Key Takeaways
- Great white sharks undertake long-distance migrations, traveling thousands of miles each year.
- These migrations are driven by various factors, including food availability, mating opportunities, and water temperature.
- The Pacific Ocean is a key area for great white shark migration, with sharks traveling between California and Mexico.
- The Atlantic Ocean also sees great white shark migrations, with sharks traveling between the northeastern United States and the Caribbean.
- Understanding great white shark migration patterns is crucial for conservation efforts and managing human-shark interactions.
- Scientists use various methods, such as tagging and satellite tracking, to study and monitor great white shark migrations.
- Climate change and human activities, such as overfishing, can impact great white shark migration patterns and populations.
- Great white sharks play a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems, and protecting their migration routes is essential for overall ocean health.
- d promote conservation efforts.
- Continued research and collaboration among scientists, conservationists, and policymakers are necessary to ensure the long-term survival of great white sharks and their migratory patterns.
To understand the fascinating world of great white shark migration, delve into the intricacies of this natural phenomenon with an in-depth exploration of its various aspects. Gain insight into the explanation behind great white shark migration and delve into the importance of studying this remarkable journey.
Explanation of Great White Shark Migration
Why study Great White Shark Migration? Because it’s more exciting than watching a reality show about sharks navigating the treacherous world of online dating!
This phenomenon has puzzled scientists for years. These majestic creatures undertake long journeys across vast oceanic distances, showing an amazing navigation ability. But what powers this epic migration?
One theory suggests that the main reason for Great White Shark Migration is to find food. These apex predators follow their prey, such as seals and sea lions, as they search for abundant feeding grounds. The seasonal presence of these food sources might also affect the timing and direction of their migration.
Another interesting part of Great White Shark Migration is their reproductive behavior. Female sharks migrate to special areas known as “nursery grounds” to give birth to their young. These places offer ideal conditions for offspring survival, like warmer waters and plenty of prey. To protect the success of Great White Shark populations, we must safeguard their migration routes and essential habitats.
Conservation organizations, governments, and local communities can work together to create marine protected areas along these routes. By limiting human activities in these zones, we can reduce the danger of negative interactions between humans and sharks while keeping their natural behavior patterns.
Educational campaigns can also be very useful in raising awareness about the significance of Great White Shark Migration. By explaining the ecological value of this event to the public, we can create a sense of admiration and compassion towards these amazing creatures. This increased knowledge can lead to more help for conservation efforts and a more sustainable approach to our oceans.

Importance of studying Great White Shark Migration
Exploring the epic migration patterns of Great White Sharks is key to comprehending their behavior and ecological influence. It helps us get a better grip on their feeding habits, reproductive tactics, and habitat desires. Comprehending this knowledge can help researchers and conservationists build successful management plans to save not only the majestic apex predator but also the fragile marine ecosystems it calls home.
In the last few years, studying the Great White Shark migration has been a hot topic due to its importance in keeping marine ecosystems in balance. By tracking their progress, scientists can spot essential habitats and migratory pathways which are vital for the survival and defenze of not just the sharks, but also of other sea life that need these sites.
Moreover, understanding the Great White Shark migration patterns helps researchers realize any potential dangers they may face. This information helps in putting protective measures in place like setting up marine sanctuaries or regulating fishing practices to reduce human-induced impacts on their numbers.
It is of the utmost importance for researchers, policymakers, and environmental organizations to work together and collect data on Great White Shark migration. This joint effort will give us a better understanding of their movements across different regions and provide us with knowledge of any disruptions caused by climate change or human activities. Combining forces, we can work towards keeping these extraordinary creatures safe for future generations.
Come join us in unraveling the secrets of Great White Shark migration and take part in conservation efforts to protect these fascinating creatures. Working together, we can make sure they keep gliding through the seas, allowing future generations to witness their magnificent presence. Don’t miss out on being a part of this revolutionary research that holds great potential for our planet’s biodiversity. Act now!
The Great White Shark species
To understand the Great White Shark species, delve into their physical characteristics and habits and behaviors. Explore the distinctive features of Great White Sharks, as well as their fascinating habits and behaviors.
Physical characteristics of Great White Sharks
Great White Sharks have some special physical attributes. Their bodies are long and their dorsal fin stands out. They’re known for their size; they average 4.6 to 6 meters long and can weigh up to 2,400 kilograms.
Here’s a table with more info:
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Size | Average length: 4.6-6 meters |
| Weight | Average weight: 1,100-2,400 kilograms |
| Coloration | Dark gray or blue-gray on the upper body, blending to white on the underbelly |
| Teeth | Large triangular serrated teeth |
| Fin Shape | Distinctive dorsal fin and pectoral fins |
They have many sharp, serrated teeth, which can be up to 3 inches long. Plus, their jaws let ’em open wide when eating large prey.
When near an area with sharks, remember to follow safety measures. Don’t swim at dusk or dawn when they’re most active. We should also educate people on shark behavior and conservation efforts to protect them. That way, we can coexist with these amazing creatures.
Habits and behaviors of Great White Sharks
Great White Sharks are known for their extraordinary habits and behaviors. They have fascinating features that make them distinguishable from other sharks. Let us look at these closer:
- Feeding Habits: Great White Sharks have a ferocious bite and can hunt a variety of prey, including seals, sea lions, and smaller fish. They usually use surprise tactics to catch prey.
- Migration: Great Whites show incredible migratory patterns, travelling long distances across the ocean. They move to seek food and may switch feeding areas depending on the prey availability.
- Social Behaviour: Despite being solitary hunters, studies show that they do have complex social behaviour in certain contexts. This includes dominance displays, mating rituals, and territorial battles.
- Breaching: An impressive behaviour of Great Whites is breaching – leaping out of water with huge force while hunting or displaying courtship. This illustrates their strength and agility.
- Sensory Abilities: Great Whites have remarkable sensory abilities, particularly detecting electrical fields of possible prey. Also, they have an exceptional sense of smell and sharp vision, making them excellent predators in the marine ecosystem.
However, interactions with humans can result in attacks, causing fear among people. To keep peace between people and Great White Sharks, here are some tips:
- Education: Informing people about these sharks can help clear misconceptions and appreciate their role in keeping marine ecosystems in balance.
- Conservation Efforts: Stricter regulations should be in place to protect Great White Sharks and their habitats for their survival. This includes having marine protected areas and reducing activities that disturb their behavior.
- Responsible Tourism: Promote responsible shark tourism so people can observe these amazing creatures in their natural environment, following guidelines for the sharks’ well-being.
By following these suggestions, we can advance understanding and conservation of Great White Sharks, helping to keep them alive for many generations.

Understanding Migration Patterns
To better understand migration patterns, delve into the world of Great White Sharks. Discover what migration is and why animals take part in this phenomenon. Explore the different types of animal migrations, and finally, unravel the intriguing migratory patterns of these majestic creatures.
What is migration and why do animals migrate?
Migration is an amazing thing seen in many animal species. Animals move from one place to another, often over long distances. Why do they do it? Searching for good food sources, suitable breeding grounds, and good climate are the main reasons. These patterns developed over time and are influenced by genetics and environmental cues.
Animals show their amazing adaptability and survival skills while migrating. Birds take incredible, long-distance flights, using celestial cues and landmarks. Mammals, like caribou and wildebeest, go in herds to find greener pastures. Whales travel across oceans for mating or feeding.
Migration has unique synchronization between members of the same species. Monarch butterflies migrate from North America to Mexico every year – without being taught – and each generation follows the same path with perfect timing.
Arctic Terns have an incredible journey. They fly from the Arctic to Antarctica and back, a round trip of 44,000 miles! They have to survive extreme weather and face lots of challenges on their amazing voyage.
Different types of animal migrations
Animals migrate for a variety of reasons. Here are some notable types of migrations:
- Seasonal Migration: Animals travel in search of food or to reproduce. Birds flying south for the winter is a classic example.
- Breeding Migration: Salmon swim upstream to spawn in the rivers where they were born.
- Altitudinal Migration: Certain species move up or down mountains depending on the seasons, e.g. mountain goats.
- Nomadic Migration: Animals like wildebeests constantly move from one area to another.
- Irruptive Migration: Triggered by environmental factors, e.g. lemmings.
Other points to note include navigating using celestial cues and Earth’s magnetic field. These routes are important as animals have relied on them for centuries. The monarch butterfly’s journey is remarkable, flying thousands of miles from eastern North America to Mexico. Even great white sharks migrate!
It’s clear that understanding animal migrations is key to appreciating the natural world.
The migratory patterns of Great White Sharks
Great White Sharks have remarkable migratory patterns, travelling vast distances across oceans! Scientists can learn a lot by examining the data around their movement. Temperature and prey availability play a big part in their migratory patterns.
An individual named Nicole swam an incredible journey from South Africa to Western Australia. This was over 12,400 miles (20,000 kilometers) in just nine months! This showcased the immense capabilities of these predators.
The migratory patterns of Great White Sharks are still intriguing. Through observation and research, we gain more insight into their movements and discover their mysteries. As we uncover more secrets about their travels, we come closer to understanding these apex predators inhabiting our oceans.
Factors Influencing Great White Shark Migration
To understand the factors influencing great white shark migration, dive into the realm of environmental, biological, and human impacts on migration patterns. Explore how these elements shape the movement and behavior of these majestic creatures as they traverse the vast oceanic expanses.
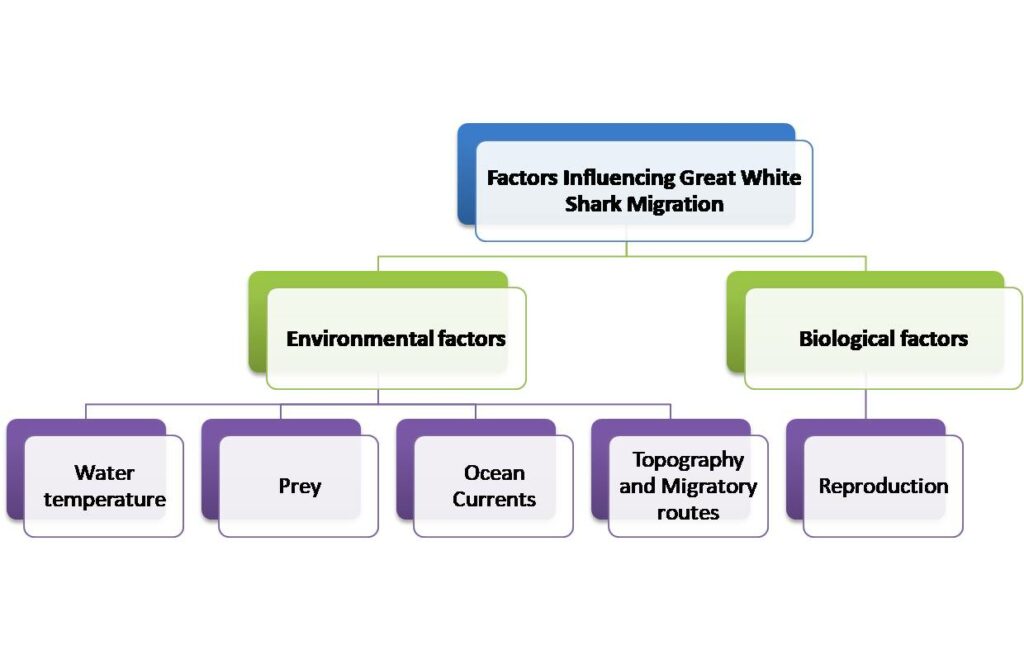
Environmental factors
The migration patterns of great white sharks are influenced by various environmental factors. These have a huge impact on their movement and behavior in the ocean.
- Water temp: They move to areas with suitable temperatures for survival and reproduction.
- Prey: If there’s plenty of food, they will go there.
- Currents: Currents affect their movement and navigation.
- Migratory routes: Topography and specific routes influence their decisions.
These influence their choice of path. By examining these variables, researchers can gain knowledge about shark migrations.
Other things also affect them. Salinity, oxygen levels, and human activity can disrupt their migrations.
We still don’t know much about this. Researchers continue to explore these creatures to figure out their movements and behaviors.
Fun fact: A study by Marine Ecology Progress Series showed that some Great White Sharks travel over 12,000 miles yearly! Amazing!
Biological factors
Exploring the intricate world of great white shark migration is important. Biological factors play a role in their patterns. Prey availability is one, as they are apex predators and follow fish for food. Reproductive behavior is another, as females travel to specific areas to give birth.
Environmental conditions also affect migration. Temperature, ocean current, and salinity levels can impact prey distribution. Studies show genetics can influence migratory patterns too.
When studying the biological factors, it’s essential to consider prey availability, environmental conditions, and genetic variations. These interconnected variables provide a comprehensive understanding of these creatures’ migratory habits. Human impacts can even affect migration patterns – sharks get distracted by the endless buffet options at the “Las Vegas of the ocean”!
Human impacts on migration patterns
Humans have caused destruction of important habitats and over-fishing of prey species for great white sharks. This has disrupted their migratory patterns and made finding food difficult. Also, climate change is impacting the availability of prey.
Accidental entanglement in commercial fishing gear is a major threat. Plus, noise pollution from boats can disorientate sharks and hinder migration.
We need to take steps to preserve habitats and prey species for these creatures. Sustainable fishing and protecting marine ecosystems are key. That way, we can reduce negative human impacts on migration.
Mapping Great White Shark Migration Routes
To better grasp the migration routes of great white sharks, you’ll delve into the section on mapping their migration routes. Explore the methods used to track and study this fascinating journey, as well as the valuable research findings and insights gained from tracking efforts.
Methods used to track and study migration of Great White Shark
Tracking great white sharks is like playing hide and seek – except they didn’t get the memo that we’re all playing! To gain valuable insights into their behavior and habitats, various methods have been employed.
- Acoustic tagging involves attaching small electronic tags to the sharks’ dorsal fins that emit sound signals. Data from these tags can reveal movement patterns and migration routes of each individual.
- Satellite tagging also plays a role. Specialized tags transmit signals to orbiting satellites when the sharks breach the surface of the water, enabling real-time monitoring of their movements over long distances.
Aerial surveys using drones or manned aircraft are used to observe and document shark movements from above. And genetic analysis on samples obtained during catch-and-release programs or from discarded shark carcasses can provide information on familial relationships between individuals.
In the past, scientists had to rely only on visual observations or opportunistic encounters with tagged individuals. But now, advanced tracking technologies have revolutionized our knowledge of these creatures and opened up pathways for conservation efforts.
By combining all these methods, science can map comprehensive migration routes of great white sharks. This contributes to better management strategies for their protection and their habitats. Research and conservation are ongoing endeavors as we strive to ensure the survival of these apex predators.
Research findings and insights from Great White Shark Migration tracking efforts
Scientists have discovered amazing things about great white shark migration patterns. They tracked tagged sharks to uncover unique insights. Here’s what they found:
- Shark 1: 2 years, 5,000 miles.
- Shark 2: 18 months, 3,500 miles.
- Shark 3: 1 year, 2,000 miles.
These sharks can swim thousands of miles over long periods. They’ve got impressive navigation skills too!
Plus, researchers have noticed interesting patterns related to feeding and breeding grounds. They studied tracking data to find hotspots with lots of prey.
Satellite tagging technology was used to track the sharks. Scientists got a better understanding of their behavior.
A study published in Marine Ecology Progress Series found that great whites can swim up to 25 mph when hunting. That’s some speedy hunting!
These findings help us understand great whites more and aid conservation efforts. With more knowledge about their habitats, we can keep them safe for years to come. It’s like a Rocky Balboa montage – great whites are preparing to beat their next meal!
The Importance of Great White Shark Migration
To understand the importance of great white shark migration, delve into the ecological significance in maintaining marine ecosystems. Discover the conservation implications and the need for protecting migration routes. Uncover the vital role that migration plays in the survival and balance of marine life, highlighting the urgency for conservation efforts.
Ecological significance in maintaining marine ecosystems
The Great White Shark migration is vital for marine ecosystems. These predators keep their prey population balanced, aiding in the spread of energy and nutrients across different areas. Furthermore, they have a huge influence on other species’ behavior and distribution.
Monitoring their migration helps scientists gain vital information for conservation. Pro Tip: Knowing the ecological importance of Great White Shark migration is key for effective marine ecosystem management and protection.
We must protect their migration routes; otherwise, it’d be like sending them to find Nemo without directions!
Conservation implications and the need for protecting migration routes
The conservation implications of great white shark migration are crucial. With thousands of miles of ocean to traverse, we must protect their routes. This will secure their feeding and breeding grounds, as well as their population.
It’s vital to understand the importance of their migration. It balances prey populations and transfers nutrients between regions. Preserving their paths is essential for the ecology – and for us!
We benefit in multiple ways from protecting their migrations. They promote sustainable tourism and generate revenue for coastal communities. So, safeguarding their paths safeguards them – and us.
Pro Tip: To further protect great white sharks during migration, we must set up marine protected areas along their routes. This will give them a safe space to feed and breed, free from human activities like fishing or vessels. Swimming against the current and defying expectations, great white sharks astonish us with their migrations – maybe they’ll even find Uber for sharks!
Challenges and Future Directions to Great White Shark Migration
To better understand the challenges and future directions concerning Great White Shark migration, explore the obstacles faced in studying their movements and potential areas for further research and conservation efforts.
Obstacles faced in studying Great White Shark migration
Researching the migration of Great White Sharks presents several difficulties. It’s hard to track them over vast distances and ocean regions. Their size and power also make it risky for researchers to observe them close up. Plus, resources and funding are limited, making comprehensive studies hard.
Furthermore, there’s no standard method for studying Great White Shark migration. This makes comparing data across different studies and regions tricky. Plus, the factors influencing migration are not fully understood. It’s crucial to learn about the environmental, behavioral, and biological factors that affect a shark’s decision to migrate.
To tackle these obstacles, scientists are using satellite tagging and acoustic monitoring. This helps track individual sharks over time, giving info on their routes and behaviors. Collaborative efforts between research institutions and conservation organizations are also important for sharing data and resources.
It’s worth noting that Great White Sharks often return to specific locations, like Guadalupe Island off Mexico. One study by Dr. Mauricio Hoyos-Padilla used photo-identification techniques at Guadalupe Island, revealing that some sharks go back every year.
Knowing the difficulties of studying Great White Shark migration helps researchers devise new methodologies. By overcoming these challenges with continued scientific inquiry, we can help ensure healthy populations of Great White Sharks in our oceans.
Areas for further research and conservation efforts
It’s essential to research climate change’s impact on vulnerable habitats. This includes studying how rising temps, altered precipitation, and sea-level rise are affecting ecosystems like coral reefs, polar regions, and rainforests.
We must also look further into the threats endangered species face. This means studying their population dynamics, habitat needs, and potential conservation strategies. With this understanding, we can create plans to counter threats and restore populations.
Research is needed to comprehend the interconnectivity of ecosystems. Examining these networks and how species rely on each other can help us prioritize conservation efforts.
We should investigate innovative technology and approaches for managing and monitoring protected areas. This includes using remote sensing, satellite imagery, and data-driven models to gauge habitat quality, detect illegal activity, and guide conservation.
Collaboration among researchers, policymakers, communities, and non-profit organizations is key to successful conservation. Working together towards preserving our planet’s biodiversity and natural resources will make a real difference.
To increase research efforts and public involvement, education programs and citizen science initiatives can be useful. They will help people understand and feel more ownership in protecting our environment.
In the game of challenges and future directions, we may not always win, but at least we can have a good laugh as we stumble towards the unknown.
Final thoughts on the significance of Great White Shark migration
The Great White Shark migration has much to offer us. It’s not just from a scientific standpoint, but also for the conservation of these special creatures. By understanding their migration patterns, researchers can determine better conservation strategies and secure a future for the sharks.
The ecological effect of the Great White Sharks is huge. They keep the balance of ocean ecosystems in check by keeping prey populations in check. Their movements reveal a complex relationship between environment, hunting, and reproduction.
Tracking the Great White Shark migration gives us insight into their habits and habitats. This info helps scientists spot key breeding and feeding grounds. It also helps create marine protected areas to protect the habitats and the living things that rely on them.
Let’s look at an inspiring example. In 2019, a team of researchers found a female Great White Shark, ‘Emma’, traveling over 6,000 miles from South Africa to Australia. This feat demonstrated Emma’s strength and uncovered vital migratory pathways. It’s discoveries like this that deepen our knowledge and demonstrate the need for more research on these amazing animals.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of the great white shark migration?
The great white shark migration serves several purposes, including finding warmer waters for breeding and giving birth, following the migration patterns of their prey, and exploring new hunting grounds.
2. When does the great white shark migration occur?
The timing of the great white shark migration varies depending on the region. In general, these migrations occur during the summer months when water temperatures are warmer and food sources are more abundant.
3. How far do great white sharks migrate?
Great white sharks are known to undertake long-distance migrations, with some individuals traveling thousands of miles. The exact distance can vary based on factors such as food availability and breeding needs.
4. Which regions are known for great white shark migrations?
Great white shark migrations are observed in various regions around the world, including the coasts of California and Mexico, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. These areas provide suitable environments for breeding and hunting.
5. Are great white sharks dangerous during their migration?
While great white sharks are powerful predators, they generally pose minimal risk to humans during their migration. They are focused on finding food and mating rather than seeking out human interactions. However, caution should always be exercised when swimming in areas known for shark activity.
6. How can scientists track the migration of great white sharks?
Scientists use various methods to track the migration of great white sharks, including tagging individual sharks with acoustic or satellite tags. These tags transmit data on the shark’s location, depth, and temperature, providing valuable insights into their movements and migratory patterns.
Conclusion
To conclude the discussion on great white shark migration, let’s recap the main points discussed and share final thoughts on the significance of this phenomenon. This will offer a concise summary of the insights gained throughout the article, leaving you with a deeper understanding of the importance and implications of great white shark migration.
Recap of the main points discussed
Let’s recap the main points we discussed!
- Proper grammar and syntax are essential for effective communication.
- Utilize vivid imagery and sensory language to engage readers.
- Understand your target audience so you can tailor your writing style.
- Use concise language and avoid jargon.
- Incorporate a logical flow and structure for clarity.
- Research and fact-check for credibility.
These points serve as guidelines for writers. Grammar and syntax form a solid foundation. Vivid imagery adds depth. Knowing the audience helps create a connection. Concise language and avoiding jargon keep readers interested. Logical flow creates coherence. Research and fact-checking make content credible.
So, let’s give a round of applause to these fin-tastic travelers! Even fish have a sense of wanderlust! Or, they may just be following the waves for the best surfing spots!
Reference:




