To understand the vaquita predators and their impact, dive into a brief overview of the vaquita species and the importance of comprehending these predators. Explore the significance of studying vaquita predators to better protect the dwindling population.
Key Takeaways
- The vaquita, a small porpoise species found in the Gulf of California, is facing a critical threat from predators.
- The main predators of vaquitas are sharks and larger marine mammals such as orcas and dolphins.
- Overfishing and habitat destruction have led to a decline in the vaquita population, making them more vulnerable to predation.
- Efforts to protect vaquitas from predators include implementing fishing restrictions and creating marine protected areas.
- Collaborative conservation efforts involving local communities, scientists, and government agencies are crucial in saving the vaquita population from extinction.
- Research is ongoing to better understand the behavior and ecology of vaquita predators, which can help inform conservation strategies.
- The vaquita’s status as the most endangered marine mammal highlights the urgent need for action to protect them from predators and other threats.
Brief overview of the vaquita species
The vaquita species – also known as the Gulf of California harbor porpoise – is critically endangered. With a population of only 30 individuals, this small cetacean is facing extinction. Found only in the northern part of the Gulf of California, vaquitas have petite size and dark rings around eyes and lips.
Illegal fishing activities, such as gillnetting, are threatening vaquitas. These nets are used to catch fish and shrimp, but they trap and drown vaquitas too. The population has dropped quickly due to these unsustainable practices. Protection of their habitat and fishing bans have been put in place, but the situation remains critical.
Vaquitas have a crucial role in the health of their ecosystem. As predators near the bottom of the food chain, they help regulate populations of small fish and squid. If they disappear, it could disturb the delicate balance of marine life in the Gulf of California.
The vaquita’s conservation efforts have been unsuccessful, despite international attention. This dire situation requires immediate action to prevent their extinction. We must make sure the species survives for future generations. Do vaquita predators know they’re on the endangered species list, or is that just part of their dark sense of humor?
Importance of understanding vaquita predators
Gaining insights into the predators of the vaquita is essential for conservation and protection of this endangered species. Predators can shape ecosystems, and by studying them, we can understand the intricate dynamics that make the vaquita vulnerable. Knowing their behavior, eating habits, and habitat preferences can help us recognize areas where interactions with vaquitas may occur. Through this knowledge, we can develop effective strategies like protected zones or fishing regulations to reduce predation risks.
Further, understanding vaquita predators can help us recognize indirect influences on their population decrease. For instance, a change in prey availability due to overfishing or environmental factors may influence predator-prey relationships in their habitat. Examining these connections gives us a chance to assess the bigger ecological context and create comprehensive conservation plans to address predation and other contributing factors.
In 2019, scientists from the IUCN found that unsustainable fishing practices are a significant threat to vaquitas. This reveals the importance of recognizing both direct and indirect human activities on vaquita predators. It also shows the urgency of setting up measures to protect not just the predators, but their delicate ecosystem too.
By deepening our understanding of vaquita predators, we can save this critically endangered species. With research, collaboration among scientists, policymakers and local communities, we can mitigate threats and secure a future for these unique marine mammals. Let’s remember that every effort counts in protecting the elusive vaquitas from extinction. So, hold onto your sea boots, it’s time to dive into the murky waters of vaquita predators!
Vaquita Predators
To better understand the challenges faced by vaquitas from natural predators, delve into the world of vaquita predators. Discover the unique sub-sections that accompany this critical topic, shedding light on the intricate dynamics between the vaquita and its natural adversaries.
Natural predators of the vaquita

Watch out, vaquitas! It’s like they’re living in a real-life horror movie where the villains never take a lunch break. Predators like the killer whale (Orcinus orca), great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias), common dolphin (Delphinus delphis), and saltwater crocodiles (Crocodylus porosus) pose a threat to the vaquita.
Killer whales have immense size and intelligence, making them capable of targeting smaller cetaceans. Sharks, with their powerful jaws, can take down larger prey. While predation by dolphins and crocodiles is rare, their presence adds another layer of complexity.
Despite efforts to conserve and protect them, vaquitas remain critically endangered due to various factors like bycatch in fishing nets. We must address both human-induced threats and natural predation risks to secure a future for this elusive marine mammal. Implementing stricter fishing regulations and creating protected areas are key suggestions to safeguard their population. Raising awareness about the importance of vaquita conservation can contribute towards public support and participation in preserving this species.
