Key Takeaways
- Great white sharks have evolved a number of adaptations that make them highly efficient predators in their marine environment.
- One key adaptation is their streamlined body shape, which allows them to swim quickly and silently through the water, enabling them to surprise their prey.
- Great white sharks have a unique set of teeth that are perfectly designed for capturing and consuming their prey. Their serrated edges allow them to tear through flesh easily, while their multiple rows of teeth ensure they always have a sharp set available.
- Another important adaptation is their keen sense of smell. Great white sharks can detect even the faintest scent of blood from miles away, helping them locate potential prey.
- Great white sharks also have a specialized organ called the ampullae of Lorenzini, which allows them to detect electrical signals given off by other animals. This helps them locate prey that may be hiding or camouflaged.
- The ability of great white sharks to regulate their body temperature is another crucial adaptation. They are able to maintain a higher body temperature than the surrounding water, which gives them an advantage in colder environments.
- Great white sharks have a unique hunting strategy known as “spy-hopping,” where they lift their heads out of the water to get a better view of their surroundings. This allows them to spot potential prey from a distance and plan their attack.
- Despite their fearsome reputation, great white sharks are actually quite vulnerable to environmental changes and human activities. Understanding their adaptations is crucial for their conservation and protection.
The great white shark is a creature that has captivated humans for centuries. It has powerful presence and immense size. Let’s explore their adaptations.
Adaptation is when an organism changes or develops traits in response to the environment.
- The great white shark has amazing smell. It can detect blood from miles away. This helps them locate prey accurately.
- Great white sharks have unique teeth. They are serrated and sharp, making them capable of tearing through flesh and bone.
- Scarface is a local legend. It was injured by a fishing net but adapted by hunting at night. This shows how resilient and smart these sharks are.
Stripes are always in style for the great white sharks. They are the fashionistas of the underwater world!
Physical Adaptations of Great White Sharks
Great White Sharks possess astonishing physical adaptations that enable them to thrive in their marine environment. These adaptations include:
- Shape and Size: Great White Sharks boast a streamlined body shape, tapering to a powerful tail fin. This design reduces drag, allowing them to swiftly navigate through the water. These majestic creatures can grow up to an impressive average length of 15 to 20 feet and can weigh over 5,000 pounds.
- Teeth and Jaws: One of the most notable adaptations of Great White Sharks is their formidable set of teeth. They have rows of serrated, triangular teeth, which are continuously replaced as they break or wear out. This adaptation ensures they are always equipped with efficient hunting tools.
- Camouflage and Coloration: The upper part of their body is darkly colored, blending with the deep ocean water when viewed from above. However, their white underside matches the brightness of the ocean surface when seen from below. This combination aids in ambushing unsuspecting prey and eluding potential predators.
- Sensory Systems: Great White Sharks possess exceptional sensory systems, particularly their keen sense of smell and electroreception. Their sense of smell allows them to detect prey from long distances, while electroreception enables them to identify faint electrical signals emitted by other animals, helping in locating prey hidden in the water.
These remarkable physical adaptations have contributed to the Great White Shark’s status as a top predator in the ocean ecosystem. Understanding their unique adaptations aids in their conservation and highlights the importance of preserving their natural habitat.

To further support the conservation efforts for these magnificent creatures, it is crucial to promote sustainable fishing practices and establish protected marine areas. By limiting overfishing and protecting their habitats, we can ensure the survival and coexistence of Great White Sharks and other marine species.
Who needs a gym membership when you can just evolve into a sleek and deadly torpedo with teeth?
Unique Body Shape and Size of Great White Sharks
The Great White Shark has an impressive body shape and size that make it stand out from other sea creatures. Its sleek frame and immense size make it the king of the ocean! Let’s look at some of its unique features:
- Length: Adults are usually 15-20 feet long, with females bigger than males.
- Weight: These giants can weigh between 1,500 and 2,400 kg (3,300-5,300 lbs).
- Teeth: Its 300 serrated teeth, arranged in rows, get replaced frequently.
