The Mourning Dove (Zenaida macroura) is a widely recognized and beloved bird species found throughout North America. Known for its gentle cooing and graceful flight, the Mourning Dove holds a special place in the hearts of bird enthusiasts and nature lovers. However, concerns have been raised about the potential extinction of this iconic species. In this article, we will delve into the current status of the Mourning Dove population, explore the factors contributing to its decline, and discuss conservation efforts aimed at preserving this beautiful bird for future generations. So, is the Mourning Dove truly facing the threat of extinction? Let’s find out.
Key Takeaways
- The mourning dove is not extinct and is a common bird species found in North America.
- It is known for its distinctive cooing sound and graceful flight.
- Conservation efforts are important to protect the mourning dove and its habitat.
The Status of the Mourning Dove: Extinct or Not?
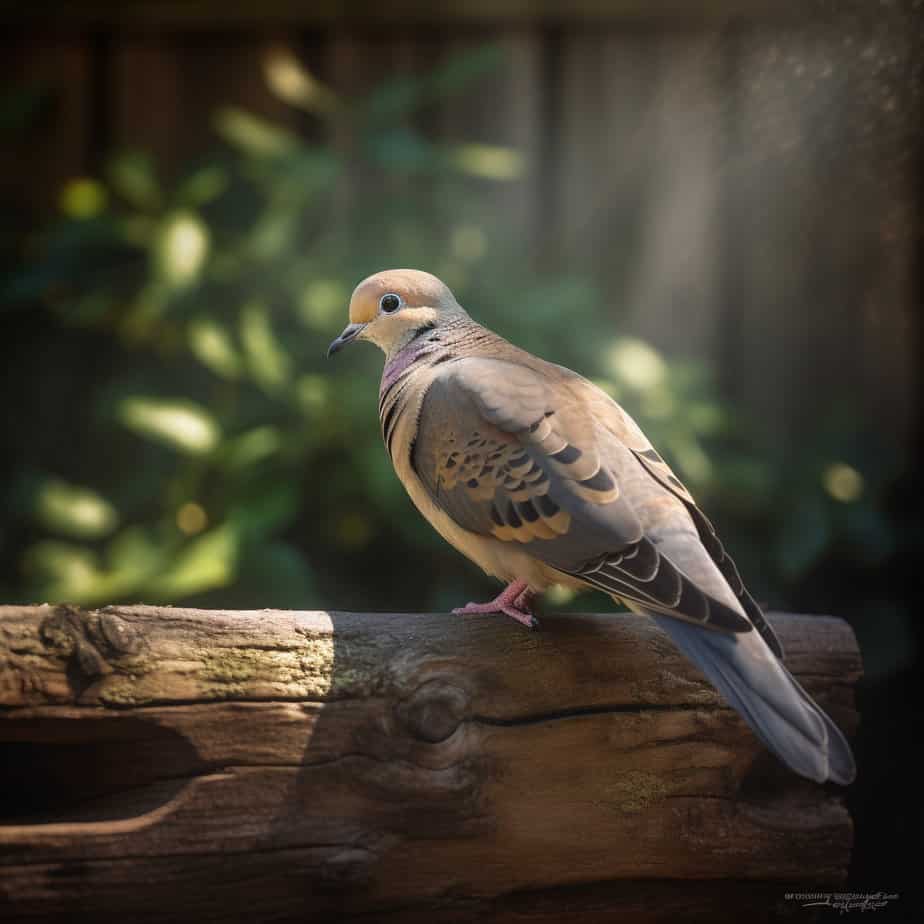

A. Current Status of the Mourning Dove
The Mourning Dove, scientifically known as Zenaida macroura, is a bird species that has captured the hearts of birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts alike. Known for its gentle cooing and graceful flight, the Mourning Dove is a common sight in many parts of North America. However, concerns have been raised about the status of this beloved bird. Is the Mourning Dove on the brink of extinction, or is it still thriving in the wild?
To answer this question, we need to examine the current population and conservation status of the Mourning Dove. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Mourning Dove is listed as a species of “Least Concern.” This means that, at present, there is no immediate threat to the survival of the Mourning Dove population.
The Mourning Dove is one of the most abundant bird species in North America, with an estimated population of over 350 million individuals. Its wide distribution range, spanning from Canada to Mexico, contributes to its overall stability. These birds can be found in a variety of habitats, including urban areas, farmlands, and open woodlands. Their adaptability to different environments has played a significant role in their continued presence in the wild.
B. Factors Influencing the Mourning Dove’s Status
While the current status of the Mourning Dove may be reassuring, it is essential to understand the factors that can influence its future. Several key factors contribute to the overall well-being of the Mourning Dove population.
-
Habitat Loss: As human populations continue to expand, the loss of natural habitats becomes a significant concern for wildlife. The conversion of forests into agricultural lands and the urbanization of rural areas can disrupt the Mourning Dove’s nesting and foraging habitats. Conservation efforts should focus on preserving and restoring suitable habitats for these birds.
-
Climate Change: The impact of climate change on bird species cannot be ignored. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the availability of food and water sources for the Mourning Dove. Additionally, extreme weather events, such as droughts and storms, can disrupt their breeding cycles and overall reproductive success.
-
Hunting and Predation: While hunting Mourning Doves is regulated in many regions, illegal hunting and predation by natural predators can still pose a threat to their population. It is crucial to enforce bird protection laws and educate the public about the importance of conserving these birds.
-
Disease and Parasites: Like any other living organism, Mourning Doves are susceptible to diseases and parasites. Avian pox, trichomoniasis, and external parasites can impact their health and reproductive capabilities. Monitoring and managing disease outbreaks are essential for maintaining a healthy population.
-
Human Disturbance: Human activities, such as excessive noise, disturbance near nesting sites, and the use of pesticides, can negatively impact the Mourning Dove population. Raising awareness about the importance of minimizing human disturbance and promoting responsible birdwatching practices is crucial for their conservation.
In conclusion, while the Mourning Dove is currently not at risk of extinction, it is essential to remain vigilant and proactive in preserving their population. By addressing the factors that influence their status, such as habitat loss, climate change, hunting, disease, and human disturbance, we can ensure the continued survival and well-being of these beautiful birds. Conservation efforts, wildlife preservation, and bird protection laws play a vital role in maintaining avian biodiversity and allowing future generations to enjoy the sight and sound of the Mourning Dove in the wild.
Understanding the Mourning Dove: An Overview

A. Characteristics and Habitat of the Mourning Dove
The mourning dove (Zenaida macroura) is a graceful and gentle bird that is widely recognized for its mournful cooing sound. It is a medium-sized bird, measuring about 9-13 inches in length and weighing between 3-6 ounces. With its slender body, long tail, and pointed wings, the mourning dove possesses a streamlined appearance that allows it to swiftly navigate through the air.
Mourning doves are known for their soft, muted colors. Their feathers are predominantly gray-brown, with lighter shades on their undersides and darker hues on their wings. They have a distinctive black spot on their cheeks and a small, black crescent-shaped mark on the back of their necks. These markings, along with their reddish feet and legs, make them easily identifiable.
In terms of habitat, mourning doves are highly adaptable and can be found across a wide range of environments throughout North America. They are commonly found in open woodlands, fields, parks, gardens, and suburban areas. These birds prefer habitats with a mix of trees for roosting and open spaces for foraging. Mourning doves are particularly fond of areas with access to water sources, as they require regular drinking and bathing.
B. Role of Mourning Doves in the Ecosystem
Mourning doves play a crucial role in the ecosystem as seed dispersers and insect controllers. They primarily feed on seeds, grains, and small insects. Their diet consists of a variety of plant materials, including grasses, weeds, and cultivated crops such as corn and sunflowers. By consuming these seeds, mourning doves help to control weed populations and aid in the natural regeneration of plant species.
Additionally, mourning doves contribute to insect control by feeding on a wide range of insects, including beetles, ants, and grasshoppers. This helps to regulate insect populations, preventing them from becoming overly abundant and causing damage to crops and vegetation.
Moreover, mourning doves are an important part of the food chain. They serve as prey for various predators, including hawks, owls, and snakes. Their presence in the ecosystem provides a vital food source for these predators, contributing to the overall balance and biodiversity of the avian community.
Conclusion
In this section, we have explored the characteristics and habitat of the mourning dove, as well as its role in the ecosystem. The mourning dove’s adaptability, gentle nature, and important ecological functions make it a valuable species to conserve. Understanding the significance of mourning doves in the natural world can help us appreciate the importance of protecting their populations and ensuring their survival for future generations.
