
The Great White Shark–one of the ocean’s most captivating creatures–dazzles with its unique way of giving birth. Unlike other species, these predators don’t lay eggs: they give live birth!
Mating time! Male Great Whites use their sharp teeth to bite into the female’s body, transferring sperm in a behavior known as “mating scars.” This sounds aggressive, but it’s a necessary step.
The female’s body now holds the embryos–as many as 10! Developing via “ovoviviparity,” they rely on nutrients from an egg yolk sac instead of the mother’s bloodstream.
The babies emerge into the world through live birth. We’ve heard a story of a marine biologist who witnessed this event firsthand. She was on a research expedition and stumbled upon a pregnant female near the coast. She watched in awe as the shark gave birth before her eyes. It was an extraordinary reminder of nature’s astounding wonders.
The mystery of Great White Shark birth captivates scientists and nature enthusiasts. By exploring this subject, we gain a greater understanding of these majestic creatures and their unusual methods of reproduction.
Key Takeaways
- Great white sharks give birth to live young, a process known as viviparity.
- The female shark carries the embryos in her uterus until they are fully developed.
- The gestation period for great white sharks is estimated to be around 12-18 months.
- The embryos receive nutrients from a yolk sac until they are large enough to feed on other sources.
- The female shark gives birth to a litter of 2-10 pups, which are usually around 4-5 feet long at birth.
- The pups are immediately independent and must fend for themselves in the ocean.
- The exact mating and birthing behaviors of great white sharks are still not fully understood and require further research.
Background Information on Great White Sharks

The Great White Shark is a captivating creature! It has a streamlined body and powerful jaws with rows of sharp teeth. This apex predator can be found in coastal waters all around the world.
It’s been swimming in our oceans for millions of years. Fossil records date back 16 million years! Their primary hunting grounds are cool coastal waters, where they hunt marine mammals like seals and sea lions.
Their size is remarkable, with adult females reaching 15-20 feet. And their sense of smell is extraordinary. They can detect tiny amounts of blood from several miles away! Plus, their coloration helps them blend into the environment for hunting prey.
Sadly, Great White Sharks have a poor reputation. Movies like “Jaws” exaggerate the danger they pose to humans. But let’s remember that these sharks deserve some love too!
Reproduction Process of Great White Sharks
Great White Sharks, one of the most fascinating creatures of the sea, have an intriguing reproduction process. Unlike most fish, they give birth to live young, a process known as viviparity. The reproduction process of Great White Sharks can be divided into several stages.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Mating | Male sharks will compete for the opportunity to mate with a female. They will bite the female’s pectoral fin to hold her in place during copulation. |
| Gestation | After mating, female sharks have a gestation period of approximately 12-18 months. During this time, the embryos develop inside the mother’s uterus. |
| Birth | Once the gestation period is complete, the female gives birth to live young, known as pups. The number of pups per litter can range from 2 to 10. The pups are fully formed and capable of swimming shortly after birth. |
| Maternal Care | Female Great White Sharks do not provide any further care to their pups after birth. The pups are left to fend for themselves and must learn to survive in the ocean. |
Additionally, it is interesting to note that female Great White Sharks have the ability to store sperm from multiple males and can produce offspring from different fathers within the same litter.
The history of the Great White Sharks’ reproduction process is filled with scientific discoveries and ongoing research. Scientists have been studying these fascinating creatures to gain a deeper understanding of their reproductive biology. Through the use of advanced technology and tagging programs, researchers have been able to track individual sharks and gather valuable data on their mating behavior and reproductive patterns.
Overall, the reproduction process of Great White Sharks is a complex and fascinating subject that continues to captivate researchers and enthusiasts alike. By studying and gaining insights into their reproduction, we can further comprehend the intricate life cycle of these magnificent predators of the sea.
If you thought dating in the human world was complicated, wait till you hear about the courtship rituals of great white sharks – it’s like a dating app for teeth-loving enthusiasts.
Mating Behavior
The mating behavior of great white sharks is both fascinating and complex, with multiple stages and rituals. Courtship involves male sharks exhibiting displays of strength and dominance to attract potential mates. They engage in jaw-locking fights with other males to prove their superiority. The chosen female then joins the male for copulation, which can last several minutes.
Female great whites have multiple uteri, allowing them to mate with multiple males at once for greater genetic diversity in their offspring. The gestation period can range from 9 to 12 months – longer than most reality TV show seasons!
