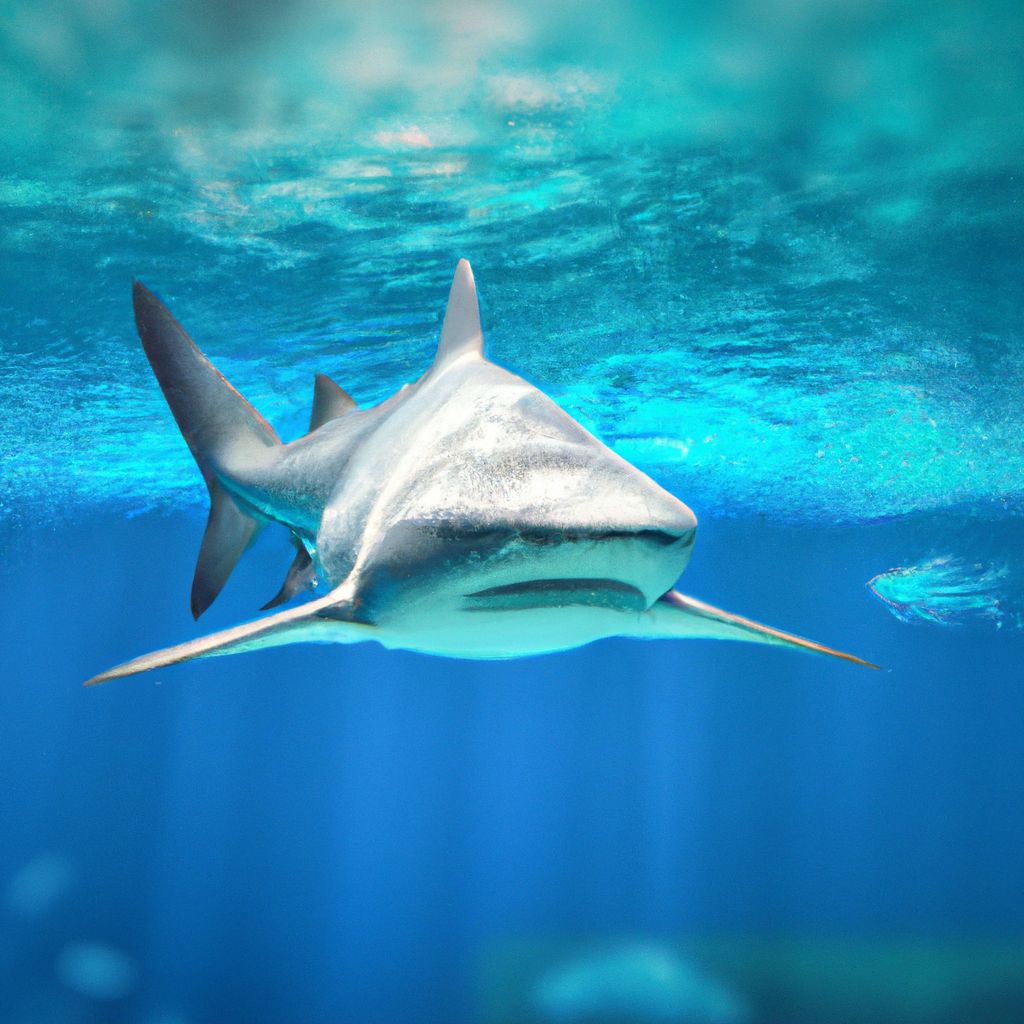

Bull sharks, renowned for their aggressive behavior and adaptability to both fresh and saltwater, have a unique way of locomotion. Their muscular bodies, designed to generate the most force while minimizing resistance, allow them to swiftly navigate through the ocean. And their caudal fin propelling them forward with agility!
What truly sets bull sharks apart is their hydrodynamic shape. This helps reduce turbulence and maintain stability during fast movements. Plus, the coordination of their pectoral fins assists in maintaining balance while providing a boost in propulsion.
Moreover, they exploit buoyancy control to further enhance their swimming skills. By adjusting their body’s position to the water’s surface, they can effortlessly change dive depths. Allowing them to pursue prey hidden at different layers of the water column with ease.
Key Takeaways
- Bull sharks are highly adaptable and can move in various ways, including swimming, gliding, and even walking.
- They have a unique ability to regulate their buoyancy by adjusting the amount of oil in their liver, allowing them to move effortlessly between different depths.
- Bull sharks are known for their powerful and efficient swimming style, which is achieved through the combination of their streamlined body shape and strong muscles.
- They can swim at high speeds, reaching up to 12 miles per hour, and are capable of making quick turns and maneuvers.
- Bull sharks also have the ability to glide through shallow waters by using their pectoral fins to lift themselves off the bottom and propel forward.
- In addition to swimming and gliding, bull sharks have been observed walking in extremely shallow waters by using their pectoral fins to support their weight and push themselves forward.
- This unique walking behavior allows them to navigate through areas with low water levels, such as flooded fields or riverbanks.
- Understanding how bull sharks move is important for researchers and conservationists to better protect and manage their populations, as well as to ensure the safety of humans who may encounter them in their natural habitats.
Anatomy of a Bull Shark
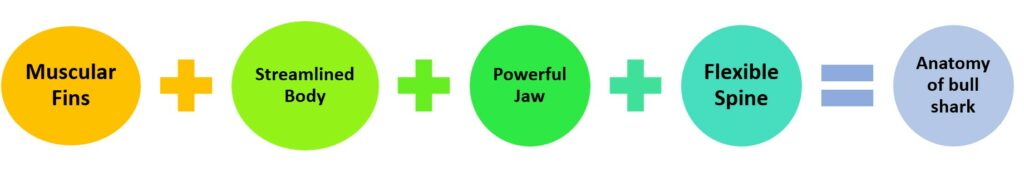
Bull sharks boast anatomical features that make them perfectly adapted for fluid movement in water. Their muscular fins, combined with their sleek body shape, allow them to zip through water with remarkable speed and precision.
Their anatomy includes:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Muscular Fins | For stability and maneuverability. |
| Streamlined Body | For swift movement. |
| Powerful Jaw | With sharp teeth for hunting. |
| Flexible Spine | To change direction quickly and with agility. |
Plus, bull sharks have an extra adaptation that sets them apart from other shark species: a special gland called a rectal gland. This helps them manage their internal salt balance by getting rid of excess salt. This means they can live in both freshwater and saltwater – making them one of the few shark species that can survive in rivers and lakes.
Remember: Bull sharks can be aggressive towards humans, so keep a safe distance when observing them. Admire their remarkable adaptations from afar and respect their natural habitat.
Swimming Techniques of Bull Sharks

Bull Sharks are known for their unique swimming abilities, making them formidable creatures of the water. Here are six points that shed light on these powerful swimmers:
- Firstly, they can swim in both salt and fresh water. This sets them apart from other shark species.
- They have a streamlined body shape that lets them effortlessly glide through the water.
- Anguilliform swimming helps them cover long distances with minimal effort. It involves moving their body in an undulating wave-like motion.
- Pectoral fins provide stability and control during maneuvers, allowing them to make sharp turns or sudden changes in direction.
- Bull Sharks can reach speeds of up to 20 miles per hour when necessary.
- Lastly, they have a unique sensory system called the ampullae of Lorenzini which helps them detect electrical signals emitted by other animals in the water.
They can also tolerate low oxygen levels in water, letting them inhabit areas where other sharks cannot survive. Also, National Geographic states that they are responsible for the highest number of shark attacks on humans due to their tendency to inhabit shallow coastal waters. Making strange hula-hoop moves look like child’s play, these Bull Sharks definitely know how to dance their way through the ocean currents.
Factors Affecting Bull Shark’s Movement
A bull shark’s movements rely on a few key elements. Water temperature, prey availability, and habitat topography all play a role. They can tolerate a broad range of temperatures, which allows them to inhabit both warm and cool waters.
They are opportunistic feeders, hunting for food in various habitats. Human activities, like pollution and overfishing, can also impact their movements.
So, what can be done to help these powerful predators? Monitoring and improving water quality, sustainable fishing practices, and protecting critical habitats are all great suggestions. Together, we can protect these magnificent creatures while preserving our own future on this planet. Watch out, fish friends, the bull shark’s adaptive features are about to give them the feeding frenzy of their lives!
Adaptive Features of Bull Sharks

Bull sharks possess remarkable features that make them proficient predators. They have a stout and muscular body shape, allowing them to move quickly in water. Also, their teeth are specially fashioned with both serrated and triangular edges, helping them grip slippery prey.
Furthermore, their kidney system helps them regulate the salinity of their bodies, enabling them to live in both freshwater and saltwater habitats. Plus, they have Ampullae of Lorenzini in their snouts which detect electrical impulses from potential prey. Their powerful pectoral fins and caudal fin give them great agility and speed.
Moreover, bull sharks have impressive reproductive abilities. Females are able to store sperm for a long time, thus increasing fertilization chances even without mating right away.
If you want to learn more about bull shark behavior, watch them during low-tide periods near coastal areas or rivers where they usually hunt for fish or small mammals.
Finally, be careful when encountering these creatures in their natural habitat and maintain a respectful distance to ensure your safety and theirs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do bull sharks move?
A: Bull sharks move by using a combination of swimming and gliding. They have a powerful muscular body and a crescent-shaped tail fin that helps them swim efficiently through the water.
Q: How fast can bull sharks swim?
A: Bull sharks are known for their impressive speed. They can swim at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour (40 kilometers per hour) in short bursts, allowing them to catch their prey quickly.
Q: Can bull sharks swim in both saltwater and freshwater?
A: Yes, bull sharks have a unique ability to swim in both saltwater and freshwater. They are one of the few shark species that can tolerate varying levels of salinity, allowing them to inhabit rivers, estuaries, and coastal areas.
Q: How do bull sharks adapt to different environments?
A: Bull sharks possess a special adaptation called osmoregulation, which allows them to regulate the salt concentration in their bodies. This adaptation enables them to move between saltwater and freshwater environments without any issues.
Q: Do bull sharks travel long distances?
A: Yes, bull sharks are known to travel long distances. They have been observed migrating thousands of miles in search of food or suitable breeding grounds. Their ability to navigate both saltwater and freshwater habitats allows them to explore various regions.
Q: Can bull sharks jump out of the water?
A: Yes, bull sharks are capable of jumping out of the water. They sometimes leap out of the water to catch prey or to escape from predators. This behavior is known as breaching, and it showcases their impressive agility and strength.
Conclusion
Bull sharks captivate scientists and lovers of nature. Uniquely, they can live in both saltwater and freshwater habitats. They are swift and agile, thanks to their muscular bodies and hydrodynamic shape.
The caudal fin, or tail fin, propels them forward. When they move their tail from side to side, they generate thrust. This technique is called lateral undulation, common in many fish species.
Bull sharks also use their pectoral fins for stability and maneuvering. They can adjust the position of these fins to make quick turns and adjustments while swimming.
Moreover, they can regulate their buoyancy through osmoregulation. Specialized cells in their rectal glands extract oxygen, even while stationary.
Studying bull sharks’ behavior and locomotion is critical for conservation efforts. By understanding how they move, we can protect their habitats and preserve this remarkable species.



