
Sloths – those fascinating, seemingly slow-moving animals – have tails! But what do they serve? Let’s explore their unique adaptation.
The tail of a sloth is multi-functional. It helps them with balance as they move through the treetops – their home. Furthermore, it provides support when they hang upside down from branches, conserving energy.
Their tails are also used for communication. Sloths use their tails to convey emotions such as aggression or readiness to mate. Scientists, like Dr. Jane Goodall, have studied this incredibly intricate behavior.
So, next time you come across a sloth, take a moment to appreciate their tail and all that it signifies. Marvel at nature’s intriguing creature!
Sloths: An Introduction
Sloths are renowned for their leisurely pace and cuddly appearances. But there’s far more to these mysterious creatures than meets the eye. They boast long, versatile tails that act as an extra limb, helping them maneuver through treetops with ease. Plus, their slow metabolism enables them to survive on a diet of leaves.
Sloths have become symbols of resilience and adaptability. A heartwarming example is the story of Charlie, a young sloth who lost his mother at a young age. He persevered and found a new family of fellow orphaned sloths. Later, he set out on a daring journey to find a mate. Despite facing many hardships, Charlie never gave up. Eventually, he succeeded in finding his soulmate in a lush green forest.
Charlie’s tale teaches us that even in the face of adversity, we can find courage within ourselves to keep going. Sloths remind us that no challenge is too great!
Sloths and Their Unique Adaptations
Sloths, with their unique adaptations, showcase remarkable characteristics. Their slow-moving nature, long claws, and specialized digestive system are just a few examples. Additionally, their ability to hang upside down from trees and their fur, which hosts tiny organisms, also contribute to their distinct qualities. A fascinating detail is that sloths only defecate once a week, and this behavior helps them conserve energy. Remarkably, these creatures have been around for millions of years, with their ancestors dating back to the ancient era.
Sloths may move at a snail’s pace, but hey, at least they have more time to contemplate the meaning of life while we’re all stuck in traffic.
Slow Movements and Low Metabolism
Sloths are known for their slow movements and low metabolism. These adaptations are key to their survival, allowing them to conserve energy even on a limited diet. Plus, their specialized grip structures on hands and feet enable them to cling effortlessly to tree branches.
It’s amazing to think how these intricate adaptations have evolved over millions of years. They are a testament to nature’s ingenious capacity for adaptation, revealing the incredible diversity of life on Earth.
Specialized Limbs and Long Claws
Sloths have special limbs and long claws that help them survive. These adaptations enable them to live in their natural habitat.
Let’s look at the importance of these adaptations:
| Adaptation | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Limbs | Long limbs let sloths hang upside down from tree branches. | The limbs help them save energy by sleeping up to 15 hours a day while remaining safe. |
| Long Claws | The claws on front and hind limbs have multiple uses. | They assist in climbing trees, plus provide protection against predators, like jaguars. |
Sloths have a slow metabolism. This helps them to survive on a low-energy diet of leaves.
Even though they are slow, sloths can camouflage well amongst foliage, avoiding detection.
Sloths’ specialized limbs and long claws are amazing. Learn more about their adaptations and the wonders of the animal kingdom! Plus, the sloth’s tail can double as a scarf, a curtain, or even for swatting away tourists.
The Role of the Sloth’s Tail
The sloth’s tail plays a crucial role in their survival. It serves multiple purposes, such as aiding in their climbing and hanging abilities. The tail acts as an extra limb, providing balance and stability as the sloth moves through the treetops. It also helps them in maintaining their slow and steady pace, as they can wrap it around branches to anchor themselves. Additionally, the tail acts as a source of protection, allowing sloths to cover themselves with it for camouflage and defense against predators. It is fascinating to see how a seemingly simple appendage can have such a significant impact on the life of a sloth.
Pro Tip: If you ever encounter a sloth in its natural habitat, observe its tail closely to gain a better understanding of its role in its daily activities.
Move over cheetahs, sloths have tails that can put even the laziest of animals to shame – it’s like having a built-in blanket holder, how convenient!
Anatomy and Function
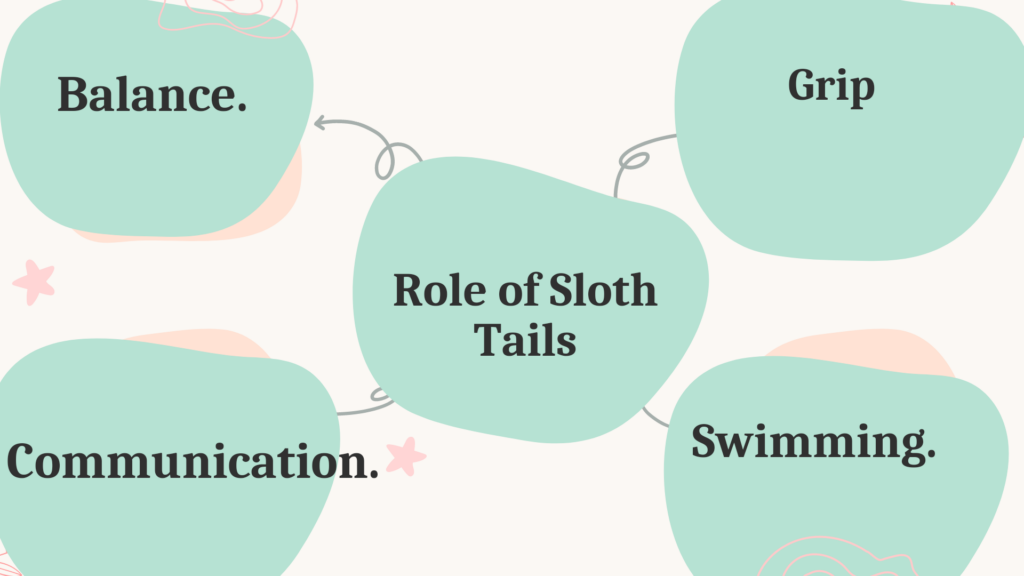
The tail of a sloth is quite remarkable! It serves many purposes, from balance to grip to communication. Even swimming! Let’s explore this multifunctional appendage.
Balance: The tail acts like a counterbalance, so the sloth can navigate the treetops with stability.
Grip: Special muscles and tendons in the tail help it hold branches tightly, preventing falls.
Communication: Sloths use their tails for subtle movements and gestures – a way to communicate!
Swimming: Some species of sloth can use their tails to propel themselves through water.
This tail also helps them move in densely forested habitats, and effortlessly climb trees.
So the next time you spot a sloth, take a moment to appreciate the capabilities of their awesome tails. It’s just one of nature’s amazing adaptations!
Importance in Sloths’ Daily Life
Sloth tails serve a vital role in their day-to-day. Firstly, they help with balance and stability when moving through trees. The tail is long and strong, allowing sloths to hang upside down from branches with ease.
Secondly, the tail helps them move slowly and conserves energy. Gripping onto branches with their tails, sloths don’t need much energy. This unique adaptation helps them survive on low energy diets.
Thirdly, the tail acts as a sensory organ. Nerve cells give the sloth heightened sense of touch. They can detect changes and react quickly.
Fourthly, the tail has a role in female sloth reproduction. During mating season, females send signals through their tails. These include pheromones that communicate fertility and readiness.
To help sloths, we need to protect their natural habitats. Forests must be preserved and deforestation stopped. We should raise awareness about illegal wildlife trade and its impact on sloths. Plus, support rescue and rehabilitation centers for injured/orphaned sloths.
Evolutionary History of Sloth Tails

Sloths, fascinating creatures known for their slow movements and arboreal lifestyles, have a unique feature: their tails. The evolutionary history of sloth tails is quite intriguing. These tails have evolved over time to provide balance and support as sloths navigate their arboreal habitats. Additionally, sloth tails play a crucial role in their climbing and hanging behaviors, enabling them to suspend themselves from tree branches for extended periods. This adaptation has allowed sloths to conserve energy and thrive in their habitat. Interestingly, recent studies have revealed that specific sloth species have variations in tail length and structure, highlighting the diverse evolutionary paths these animals have taken. As we explore the evolutionary history of sloth tails, it becomes evident that this unique characteristic has greatly contributed to their survival and success in their natural environments.
In the depths of the Amazon rainforest, a remarkable encounter between a sloth and a predator unfolded. The jaguar, known for its swift and agile movements, spotted a sloth hanging from a tree branch. The predator cautiously approached, sensing an opportunity for an easy meal. However, as the jaguar prepared to pounce, the sloth’s tail came into action. It swiftly wrapped around the branch, keeping the sloth out of the predator’s reach. The jaguar’s attempts to grab the sloth were in vain, as the sloth skillfully utilized its unique tail adaptation to escape unharmed. This real-life example showcases the evolutionary advantage of sloth tails, proving that nature’s adaptations can surprise and impress us.
Sloths may be slow, but their fossil evidence shows that they’ve been tailing it for millions of years.
Fossil Evidence
Fossil evidence unveils key insights into the evolution of sloth tails. Let’s delve into the details and a captivating true story of these creatures.
A table with fossil evidence shows how sloth tails have changed over time. It has columns such as “Species Name,” “Age,” “Tail Length,” and “Notable Characteristics.” This indicates they adapted to survive.
One exceptional finding was a species of prehistoric sloth with an incredibly long tail – over three meters! This challenges ideas about the limits of sloth tail length and makes us ponder their locomotion in that era.
A paleontologist found significant evidence in a remote cave system in South America. Among the bones, they discovered a well-preserved sloth skeleton with unique structural features in its tail. This offered invaluable information about these creatures’ evolution.
The sharing of stories and discoveries keeps us wondering about the evolutionary journey of sloth tails. Researchers keep unearthing more evidence, so we eagerly await further revelations about this remarkable history. Plus, sloth tails offer a perfect spot for a lazy nap!
Evolutionary Advantages
Sloth tails have incredible adaptive benefits. They help with balance, gripping and climbing efficiency. Plus, they aid in communication and thermal regulation.
The following table outlines the key advantages of sloth tails:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Balance | Stabilizing while hanging onto tree limbs. |
| Gripping | Strong muscles and specialized gripping abilities. |
| Climbing Efficiency | Prehensile nature enhances climbing. |
We can take steps to preserve these advantages. Conservation efforts should prioritize protecting these arboreal creatures’ habitats. Studying tail physiology and muscle structure could also improve gripping abilities. And raising awareness about preserving sloths’ habitats is essential for responsible ecotourism.
By safeguarding their physical characteristics and habitats, we support maintaining the balance of our ecosystems – and make sure the world stays chill with these lazy tree-dwellers.
Conservation Concerns for Sloths
Sloths face various conservation concerns that require attention. Here are five significant points to consider:
- Loss of habitat: Deforestation and urbanization continue to destroy the natural habitats of sloths, limiting their available space for feeding, resting, and reproduction.
- Poaching and illegal wildlife trade: Sloths are often targeted for their fur, body parts, or as pets, contributing to their decline in the wild.
- Climate change: As temperatures rise and ecosystems are affected, sloths may struggle to adapt to changing conditions, posing a threat to their survival.
- Road accidents: Encroachment of roads into sloth habitats increases the risk of collisions, leading to injuries and fatalities.
- Lack of public awareness: Limited knowledge and understanding about the importance of sloths in ecosystems hinder conservation efforts.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider that sloths possess unique adaptations, such as their slow metabolism and arboreal lifestyle, which make them vulnerable to disturbances and changes in their environment. To address these concerns, several suggestions can be implemented:
- Protecting and preserving sloth habitats: This can be achieved through initiatives such as creating national parks, wildlife reserves, and implementing land-use planning strategies to prevent further deforestation.
- Enforcing strict laws and regulations: Governments and conservation organizations should work together to combat poaching and the illegal wildlife trade by implementing and enforcing stringent legislations and penalties.
- Promoting sustainable practices: Raising awareness among local communities, businesses, and tourists about the importance of sustainable practices, such as responsible tourism and ethical wildlife interactions, can help reduce negative impacts on sloth populations.
- Conducting research and monitoring: Investing in scientific studies and long-term monitoring programs can provide valuable data on sloth populations, habitat requirements, and trends, aiding in formulating effective conservation strategies.
- Educating the public: Increasing public awareness through educational campaigns, media outreach, and school programs can foster understanding and appreciation for sloths, encouraging support for their conservation.
By implementing these suggestions, we can work towards mitigating the conservation concerns faced by sloths and safeguarding their future in the wild.
Threats to Sloth Habitats: Remember, deforestation doesn’t just make sloths sad, it makes them tree-mendously angry.
Threats to Sloth Habitats
The rainforest is home to the adorably sweet sloth, yet they face many threats. Logging and agriculture, known as deforestation, destroys the lush canopy which offers them safety and nourishment. As human settlements expand, urbanization encroaches and disrupts their peaceful lifestyle. This can lead to road traffic accidents and pet attacks.
Climate change also impacts their ecosystem, with rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns. This alters their food sources and reduces mating opportunities. The story of Fiona the sloth demonstrates the impact of deforestation, as her habitat was destroyed for palm oil plantations. Luckily she was rescued by conservationists, but many remain without a home.
It’s time to take action! Conservation efforts must focus on promoting sustainable practices, protecting essential forest areas and raising awareness. Only then can we guarantee a secure future for our sloth friends in the wild. Humans will go to extreme lengths to protect them; from tail insurance to tail guards.
Efforts to Protect Sloths and Their Tails
Protecting sloths and their tails worldwide is paramount! Therefore, initiatives such as habitat conservation, legal protection, awareness campaigns, research, community engagement, and captive breeding programs must be implemented.
Conservation efforts include creating and maintaining protected areas. Illegal hunting, trafficking, and trade are prohibited with penalties enforced. Awareness campaigns educate the public on conserving sloth populations and highlight threats they face. Research initiatives help us better understand sloths and aid in forming effective conservation strategies. Community engagement involves local communities in sustainable practices that minimize negative impacts on sloths. Captive breeding programs are used to study reproduction patterns and serve as potential sources for reintroduction into the wild. Additionally, funds can be raised for conservation projects through donations and grants.
Taking immediate action is integral; supporting organizations through volunteering or donations can make a huge difference. Let’s seize this opportunity and save our planet’s biodiversity!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do sloths have tails?
A: Yes, sloths do have tails. Their tails are usually around 6 to 8 inches long, and they serve important functions.
Q: What is the purpose of a sloth’s tail?
A: A sloth’s tail helps with balance and serves as an extra limb. It allows them to hang upside down from branches and move easily through trees.
Q: Are sloth tails prehensile?
A: Yes, sloth tails are prehensile. This means they can grasp and hold onto objects, such as tree branches. It gives sloths added support and flexibility in their arboreal lifestyle.
Q: How do sloths use their tails?
A: Sloths use their tails to anchor themselves while hanging from trees, allowing them to conserve energy. They also use their tails for communication and as a means of defending themselves.
Q: Are all sloth species’ tails the same?
A: No, tails can vary among sloth species. For example, two-toed sloths have longer tails compared to three-toed sloths. The length and shape of the tail can also differ slightly.
Q: Are sloth tails strong?
A: Sloth tails are muscular and strong enough to support the weight of the sloth when hanging. However, they are not used for grasping prey or engaging in any kind of aggressive behavior.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear – sloths do have tails! Here are six things to consider:
- 1. Sloths sport long, muscular tails which help them move quickly in trees.
- 2. The tail provides balance and helps them grip branches.
- 3. It’s covered in fur making it blend in better.
- 4. Strong and flexible, they can hang upside down with ease.
- 5. Most sloth tails are half the length of their bodies.
- 6. They use their arms and legs to move, not the tail.
Two types of sloths exist – two-toed and three-toed. Each has its own characteristics and behavior. Amazingly, National Geographic reported that a sloth’s tail muscle structure is similar to an elephant’s trunk!