Are Doves Going Extinct?
A. The Global Picture: Dove Species at Risk
Doves, with their gentle cooing and graceful flight, have long been a symbol of peace and tranquility. However, these beloved birds are facing increasing threats to their survival. While the mourning dove, a common species of dove found in North America, is not currently classified as extinct, there are concerns about the overall decline in dove populations worldwide.
Dove species, including the mourning dove, are facing various challenges that put them at risk of extinction. Habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and hunting are among the primary factors contributing to the decline in dove populations. As human activities continue to encroach upon their natural habitats, doves are losing the places they rely on for nesting, feeding, and breeding.
B. The Impact of Human Activities on Dove Populations
-
Habitat Loss: One of the most significant threats to dove populations is the loss of suitable habitat. Urbanization, deforestation, and agricultural expansion have resulted in the destruction and fragmentation of dove habitats. As forests are cleared for development or converted into farmland, the availability of nesting sites and food sources for doves diminishes. This loss of habitat directly impacts their ability to survive and reproduce.
-
Pollution: Pollution, particularly from pesticides and chemical contaminants, poses a significant risk to dove populations. These toxic substances can accumulate in the birds‘ food sources, such as seeds and insects, leading to reduced reproductive success, weakened immune systems, and overall population decline. Additionally, pollution can contaminate water sources, affecting the availability of clean drinking water for doves.
-
Climate Change: The changing climate has far-reaching consequences for all species, including doves. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can disrupt dove habitats and food availability. Doves are also sensitive to temperature changes during their breeding season, and even slight shifts can impact their reproductive success. As climate change continues to unfold, doves face an uncertain future.
-
Hunting: While hunting regulations exist in many regions to protect dove populations, illegal hunting remains a significant threat. Doves are often hunted for sport or for their meat, leading to unsustainable levels of harvesting. The loss of adult doves from hunting can disrupt breeding dynamics and further contribute to population decline.
It is crucial to address these threats and take action to conserve dove populations. Efforts such as habitat preservation, conservation education, and the enforcement of bird protection laws are essential steps in safeguarding these beautiful birds. Additionally, supporting organizations dedicated to avian biodiversity and engaging in responsible birdwatching practices can contribute to the preservation of dove populations.
In conclusion, while the mourning dove is not currently extinct, the global picture for dove species is concerning. The impact of human activities, including habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and hunting, poses significant risks to dove populations. It is imperative that we recognize the importance of these birds and take steps to protect their habitats and ensure their survival for future generations to enjoy.
Why is the Mourning Dove Going Extinct?
The Mourning Dove, a beloved bird species known for its gentle cooing and graceful flight, is facing the threat of extinction. Several factors contribute to the decline in the Mourning Dove population, including threats to their habitats, the impact of climate change, and the encroachment of urbanization on their natural habitats.
A. Threats to the Mourning Dove Population
The Mourning Dove population faces various threats that put their survival at risk. One significant threat is the loss and degradation of their habitats. As human activities continue to encroach upon natural areas, the Mourning Dove’s nesting and foraging grounds are being destroyed. Deforestation, agriculture expansion, and urban development all contribute to the loss of suitable habitats for these birds.
Another threat to the Mourning Dove population is the increase in predation. As their habitats shrink, Mourning Doves become more vulnerable to predators such as cats, snakes, and birds of prey. These predators take advantage of the reduced cover and increased exposure of the doves, leading to a decline in their numbers.
Additionally, the Mourning Dove faces threats from hunting and trapping. While regulated hunting is allowed in some regions, illegal hunting and trapping pose a significant risk to the population. Unregulated hunting can lead to overharvesting, disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem and further endangering the species.
B. The Role of Climate Change in Dove Extinction
Climate change is another factor contributing to the decline of the Mourning Dove population. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns affect the availability of food and water sources for these birds. As the climate becomes more unpredictable, the timing of plant growth and insect emergence, crucial food sources for Mourning Doves, may no longer align with their breeding and migration patterns.
Extreme weather events, such as droughts and storms, also pose a threat to the Mourning Dove population. Droughts can lead to a scarcity of water, making it difficult for doves to find suitable drinking and bathing spots. Storms, on the other hand, can destroy nesting sites and displace the birds, disrupting their breeding cycles and overall population stability.
C. The Impact of Urbanization on Mourning Dove Habitats
Urbanization plays a significant role in the decline of the Mourning Dove population. As cities expand and suburbs sprawl, natural habitats are replaced with concrete jungles. The loss of open spaces, woodlands, and grasslands deprives Mourning Doves of their preferred habitats.
Furthermore, the increase in artificial structures, such as buildings and roads, creates barriers that impede the movement and dispersal of Mourning Doves. These birds rely on open areas for foraging and nesting, and the lack of suitable habitat within urban environments limits their ability to thrive.
In conclusion, the Mourning Dove population is facing numerous challenges that threaten their survival. Loss of habitat, predation, hunting, climate change, and urbanization all contribute to the decline in their numbers. Efforts must be made to protect and preserve their habitats, regulate hunting practices, and mitigate the effects of climate change to ensure the long-term survival of this iconic bird species. By understanding the threats they face and taking action to address them, we can help protect the Mourning Dove and maintain the biodiversity of our avian populations.
The Mourning Dove in 2023: A Projection
A. Predicted Trends for Mourning Dove Populations
The mourning dove, known for its gentle cooing and graceful flight, has long been a familiar sight in North America. However, concerns have been raised about the declining population of this beloved bird species. As we look ahead to 2023, it is important to understand the predicted trends for mourning dove populations and what can be done to ensure their survival.
1. Declining Numbers
Over the past few decades, there has been a noticeable decline in mourning dove populations. This decline can be attributed to various factors, including habitat loss, climate change, and increased predation. As human activities continue to encroach upon their natural habitats, mourning doves are finding it increasingly challenging to find suitable nesting sites and sources of food.
2. Conservation Efforts
To combat the decline in mourning dove populations, conservation efforts have been put in place. These efforts aim to protect and restore the habitats that are crucial for the survival of these birds. Conservation organizations, such as the Audubon Society and the National Wildlife Federation, have been working tirelessly to raise awareness about the plight of mourning doves and implement measures to safeguard their future.
B. Conservation Efforts for the Future
While the decline in mourning dove populations is concerning, there is hope for their future. Conservation efforts play a vital role in ensuring the survival of these beautiful birds.
1. Habitat Preservation
One of the key strategies in conserving mourning doves is habitat preservation. By protecting and restoring their natural habitats, we can provide them with the necessary resources to thrive. This includes preserving open grasslands, agricultural fields, and woodlands, which are essential for nesting, feeding, and roosting.
2. Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the importance of mourning doves and their conservation is crucial. By educating people about the threats facing these birds and the actions they can take to help, we can foster a sense of responsibility and encourage individuals to make a positive impact. Birdwatching clubs, nature centers, and educational programs can all play a role in spreading awareness and engaging the public in conservation efforts.
3. Collaboration and Research
Collaboration between researchers, conservation organizations, and government agencies is essential for effective conservation of mourning doves. By conducting scientific studies and monitoring populations, we can gain a better understanding of their behavior, distribution, and habitat requirements. This knowledge can then be used to inform conservation strategies and policies.
4. Bird Protection Laws
Implementing and enforcing bird protection laws is another crucial aspect of conservation. These laws help regulate activities that may harm or disturb mourning doves, such as habitat destruction, hunting, and the use of pesticides. By ensuring legal protection for these birds, we can create a safer environment for their survival.
In conclusion, while the mourning dove population has been declining, there is still hope for their future. By implementing conservation efforts focused on habitat preservation, public awareness and education, collaboration and research, and bird protection laws, we can work towards ensuring the survival of this iconic bird species. It is up to us to take action and protect the mourning doves for generations to come.
The Importance of Dove Conservation

A. The Ecological Importance of Doves
Doves play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems. These gentle birds contribute to the pollination of plants and the dispersal of seeds, making them essential for the growth and survival of various plant species. As they forage for food, doves inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another, aiding in the fertilization process. This process is vital for the reproduction of flowering plants, ensuring the continuation of diverse plant communities.
Furthermore, doves help in the dispersal of seeds. As they consume fruits and berries, they swallow the seeds, which then pass through their digestive system unharmed. When the doves excrete these seeds in different locations, they effectively contribute to the dispersal and germination of plants, enhancing biodiversity and promoting the growth of new vegetation.
B. How Individuals Can Contribute to Dove Conservation
Conservation efforts are not limited to experts and organizations alone; individuals can also make a significant impact in preserving dove populations. Here are a few ways you can contribute to dove conservation:
-
Create Dove-Friendly Habitats: You can create a welcoming environment for doves in your own backyard or garden by providing them with suitable nesting sites, such as birdhouses or platforms. Additionally, planting native trees and shrubs that produce fruits and seeds can attract doves and provide them with a reliable food source.
-
Avoid Pesticide Use: Pesticides can have detrimental effects on doves and other wildlife. Opt for natural pest control methods or seek alternatives that are less harmful to the environment. By reducing pesticide use, you can help maintain a healthy ecosystem for doves and other bird species.
-
Support Bird Conservation Organizations: Many organizations dedicated to bird conservation work tirelessly to protect endangered species like the mourning dove. Consider supporting these organizations through donations or volunteering your time to contribute to their efforts in preserving dove populations.
-
Promote Awareness: Spread the word about the importance of dove conservation to your friends, family, and community. Educate others about the ecological role of doves and the threats they face. By raising awareness, you can inspire others to take action and make a difference in preserving these beautiful birds.
In conclusion, the conservation of doves is crucial for maintaining avian biodiversity and the overall health of our ecosystems. By understanding the ecological importance of doves and taking individual actions to support their conservation, we can contribute to the survival and well-being of these remarkable birds. Let us all play our part in ensuring a future where doves continue to grace our skies with their gentle presence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mourning dove is not extinct. Despite facing various threats and challenges, this beautiful bird continues to thrive in many parts of North America. Its adaptability, widespread distribution, and ability to reproduce quickly have helped it maintain stable populations. However, it is important to remain vigilant and take measures to protect the mourning dove and its habitat. Conservation efforts, such as preserving nesting sites, reducing pesticide use, and promoting sustainable land management practices, are crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of this iconic bird species. By appreciating and safeguarding the mourning dove, we can contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the natural beauty of our environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is the mourning dove going extinct?
The mourning dove is not currently going extinct. However, like many bird species, it faces threats such as habitat loss, predation, and climate change. It’s crucial to continue wildlife preservation efforts to maintain avian biodiversity and protect the mourning dove population.
2. Are doves extinct?
No, doves as a whole are not extinct. There are many species of doves, including the mourning dove, which are still thriving. However, certain species may be at risk due to factors like habitat loss and climate change.
3. Is the mourning dove extinct?
No, the mourning dove is not extinct. It is a common bird species in North America and its population is currently stable, although it faces threats common to many bird species.
4. Are doves going extinct?
While some specific species of doves may be at risk of extinction, doves as a group are not going extinct. The conservation status of each species varies, and efforts are ongoing to protect threatened bird species.
5. Is the mourning dove extinct in 2023?
As an AI, I cannot predict future events. As of the latest data, the mourning dove is not extinct and its population is stable. However, ongoing conservation efforts are necessary to ensure its survival.
6. What is the current status of the Mourning dove population?
The mourning dove population is currently stable. However, like many bird species, it faces threats such as habitat loss, predation, and climate change. Birdwatchers and ornithologists continue to monitor their numbers to ensure their survival.
7. How does the Mourning dove habitat affect its survival?
The mourning dove habitat, which typically includes open and semi-open environments, plays a crucial role in its survival. Changes in land use, deforestation, and urban development can lead to habitat loss, posing a threat to the mourning dove population.
8. What are the characteristics of the Mourning dove?
The mourning dove is a small, slender dove with a long, pointed tail. It is light gray-brown in color with slightly pinkish hue on the chest. It’s known for its soft, mournful cooing, hence its name.
9. What is the distribution of the Mourning dove?
The mourning dove is widely distributed across North America. It can be found from southern Canada to Central America. This bird species is common in both rural and urban settings.
10. How can we contribute to the preservation of endangered birds like the Mourning dove?
Individuals can contribute to the preservation of endangered birds by supporting wildlife preservation efforts, respecting bird protection laws, and participating in birdwatching citizen science projects to help monitor bird populations. Habitat conservation and promoting biodiversity in our own backyards can also make a significant difference.