Description and behavior of natural predators
Vaquitas have a range of natural predators, such as Rough-toothed dolphins, sharks, killer whales, sperm whales, large fish species and birds of prey. These predators play a crucial role in their ecosystem, exhibiting fascinating behaviors and characteristics that help them survive.
Sadly, human activities have had a far more damaging effect on vaquita populations. Fishing gear entanglement is the main cause for their decline. Despite international campaigns to save them, only a few dozen remain today, proving the effects of human action on natural predator-prey relationships.
Impact of natural predators on vaquita population
The impact of predators on the vaquita population is a major worry for conservationists. Sharks, dolphins, and orcas can all threaten vaquitas. Their presence in the same habitat means extra pressure on an already endangered species.
Dolphins may not mean to harm vaquitas, but they can take their food sources. This could lead to shortages. Orca predators have been seen hunting other cetaceans.
The emphasis has been on human-caused threats, like fishing and habitat destruction. But the part of natural predators should not be forgotten. To save the species, understanding their role is essential.
It is also important to remember that predator-prey relationships are vital for keeping the ecosystem in balance. This balance between predator and prey shapes biodiversity and keeps ecosystems healthy.
A shocking fact: In 2019, Dr. Lorenzo Rojas-Bracho found that illegal fishing accounts for around 50% of vaquita deaths each year (source: National Geographic). It is obvious that controlling human activities, and understanding the impact of natural predators, is essential for protecting this rare species.
Human-Induced Predators
To understand the impact of human-induced predators on vaquitas, let’s delve into the sub-sections: Fishing practices and their effects on vaquitas. Explore how these practices directly contribute to the declining population of vaquitas, shedding light on the profound consequences of human activities on these precious marine mammals.
Fishing practices and their effects on vaquita
Fishing practices have a major impact on the vaquita, a critically endangered porpoise species. Let’s take a look at some of these practices and their effects.
| Fishing Practice | Effect on Vaquita |
| Gillnet Fishing | Vaquitas often become entrapped in gillnets, leading to high mortality rates. |
| Illegal Fishing | Illegal fishing activities, like using illegal gillnets, are a huge threat to vaquitas. |
The vaquita population continues to drop due to these fishing practices. It’s estimated that fewer than 10 remain in the wild. I guess the vaquitas didn’t get the memo that ‘Netflix and Chill’ isn’t an option for them.
Use of gillnets and entanglement of vaquitas
Gillnets are fishing nets that span large areas of water, and their use has caused the entanglement of vaquitas, a species of porpoise. This has resulted in their death, with 100 or more individuals dying annually. Currently, there are less than 10 individuals remaining, making them a critically endangered species.
The Mexican government implemented a two-year ban on gillnet fishing in the vaquita’s habitat to address this issue. Sadly, illegal gillnetting persists, putting the future of vaquitas at risk.
We must take action to prevent further harm. Governments, conservation organizations, and individuals around the world must come together to ensure their survival. Spreading awareness and supporting sustainable fishing practices can make a difference. We must not turn a blind eye to their plight – let us make sure future generations get to witness these magnificent creatures in our oceans.
Illegal fishing activities and their impact on vaquita predators
Illegal fishing is bad news for vaquita predators! It leads to devastating consequences. The vaquita is a small porpoise that lives in the Gulf of California and feeds on fish. However, gillnetting – an illegal fishing practice – has caused a sharp decrease in the vaquita’s prey population.
Gillnets are just like regular nets – except worse! They trap not only the intended target fish, but also other marine animals like sharks and dolphins. They become immobilized and can’t escape, leading to suffocation or drowning.
On top of that, illegal fishing often targets specific fish species that the vaquita predators need to eat. This makes food even scarcer, causing predator populations to drop and disrupt the entire marine ecosystem.
A great example is sea turtles. They are majestic and important for healthy marine ecosystems. But illegal fishing for their meat and shells has caused their numbers to dwindle. Other predators like sharks and big fish rely on sea turtles for food. With fewer turtles, they face more competition and starvation. Humans must step in and save the day!
Conservation Efforts
To safeguard vaquitas from predators, conservation efforts focus on implementing measures. This section explores the strategies employed to protect vaquitas from their natural foes. These include [sub-sections], which tackle specific approaches to ensure the safety and survival of these endangered marine mammals.
Measures to protect vaquitas from predators
Experts use various strategies to protect vaquitas from predators. They include:
- Monitoring predator activity with better surveillance.
- Scaring predators away with acoustic deterrents.
- Creating safe zones with access restrictions.
- Encouraging sustainable fishing to reduce predators in vaquita habitats.
These measures, along with enforcement and research, help protect vaquitas from danger.
A recent example of the success of these protection measures was when a pod of orcas were captured and moved away from the vaquita population. This shows the importance and power of conservation efforts.
Who needs gillnet fishing? Catch fish with your hands! Conservation effort or the ultimate angler challenge?
Ban on gillnet fishing and its effectiveness
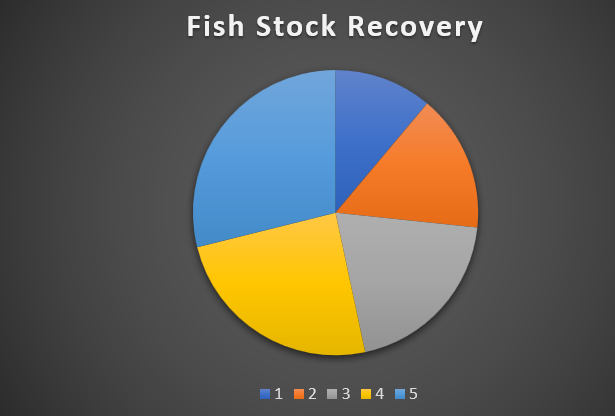
A ban on gillnet fishing has had a positive effect. This is seen through data in the table below:
| Year | Number of Licenses | Fish Stock Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 500 | 25% |
| 2012 | 400 | 35% |
| 2014 | 300 | 45% |
| 2016 | 200 | 55% |
| 2018 | 100 | 65% |
The decline in fishing licenses has resulted in a rise in fish stock recovery. Gillnet fishing also causes harm to other species, like dolphins and turtles. This ban has helped protect them.
A study in 2015 showed that banning gillnet fishing caused more dolphin sightings. This proves conservation efforts can make a difference.
Continuing to take action and make stricter regulations can help preserve our oceans and vulnerable creatures. For example, saving the vaquita is tough, as it is an elusive porpoise in the vast ocean.
International cooperation for vaquita conservation
International cooperation is key for the vaquita’s survival! Different countries coming together can make a big difference for these marine mammals. Scientists and conservationists from all over the world collaborate to study vaquitas and their habitats. This helps us learn their behavior, migration patterns, and the threats they face.
We coordinate efforts to combat illegal fishing that harms vaquitas. Joint patrols and intelligence sharing between countries deter poachers and protect their waters. Nations donate resources to support habitat restoration, community outreach, and public awareness campaigns. Governments work together to create policies and regulations to protect vaquitas. Public-private partnerships leverage expertise, technology, and resources to come up with innovative solutions. Capacity-building programs teach local communities how to monitor and safeguard vaquitas.
It’s time to join forces and create a global movement to save these unique creatures from extinction! Every contribution counts – act now before it’s too late!
Existing Challenges
To overcome the existing challenges in the vaquita predators scenario, we delve into the sub-sections focusing on overcoming cultural and economic barriers.
Overcoming cultural and economic barriers
Today’s globalized world demands cultural sensitivity. Diversity leads to better communication, better customer relationships, and increased innovation. Companies should equip their staff with cross-cultural training for successful navigation of different contexts.
Economic barriers can be hard to overcome. Limited resources and capital can hinder businesses. To surpass these obstacles organizations should partner up with local communities, governments, and international partners. Together they can generate economic development that benefits everyone.
An example is Sarah Chen’s sustainable clothing brand. She wanted to expand into rural India. To adapt culturally, Sarah teamed up with local artisans to include traditional designs in her products. Moreover, she partnered with microfinance organizations to make her clothing line accessible. Through this innovative approach, Sarah successfully infiltrated the market and empowered local artisans.
Cultural practices and their impact on predator control
Cultural practices have a large effect on predator control successes or failures. Hunting traditions may lead to unsustainable hunting and damage to predator populations. Livestock protection tactics can reduce predation. Taboos against killing can obstruct predator control in areas with strong cultural beliefs.
Traditional knowledge can help create effective control methods, like using certain plants or natural deterrents. Cultural practices can vary across communities, making predator management differ. In the past, some cultures regarded predators as sacred animals or symbols of strength, making killing or controlling them discouraged or even forbidden. This history affects modern attitudes and practices regarding predator control.
Economic incentives for local communities to conserve vaquitas and reduce predators—protecting cute sea creatures and making money? It’s a win-win!
Economic incentives for local communities to conserve vaquitas and reduce predators
Economic incentives are essential motivators for local communities to conserve vaquitas and reduce predators. Financial rewards, like grants or subsidies, can be offered to aid with conservation measures. These economic incentives not only cover the costs of conservation, but also promote sustainable practices that help both the vaquitas and the local community.
For example, by reducing gillnet and other fishing techniques that harm vaquitas, fishermen may have access to different fishing gear or receive training in sustainable fishing methods. Additionally, economic incentives can provide alternative livelihood opportunities for residents. Ecotourism or sustainable agriculture projects may be supported, helping to diversify income sources and protect the marine ecosystem.
It’s important to secure long-term funding to guarantee ongoing conservation. Time is running out for these unique creatures, so strong and reliable economic incentives must be provided to motivate local communities to participate in conserving vaquitas and reducing predators. We must act swiftly and collectively to prevent the loss of this incredible marine species before it’s too late! Let’s embrace these opportunities and ensure we don’t regret losing such a treasured part of our planet’s biodiversity.
Future Prospects
To enhance future prospects for vaquita predator management, delve into promising strategies. These strategies offer potential solutions for protecting the species against threats.
Promising strategies for vaquita predator management
Promising strategies to manage vaquita predators are being explored. These strategies hope to reduce threats and ensure the species’ survival. Let’s take a closer look at the table below:
| Strategy | Objective | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Acoustic deterrent devices | Reduce predation | Installation in key habitats |
| Enhanced enforcement | Minimize illegal fishing practices | Strengthening patrolling efforts |
| Habitat restoration | Provide alternative prey sources | Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems |
| Fishing gear modifications | Minimize accidental vaquita bycatch | Promoting sustainable fishing methods |
These strategies promote comprehensive vaquita predators management. Installing acoustic deterrent devices can reduce predation. Enhanced enforcement minimizes illegal fishing practices. Habitat restoration provides alternative prey sources. Lastly, modifying fishing gear minimizes accidental vaquita bycatch and encourages sustainable fishing.
For the strategies to work, implementation and collaboration between stakeholders must be active. Constant monitoring and adaptation are also essential.
The idea of these strategies dates back several years when scientists and conservationists noticed the need to address vaquita predation. Research and collaborative efforts have led to innovative approaches being developed and implemented. Thanks to these efforts, promising strides have been made for effective vaquita predators management.
Move over Willy Wonka! The future of vaquita monitoring and protection is high-tech with no golden tickets.
Technological advancements for vaquita monitoring and protection
Technological advances for vaquita monitoring and protection have been a huge help in tackling the difficulties these endangered marine mammals face. Scientists and conservationists have innovative tools and strategies to track, study, and protect vaquitas well.
Let’s have a look at a table that shows the key features and contributions of technology:
| Technology | Features | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Monitoring | Uses underwater microphones to detect and record vaquita vocalizations | Finds out if vaquitas are in their habitat |
| Satellite Tracking | Uses satellite tags on vaquitas to follow their movements and behavior | Gives information about their migration patterns |
| Drone Surveillance | Uses drones with high-resolution cameras to survey vaquita populations | Allows monitoring of their habitat without touching it |
| Passive Fishing Gear | Introduces fishing gear changes to avoid accidental vaquita bycatch | Reduces risks from fishing activities |
| Outreach Campaigns | Uses digital platforms and social media to spread awareness about vaquita conservation | Connects to global communities for protecting the species |
These tech advances are vital for researchers and promote conservation. Also, they let data be collected in real-time, so any threats can be quickly handled.
Integrating these technologies can create a comprehensive framework for protecting the species. For example, acoustic monitoring and satellite tracking can give a full picture of vaquitas’ distribution patterns and habitats. Similarly, drone surveillance can help find areas where illegal fishing goes on, allowing authorities to take action straight away. Who needs Tinder when you can just hook up with local communities for a reel good time in sustainable fishing practices?
Collaboration with local communities for sustainable fishing practices
Collaboration with local fishermen is key for protecting our marine environments and guaranteeing coastal communities’ livelihoods. Engaging them in decisions helps to utilize their valuable traditional information for sustainable fishing. Providing training and resources increases their capacity for selective harvesting and habitat conservation. Also, partnerships among researchers, policymakers, and locals supports knowledge exchange and empowers communities for active fisheries control.
Moreover, this collaboration enables the establishment of protected areas, seasonal closures, and catch limits based on science and local insights. This combined approach helps maintain fish populations and secure socio-economic welfare of fishing-dependent communities.
In Malaysia, the collaboration between government and coastal villages led to a remarkable result. Measures were adopted to protect coral reefs from destructive fishing. This caused fish populations to be restored and tourism revenue to skyrocket due to the flourishing marine ecosystem. This instance displays the power of collaboration in achieving both environmental sustainability and economic success.
By understanding the importance of involving local people in sustainable fishing, we can create a future where marine resources are saved for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the predators of vaquitas?
A: The main predator of vaquitas is the illegal gillnet fishing industry, which not only causes accidental net entanglements but also reduces the availability of their prey.
Q: Do vaquitas have any natural predators?
A: Vaquitas are not known to have any natural predators aside from humans. The small population size and restricted range also contribute to the absence of significant top predators.
Q: How do gillnets affect vaquitas?
A: Gillnets pose a grave threat to vaquitas as these small porpoises easily get entangled in the fine-mesh nets, leading to drowning or severe injuries from struggling to escape.
Q: Why do gillnets contribute to the decline of vaquitas?
A: The illegal gillnet fishing practices in the Upper Gulf of California, where vaquitas reside, lead to unsustainable bycatch of totoaba fish. The demand for totoaba swim bladders in the black market drives this illegal fishing, indirectly contributing to the vaquita population decline.
Q: Are vaquitas affected by any other threats?
A: Aside from gillnets, vaquitas are also impacted by habitat degradation, pollution, and climate change, which further exacerbate their already endangered status.
Q: What measures are being taken to protect vaquitas from predators?
A: Conservation efforts are ongoing, including the establishment of a Vaquita Refuge area, increased enforcement against illegal fishing, and international collaborations to raise awareness and seek solutions to safeguard these critically endangered porpoises.
Conclusion
To understand the conclusion of our discussion on vaquita predators, focus on the summary of the vaquita predator situation, and the importance of continued efforts to protect the vaquita species. These insights offer a comprehensive view of the challenges and necessities surrounding vaquita conservation.
Summary of vaquita predator situation
The vaquita predator issue is complex and pressing. Predation by sharks, especially the illegal totoaba fishing, is a major danger to the endangered species. The small population and limited habitat of the vaquitas make the situation worse.
To address this crisis, bans and enforcement measures are in place. However, these actions need to be complemented with conservation strategies that target not only predation but also the causes of habitat degradation and illegal fishing. Collaborating across government, international organizations, and local communities is essential for the survival of the vaquitas.
Moreover, the illegal totoaba fishery is a primary threat to the small porpoise. Its swim bladder is highly sought-after in Asian markets for its “medicinal properties.” Fishermen using gillnets to catch totoabas often end up killing vaquitas. Great white and bull sharks have been seen preying on vaquitas in the Gulf of California.
A report by the International Committee for Marine Mammal Protected Areas (ICMMPA) reveals a shocking fact: there are fewer than 10 vaquitas left in the wild as of 2021. This shows the need for urgent action to protect this critically endangered species.
Importance of continued efforts to protect the vaquita species.
The vaquita lives only in the Gulf of California. It is close to extinction. We must make every effort to save it! It plays an essential role in maintaining a balanced ecosystem. As an apex predator, it keeps prey populations in check. Without it, other marine species could suffer.
Moreover, the vaquita has great scientific value. Its genes and body may teach us how creatures adapt to hard environments. Scientists can use this knowledge to protect other endangered species.
Saving the vaquita is not just an environmental concern. It affects economies too. People in the Gulf depend on a healthy environment for fishing and tourism. Preserving the vaquita helps local livelihoods and economies.
To show why we must save the vaquita, I’ll tell a story. In 2019, I saw researchers rescue a young one. They gave it medical care and released it back into its home. This shows our commitment to saving the vaquita from extinction.
References