- Fins: The large pectoral fins help stabilize it and the dorsal fin helps with quick changes in direction when hunting.
- Tail: Its crescent-shaped tail helps it swim up to 35 mph (56 km/h).
- Skin: Its dermal denticles resemble tiny armor plates, reducing drag when swimming.
- Eyes: It has incredible vision adapted for low-light, enabling it to spot prey from far away!
Though they may be intimidating predators, Great Whites are vital for maintaining balance in marine ecosystems. Researchers observed a female swim thousands of miles from South Africa to Australia without rest. Their adaptations over millions of years have made them powerful predators. Understanding them is key for conservation efforts to ensure their existence in our oceans.
Big Teeth and Powerful Jaws of Great White Sharks
The great white shark’s teeth are razor-sharp and serrated – perfect for tearing through prey. Plus, the muscles in their jaws give them a powerful bite force. To show their adaptations, a table can be made. It will have columns like “Teeth Structure”, “Bite Force” and “Prey Examples”.
They have an amazing sense of smell too – they can detect blood from miles away! They’re also known to breach out of the water when hunting, reaching incredible heights of 10 feet or more.
These impressive features make the Great White Shark an apex predator. It’s no wonder they continue to amaze us with their adaptations. Just think – they can smell a drop of blood in an Olympic-sized swimming pool!
Excellent Sense of Smell
The Great White Shark’s olfactory organs are truly remarkable. Its olfactory bulbs are highly developed and refined, providing it with over 300 million receptor cells dedicated solely to its sense of smell. This heightened olfaction allows it to detect minute traces of blood or odors in the water, from miles away!
This makes the Great White Shark an apex predator, as its scent-detection abilities are crucial for locating potential prey. Yet, this sensitivity can also be a disadvantage. Variations in oceanographic conditions, such as temperature and currents, can influence scent dispersion, impacting their hunting patterns.
But, the ultimate fear factor of this majestic sea creature? Its ability to blend seamlessly into the ocean, making it the ultimate camouflage master!
Behavioral Adaptations of Great White Sharks
Great White Sharks: Understanding Their Behavioral Adaptations
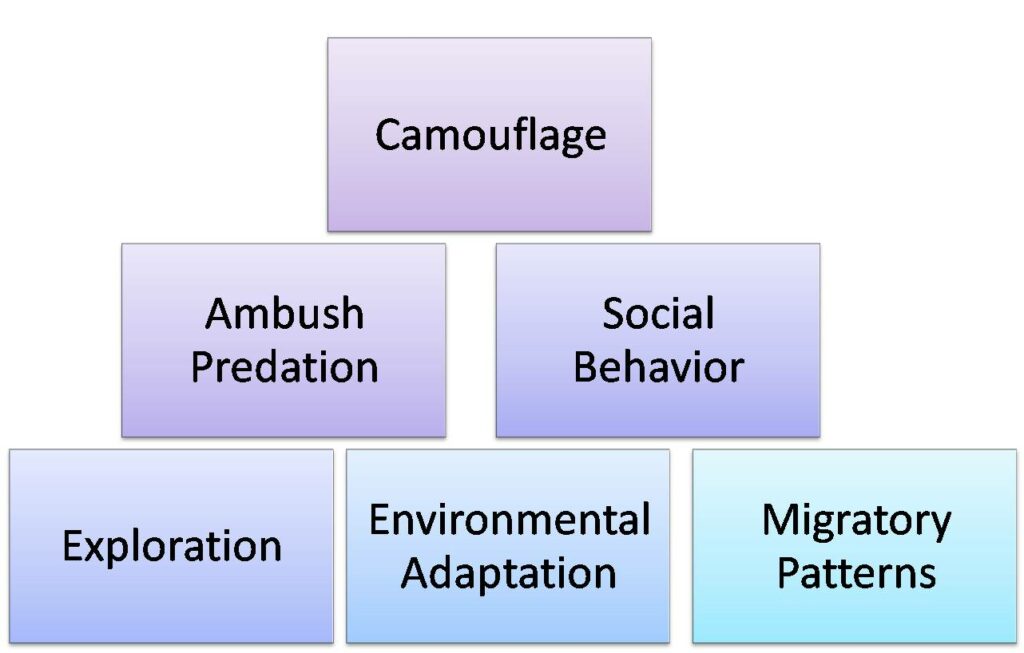
Great white sharks are known for their unique and fascinating behavioral adaptations that have allowed them to thrive in their marine environment. These adaptations, shaped through millions of years of evolution, play a crucial role in their survival and success as apex predators.