To illustrate, let’s consider Sharky and Sandy. After a courtship dance that lasted hours, they successfully copulated. This brief glimpse into the world of great white shark reproduction reveals how important their mating behavior is for the species. We must understand these processes to ensure a prosperous future for these magnificent creatures.
Gestation Period
The gestation period of Great White Sharks is a key part of their reproductive cycle. It’s the time it takes for a female shark to carry and develop her embryos until they are ready to be born. Knowing this period is vital in understanding the life of these majestic predators.
Let’s break down the gestation period into an illustrative table:
| Length | Duration |
|---|---|
| 12-18 feet (3.6-5.5 meters) | 11 months |
The table above shows the connection between the length of a female Great White Shark and her gestation period. Generally, it’s about 11 months for sharks measuring 12 to 18 feet (3.6-5.5 meters).
Though we tend to link mammals and long pregnancies, it’s awesome to learn that Great White Sharks have fairly long gestation periods compared to other fish species. This extended duration lets the embryos grow and develop in the female shark’s uterus.
Birth Process
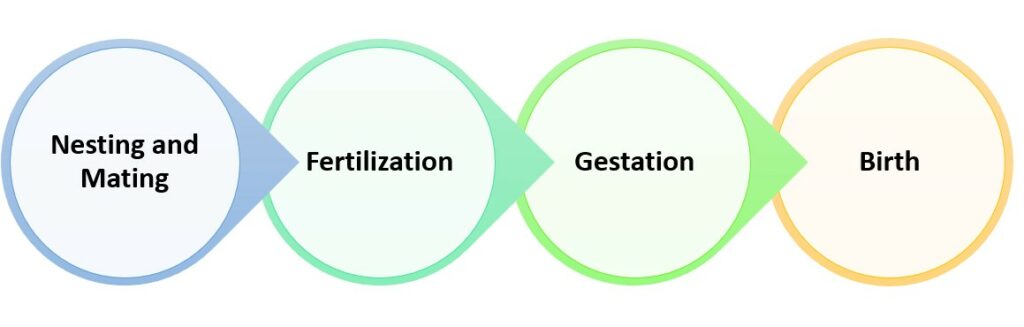
The birth of great white sharks is an amazing and complex event. Knowing how they arrive in the world can make us appreciate their strength and adaptability. Let’s look at the steps of the birth process.
- Nesting and Mating: Female great whites become mature for reproduction around 12 to 14 years old. They then go to mating grounds to do courtship rituals with male sharks. These rituals show dominance and strength.
- Fertilization: After courtship, mating happens inside the female’s body. The male transfers sperm to her through special organs called claspers. This fertilizes her eggs and starts the creation of life.
- Gestation: Great whites have a rare type of pregnancy called ovoviviparity. Fertilized eggs grow inside the mother without a placenta or nourishment. Each embryo gets nutrition from an egg yolk sac through a vitelline duct.
- Birth: The gestation period for great whites is 9 to 12 months. When it’s time for birth, female sharks give live birth to fully formed pups that are usually 5 feet long. Sometimes multiple pups are born at once.
We must protect the habitats of great white sharks and reduce threats like overfishing and pollution. Sustainable fishing can also help them thrive.
By understanding the birth process of great whites, we can encourage conservation and be better guardians of their future. So let us help keep them alive for future generations.
Environmental Factors Affecting Shark Births
The birthing habits of great white sharks are significantly influenced by environmental factors. These factors play a crucial role in determining where and when female sharks give birth. By analyzing data, we can gain valuable insights into the relationship between these factors and shark births.
To better understand the environmental influences on shark births, let’s explore some key factors and their impact:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Temperature | Warm water is preferred by female sharks for giving birth, ensuring optimal embryo growth. |
| Salinity | The appropriate level of salinity is crucial for the health and survival of shark embryos. |
| Oxygen Levels | Sufficient oxygen supply in the water is essential for the development of shark embryos. |
| Coastal Upwelling | Upwelling of nutrient-rich waters along coastal areas provides ample food for pregnant sharks. |
| Predation Pressure | Areas with lower predation pressure offer safer environments for pregnant sharks. |
These factors work synergistically to create favorable conditions for the successful gestation and birth of great white sharks. Each factor contributes to the overall well-being of the mother and her offspring, ensuring their survival.
While these factors are crucial, it is important to note that each shark species may have unique preferences and adaptations when it comes to giving birth. The great white shark, being a top predator, has specific requirements that align with the availability of resources and the suitability of the environment.
Throughout history, the study of environmental influences on shark births has been a fascinating field of research. Scientists and marine biologists have made significant strides in understanding the intricate relationship between the natural environment and the reproductive behaviors of these magnificent creatures.
By delving deeper into the environmental factors affecting shark births, we can enhance our knowledge of shark populations and contribute to effective conservation efforts aimed at preserving these apex predators and their habitats.
Great white sharks have a tough time explaining to their offspring the perks of being born in warmer waters without sounding like they’re just vacation planners.
Temperature and Seasonal Changes
Temperature and season changes have a huge impact on shark reproduction. This relationship between environment and shark births is critical for conservation.
Temperature changes can affect metabolic rate and reproduction. Sharks are ectothermic, which means their body temperature is based on the environment. Fluctuations in water temperature can cause big changes.
Seasons also play a role. Different seasons bring water temperature shifts, as well as changes in prey availability and other environmental conditions. Certain sharks mate during seasons when temperatures are best for egg development.
Other details matter too. Ocean currents, salinity levels, and prey abundance can all influence shark births. These interactions show how environment affects shark reproduction.
A notable example is tiger sharks in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. In the late 1960s, a decline in pup production occurred due to pollution and bay temperature changes. This highlighted sharks’ vulnerability to human-made environmental impacts.
By understanding temperature, seasonal, and ecological factors, scientists can create conservation strategies to protect sharks. If they had a say in their birth conditions, they’d probably opt for an underwater hotel with ocean views and a seafood buffet!
Habitat Selection
Sharks carefully select their birthing grounds, taking into account various environmental factors. To understand these factors is key to preserving their populations. Temperature, salinity, food availability, predator presence, and shelter are the major considerations for these fascinating creatures.
To protect shark birthing areas, one should tell them they’re becoming Starbucks! This smell clears out sharks like nothing else!
Preservation and Protection of Great White Shark Birthing Areas
We must preserve and protect birthing areas of Great White Sharks – vital for their species’ survival. These zones provide a sanctuary for newborns and a vital role in marine ecosystems. Regulations limit human activities like fishing and tourism, so these habitats remain undisturbed.
The protected zones also serve as research sites for scientists. They study the behavior and biology of these sharks, gaining valuable insights into their reproductive strategies and population health. This knowledge is key for creating effective conservation plans.
We must act now. Supporting organizations and advocating for stricter regulations can help us safeguard these habitats. Let’s ensure future generations can witness nature’s wonders firsthand. Keep your water birth plans on hold – Great White Sharks have a delivery method that would make even the most fearless moms cringe!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do great white sharks give birth?
Great white sharks are viviparous, which means they give birth to live young. The females have internal fertilization, and after mating, embryos develop in the uterus. The embryos receive nourishment from a yolk sac, and as they grow, they feed on unfertilized eggs in the uterus.
Where do great white sharks give birth?
Great white sharks give birth in warm, shallow waters near the coast. They tend to choose safe and protected locations such as bays, lagoons, or rocky crevices. These areas provide the newborn sharks with a higher chance of survival and protection from predators.
How many pups do great white sharks give birth to?
Great white sharks give birth to a relatively small number of pups compared to other shark species. The average litter size is usually around 4 to 6 pups, but it can range from 2 to 10. The mother shark invests a significant amount of energy into each pup during gestation.
What is the gestation period for great white sharks?
The gestation period for great white sharks is estimated to be around 11 to 12 months. However, the exact duration is not well-documented as studying the mating and gestation processes of these sharks is challenging due to their elusive nature. Further research is required to obtain more accurate information.
Do great white sharks provide parental care to their young?
No, great white sharks do not provide any parental care to their young after giving birth. Once the pups are born, they are left to fend for themselves. They must quickly develop their hunting and survival skills to survive in their marine environment.
Are there any threats to newborn great white sharks?
Yes, newborn great white sharks face various threats in their early stages. Predators like larger sharks, orcas, and even cannibalism among their own kind pose a risk. Additionally, pollution, overfishing, and habitat degradation can also impact their survival. Protecting their habitats is crucial for their long-term survival.
Conclusion
The lifecycle of great white sharks is truly captivating. After mating, female sharks go through a long gestation period of 12 to 18 months. During this, pup embryos develop inside them. When they reach maturity, they are born live, not from eggs like other shark species.
Great white sharks have a unique reproduction style. It’s called ovoviviparity. This means the fertilized eggs develop internally until they are ready to be born. It’s amazing how these powerful creatures give birth to fully formed pups.
One fact about great white births is they usually take place in warm waters near coasts. This could be because these areas provide plenty of food and protection for newborns in their vulnerable early life stages.
References
White shark – Reproduction, Migration, Behavior | Britannica


