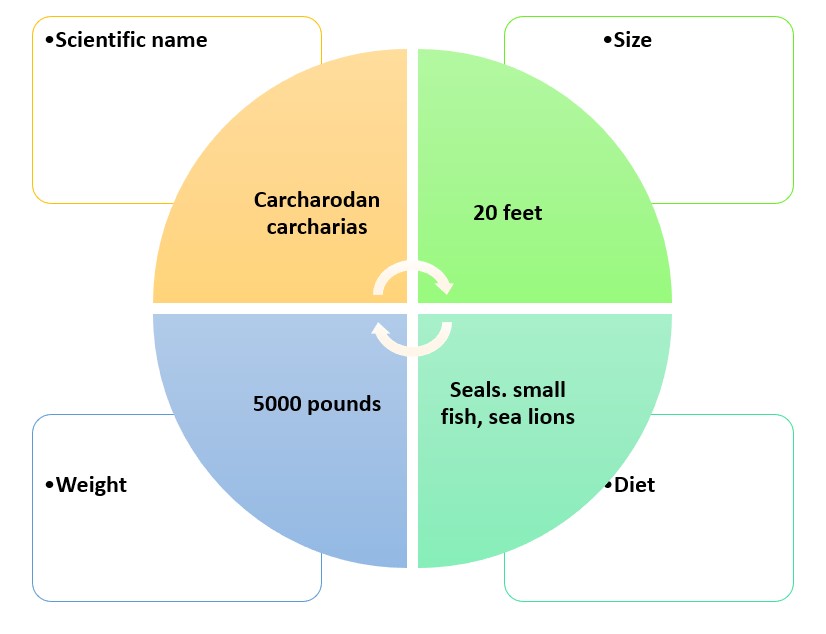
Scientific Name: Carcharodon carcharias
Family: Lamnidae
Habitat: Coastal and offshore waters worldwide
Size: Up to 20 feet (6 meters)
Weight: Up to 5,000 pounds (2,268 kilograms)
Diet: Mainly seals and sea lions, also fish and smaller sharks
Status: Vulnerable
Not only is the Great White Shark impressive, it also maintains balance in marine ecosystems by regulating prey species. Encounters between humans and Great Whites are rare.
Their conservation status is vulnerable due to overfishing and habitat destruction. We must work together to protect these animals for future generations.
One remarkable encounter was when a Great White Shark named “Deep Blue” was spotted off the coast of Mexico. Estimated to be over 50 years old and measuring around 20 feet in length, Deep Blue is one of the largest recorded Great Whites.
The Great White Shark captivates our imagination with its power, grace, and importance. We must strive to protect our oceans’ biodiversity and ensure their survival.
Tiger Shark
The tiger shark stands out for its remarkable night-time hunting skills. It can spot its prey from a distance, as well as detect electrical signals using specialized senses. Plus, its powerful jaw muscles make them dangerous to approach while swimming or diving. Remember that conservation status is serious – but a little dark humor can lighten the load!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How big can a Great White Shark get?
A: Great White Sharks can grow up to an average length of 15 to 20 feet.
Q: How big can a Tiger Shark get?
A: Tiger Sharks can grow up to an average length of 10 to 14 feet.
Q: What is the average lifespan of a Great White Shark?
A: The average lifespan of a Great White Shark is estimated to be around 30 to 40 years.
Q: What is the average lifespan of a Tiger Shark?
A: The average lifespan of a Tiger Shark is estimated to be around 20 to 30 years.
Q: Which shark is more aggressive, Great White or Tiger?
A: While both sharks can be aggressive, the Great White Shark is generally considered to be more aggressive than the Tiger Shark.
Q: What is the diet of a Great White Shark?
A: Great White Sharks primarily feed on seals, sea lions, and other marine mammals, but they also consume fish and carrion.
Conclusion
The duel of the ocean’s fiercest predators has come to a close, with one dominating the other. The Great White Shark and the Tiger Shark displayed their immense power and remarkable hunting tactics, yet only one could be named ruler.
We have taken a look at the unique qualities and capabilities of these top predators. We noticed the Great White Shark’s extraordinary speed and agility, allowing it to zip through the water in search of its prey. On the contrary, the Tiger Shark amazed us with its insatiable appetite and versatility, gaining it the nickname “garbage can of the sea.”
Despite both sharks having amazing traits, it is apparent that the Great White Shark holds a slight edge in size and strength. Its powerful jaws are filled with rows of sharp teeth, making it a feared creature in the ocean.