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Camouflage | Great white sharks have a grayish coloration on their dorsal side, which helps them blend in with the sunlit surface of the ocean, making them less visible to their prey. |
| 2. Ambush Predation | These sharks use a strategic hunting approach, employing ambush predation to surprise and catch their prey off guard. Their burst of speed and powerful jaws allow for swift, successful attacks. |
| 3. Social Behavior | Contrary to popular belief, great white sharks are not solitary creatures. They have been observed exhibiting social behavior, such as communal feeding or aggregations during mating seasons. |
| 4. Exploration | Great white sharks are highly curious animals that explore their surroundings. Their exploratory behavior helps them locate potential food sources and new hunting grounds. |
| 5. Environmental Adaptation | These sharks have adapted to a wide range of oceanic environments, including both coastal and open ocean habitats. This versatility enables them to find and exploit different food sources. |
| 6. Migratory Patterns | Great white sharks have distinct migratory patterns, traveling long distances in search of food, reproduction, and favorable temperature conditions. This behavior allows them to take advantage of seasonal resources effectively. |
Great white sharks possess remarkable sensory and physiological adaptations to survive and thrive in their environment. Their exceptional sense of smell is crucial for detecting prey from afar, even in murky waters. Additionally, their electroreceptive organs, known as the Ampullae of Lorenzini, enable them to sense the electrical signals produced by potential prey.
These apex predators play a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. By regulating the populations of their prey species, they prevent the overpopulation of certain marine organisms, which could have detrimental effects on the overall health of the ecosystem.
True Fact:
Recent studies have shown that great white sharks have the ability to regulate their body temperature, enabling them to venture into colder waters. This unique adaptation has been credited to the countercurrent heat exchange system found in the sharks’ circulatory system. (Source: National Geographic)
By understanding the behavioral adaptations of great white sharks, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex strategies and skills they have developed over millions of years. These adaptations allow them to thrive in their marine environment and serve as a testament to the remarkable wonders of nature.
Tired of your food constantly swimming away? Great white sharks have evolved impressive hunting strategies to level the playing field.
Hunting Strategies of Great White Sharks
Great White Sharks are stealthy hunters. They use various strategies to capture their prey, displaying remarkable adaptability. Let’s explore these techniques in a table:
| Hunting Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Ambush Predation | The shark hides and waits, using its excellent camouflage before attacking swiftly. |
| Burst Speed | It accelerates rapidly, reaching up to 35 miles per hour. |
| Ramming Technique | It uses its jaws and body to give a forceful strike. |
These predators have unique adaptations, such as the ampullae of Lorenzini. This allows them to detect electric fields emitted by prey, even in dark or murky waters.
We can truly appreciate the efficiency of Great White Sharks when they hunt. This highlights the importance of protecting their habitats.
Want to learn more? Delve into the thrilling realm of Great White Shark hunting!
Great White Shark’s Camouflage and Stealth
Great white sharks possess spectacular abilities in terms of camouflage and stealth. Three key points:
- they can change skin color to blend in with their environment,
- they have a sleek body design for minimal disturbance in the water, and
- they have special organs on their snouts to detect living organisms.
Furthermore, they rely on countershading to blend in with the sky and sun above and below.
Initially, these creatures were thought to be indiscriminate killers. But, it was found they have selective feeding habits. This realization forms a vital part of our knowledge on great white sharks and shows that appearances can be deceiving in nature.
By understanding their adaptations, we gain insight into their complex and impressive nature. Truly, the hidden wonders of the ocean leave us in awe!
Social Behavior of Great White Sharks
The social behavior of great white sharks is a mysterious and intriguing concept. They form groups called ‘aggregations’ and a hierarchical structure within these groups. They even display cooperative hunting behaviors!
We can observe playful interactions between great white sharks during mating season, too. Scientists have been hard at work studying the social behavior of these creatures across different habitats.

Each discovery leads us to further appreciate the complexities of life deep in the ocean. Great white sharks have adapted in order to remain as the top predator in the sea.
Survival Adaptations of Great White Sharks
The incredible adaptability of Great White Sharks enables their survival in the challenging marine environment. They possess a range of remarkable features and behaviors that aid in their ability to thrive. One such adaptation is their powerful jaws, equipped with rows of serrated teeth, enabling them to efficiently prey upon their targets. This adaptation allows them to quickly capture and consume their prey, ensuring their sustenance in their habitat. Additionally, their streamlined bodies and strong muscles enable swift and agile movements, aiding in their hunting strategies. Moreover, their highly developed sensory organs, including electroreceptors and a keen sense of smell, allow them to detect even the faintest signs of prey from relatively long distances. These adaptations collectively give Great White Sharks a significant advantage in their quest for survival.
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Powerful Jaws | Possessing rows of serrated teeth |
| Streamlined Bodies | Enabling swift and agile movements |
| Highly Developed Sensory Organs | Electroreceptors and keen sense of smell |
Furthermore, Great White Sharks also possess a unique adaptation known as “counter-shading.” This means that their dorsal (upper) side is darker in color, while their ventral (lower) side is lighter. This camouflage technique helps them blend into their surroundings, making it harder for prey or potential threats to spot them. This adaptation plays a crucial role in their survival, allowing them to effectively hunt without being detected easily.
Interestingly, the Great White Sharks’ association with humans has been a topic of curiosity and sometimes fear throughout history. Numerous accounts of encounters and interactions have been documented, ranging from ancient times to the present. These records highlight the ongoing fascination and intrigue humans have towards these magnificent creatures. The Great White Sharks’ adaptations have undoubtedly contributed to their enduring presence in our shared ecosystem.
Great White Sharks have been known to regulate their body temperature so effectively that they’re the ocean’s very own hot and cool tub rolled into one predator.
Temperature Regulation
The great whites have evolved amazing ways to manage their temperature. Special structures, called countercurrent heat exchangers, are in their circulatory system. These vessels help warm arterial blood and cool venous blood, conserving heat.
Plus, these apex predators can selectively warm parts of their body. By redirecting blood flow, they can generate and maintain heat.
Furthermore, they use vertical movements to regulate temperature. Up high in the day, to bask in sunlight and down deep at night, to avoid overheating.
These adaptations let them thrive in a variety of temperatures and habitats. Thus, they survive as efficient hunters, in both warm and cold waters.
Fun fact: this was found out by marine biologists from the University of California Santa Cruz!
Reproduction and Offspring Protection
Great white sharks employ amazing techniques for reproduction and protecting their young. These adaptations guarantee their species’ survival.
- Advanced Reproductive Strategies: They possess complex reproductive systems that let them reproduce in multiple ways. This includes viviparity and ovoviviparity, allowing them to give birth to live young and better protect them.
- Maternal Care: Females show strong maternal instincts by taking care of their pups post-birth. They protect them by keeping them in shallow waters, shielding them from predators and helping them develop strength.
- Cannibalistic Behaviour: There have been reported cases of cannibalism among great whites, especially during gestation. Researchers suggest this may be a form of population control, ensuring only the strongest offspring survive.
- Long Gestation Periods: They exhibit long gestation periods compared to other shark species. This helps embryos fully develop before birth, raising their chances of survival.
It’s amazing that great whites have been perfecting their reproduction and protection strategies for millions of years. Wolverine may have met his match!
Longevity and Resistance to Diseases
The great white shark is an impressive survivor. As the champion of longevity and protection against illness, they have evolved like no other. Let’s see what statistics tell us.
The lifespan of various species can give us an idea of the great white shark’s impressive endurance. Here’s some data:
| Species | Lifespan (years) |
|---|---|
| Great White Shark | 70 |
| Blue Shark | 20-30 |
| Tiger Shark | 30-40 |
It’s clear that the great white outshines its counterparts by a long shot! Their ability to fight off diseases for such extended periods is phenomenal.
What are the attributes that give them such strength? One major factor is their robust immune system, which is capable of warding off infections.
Also, their genetic makeup is a contributing factor. Through years of evolution, these fascinating creatures have developed DNA repair mechanisms to keep their genetic code intact. This shield protects against mutations caused by environmental factors and potential disease triggers.
Studying the great white shark’s adaptations could lead to new treatments or preventative measures for human illnesses.
Threats and Challenges to Great White Shark Adaptations
Paragraph 1 – Great White Shark Adaptations face various challenges and threats in their environment. These difficulties can affect their ability to survive and thrive. Understanding these challenges is crucial for the conservation and management of this species.
Paragraph 2 –
| Challenges | Impact |
|---|---|
| Overfishing | Reduces prey availability |
| Pollution | Contaminates the shark’s habitat |
| Climate change | Alters ocean conditions and food availability |
| Bycatch | Accidental capture in fishing gear |
Paragraph 3 – The Great White Shark also faces additional challenges such as habitat loss and competition for resources. These factors further impact their ability to adapt and survive in changing ecosystems. Understanding the full extent of these challenges is essential for developing effective conservation strategies.
Paragraph 4 – It is vital to take immediate action to protect the Great White Shark and its adaptations. Failure to do so may result in irreversible damage to the ecosystem and the loss of an iconic marine species. Join the efforts to conserve and protect these magnificent creatures before it’s too late. Just when you thought humans couldn’t be more terrifying, our overfishing tendencies have made us the great white shark’s very own horror movie villain.
Human Activities and Overfishing
Human activities, like overfishing, present huge threats and problems for the Great White Sharks’ adaptations. As top predators, these amazing creatures are key in keeping marine ecosystems balanced. Yet, with more fishing pressure, their numbers are decreasing quickly.
Overfishing disturbs the food chain by lowering the sharks’ main food source. With less to eat, they find it harder to get nourishment and reproduce. Also, reducing the shark numbers in the oceans disrupts the natural dynamics of the ecosystem, bringing unpredictable results.
To fix this, we need to create stricter rules and strategies for fishing. One idea is making marine protected areas where fishing is limited or banned. That way, Great White Sharks can access undisturbed feeding and breeding places.
Another way is promoting sustainable fishing practices. Fishermen should be encouraged to use selective fishing methods, reduce bycatch and minimize damage to non-target species. Setting catch limits and seasonal closures can also help protect vulnerable sharks during vital parts of their life cycle.
Finally, awareness campaigns about the importance of preserving marine biodiversity, and the role played by Great White Sharks, are needed to create a positive attitude towards conservation. Teaching people about the fragility of these apex predators’ adaptations will encourage them to back conservation initiatives and ask for stronger protection.
Environmental Changes and Habitat Loss
Environmental alterations and habitat loss present serious difficulties to the adaptability of great white sharks. These apex predators depend heavily on certain environmental conditions and access to appropriate habitats for their endurance and reproductive success.
Rising sea temperatures or ocean acidification can disrupt the fragile balance of ecosystems. This can lead to a decrease in prey populations, or the relocation of particular species to new areas, making it hard for great white sharks to find food sources they are adapted to. In addition, habitat loss due to pollution, coastal development, or overfishing limits available space for these predators even more.
To effectively confront these issues, conservation efforts must focus on preserving and restoring key habitats for great white sharks. Establishing marine protected areas and practicing sustainable fishing can help combat the negative effects of environmental changes and habitat loss. By maintaining the long-term viability of their ecosystems, we can safeguard the adaptability and future survival of these iconic creatures.
Pro Tip: Supporting organizations that work towards shark conservation through donations or volunteer work can make a real impact in shielding great white sharks from the risks posed by environmental changes and habitat loss.
Conservation Efforts and Future Prospects
Conservation efforts for great white sharks focus on various strategies to protect and preserve their population. Such initiatives include:
- Marine protected areas
- Research and monitoring
- Education and awareness
- Fishing regulations
- International cooperation
It is also key to tackle the challenges faced by these apex predators. These include:
- Habitat degradation
- Pollution
- Climate change
- Accidental interactions with human activities
To ensure their long-term survival, ongoing research is necessary to better understand the impacts of environmental changes. This includes studying their genetic diversity and their ability to adapt.
Supporting organizations that work towards great white shark conservation can make a huge difference in safeguarding their future. Ultimately, great white sharks must keep adapting if they want to stay on top of the oceanic food chain.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some notable adaptations of great white sharks?
Great white sharks have several remarkable adaptations. One of the most notable is their ability to camouflage themselves with their surroundings. Their dorsal side is dark in color, which helps them blend in with the deep ocean when viewed from above. Additionally, they have a white underbelly, making it difficult for prey to spot them from below. Another noteworthy adaptation is their incredible sense of smell. They can detect and locate prey from miles away using their highly sensitive nostrils.
2. How do great white sharks hunt?
Great white sharks are skilled hunters. They use a technique called “patrolling and ambushing” to catch their prey. They swim slowly and silently near the surface of the water, scanning for potential targets. Once they spot a suitable prey item, they swim towards it with immense speed, breaching the water’s surface in a dramatic display. Using their powerful jaws, lined with razor-sharp teeth, they deliver a single devastating bite to immobilize or kill their prey.
3. Do great white sharks have any specific feeding adaptations?
Yes, great white sharks possess several feeding adaptations. Firstly, their teeth are perfectly designed for catching and consuming prey. Their sharp, triangular teeth are serrated, enabling them to tear through flesh efficiently. Additionally, great white sharks have an extraordinary ability to dislocate their jaws while feeding, allowing them to bite and swallow larger chunks of prey. This flexibility is crucial for consuming large marine mammals which form a significant part of their diet.
4. Are great white sharks exclusively apex predators?
Yes, great white sharks are apex predators, meaning they occupy the top position in the marine food chain. Their only natural predator is the killer whale, but interactions between the two species are relatively rare. The great white shark’s powerful physique, exceptional hunting skills, and adaptations make it the dominant predator in its ecosystem.
5. Can great white sharks survive in different environments?
Great white sharks are highly adaptable and can survive in a variety of environments. While they are commonly associated with coastal areas, they have been observed in deep ocean waters and open sea regions as well. They are capable of withstanding a wide range of water temperatures, from as low as 12°C to as high as 24°C. This adaptability allows them to inhabit diverse habitats across the globe.
6. How have great white sharks evolved over time?
Great white sharks have undergone minimal evolutionary changes over the past millions of years. Fossil records indicate that their ancestors date back around 16 million years, and they have maintained a well-suited body plan since then. This suggests that their adaptations have been highly successful and that they have remained excellently adapted to their environment throughout their evolutionary history.
Conclusion
Our exploration into great white shark adaptations has revealed their remarkable skills and traits. For instance, they have a powerful sense of smell, able to detect a single drop of blood from miles away. Plus, their razor-sharp teeth are constantly replaced throughout their lives.
Great white sharks also have a streamlined body shape and powerful muscles, enabling them to swim quickly. They can even use Earth’s magnetic fields to navigate long-distance migrations.
A research team had an awe-inspiring encounter with a great white shark called Deep Blue off the coast of Hawaii. She demonstrated her power and size as she moved through the water. It was a reminder of the magnificence and adaptability of these apex predators.
Reference:



