Porpoises are cetaceans – a diverse group of mammals. They look and act like dolphins, but have unique features. They can use echolocation to find objects and detect danger or prey. Porpoises have a streamlined shape, strong muscles and fins. That helps them move quickly and conserve energy.
Now, here’s a wild story about Dolly. She was stranded on a beach in a storm. But luckily, compassionate people saved her. They nursed her back to health and released her into the wild. Dolly’s story shows the resilience of porpoises, and our capacity for empathy and conservation.
Key Takeaways
- A porpoise is a type of mammal that belongs to the same family as dolphins and whales.
- Porpoises are known for their small size, typically ranging from 4 to 6 feet in length.
- They have a streamlined body shape, a rounded head, and a small mouth with sharp teeth.
- Porpoises are highly intelligent creatures and are known for their playful behavior.
- They are found in oceans and seas around the world, preferring coastal areas and shallow waters.
- Porpoises primarily feed on fish and squid, using echolocation to locate their prey.
- Unlike dolphins, porpoises are generally more shy and less social, often found in small groups or alone.
- There are several different species of porpoises, including the harbor porpoise and the Dall’s porpoise.
- Porpoises face various threats, including pollution, habitat loss, and accidental entanglement in fishing gear.
- Conservation efforts are being made to protect porpoises and their habitats to ensure their survival.
Definition of a Porpoise Mammal
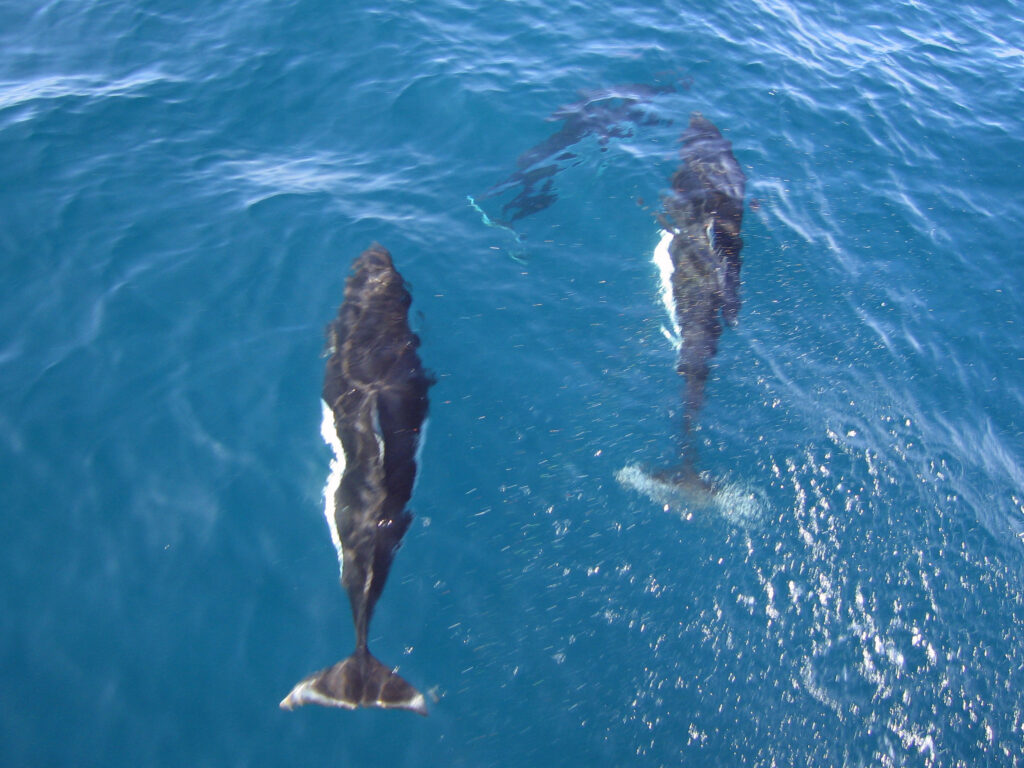

Porpoises – these fascinating creatures who belong to the cetacean family, which includes dolphins and whales – are known for their agility, intelligence, and sociability. With their sleek bodies and streamlined shape, they are built for speed and maneuverability in the water.
One of their distinctive features is their small mouths with sharp teeth, which helps them catch and consume their prey. Unlike dolphins, porpoises have spade-shaped teeth instead of conical ones.
They also have a triangular dorsal fin on their back, which helps stabilize them in the water. Generally, they are smaller compared to dolphins, measuring around 4-6 feet in length.
Porpoises tend to be more reserved than dolphins. They usually live in small groups called pods, and communicate using clicks, whistles, and other vocalizations. They use echolocation to navigate and locate prey.
Do not miss out! Explore further into porpoises’ underwater realm and discover the wonders of nature. Their sleek and sexy figure is sure to awe you!
Physical Characteristics of Porpoises
Porpoises are small cetacean mammals that belong to the Phocoenidae family. They have a streamlined body and a triangular dorsal fin. Porpoises are usually dark gray or black on top, fading to white or lighter shades on their bellies. This helps them camouflage from predators.
Their teeth are unique too. They are spade-shaped without notches or cusps, perfect for catching slippery prey. On top of their heads they have a blowhole. This helps them breathe without fully exposing their bodies.
Lastly, a thick layer of blubber under their skin provides insulation and reduces drag. It also enables them to throw the best underwater house parties!
Habitat and Distribution
Porpoises are small, marine mammals that inhabit different parts of the world. They are intelligent creatures that have adapted to various habitats, such as shallow coastal waters and deep offshore regions. You can find them in the Northern Hemisphere’s temperate and cold seas like the North Atlantic Ocean and Arctic seas. Plus, some species have even spread to the Southern Hemisphere, near Antarctica.
The habitat preferences of porpoises depend on the species. For example, the harbor porpoise likes shallow coastal waters with sandy or muddy bottoms. Others, like the Dall’s porpoise, prefer deeper offshore waters and even sometimes venture out to open ocean areas.
These sociable animals often swim in groups called “pods”. The composition and size of these pods is affected by things like food availability and reproduction cycles. If you want to study or observe porpoises in their natural environment, try Scotland’s coast, Canada’s Bay of Fundy, or California’s Monterey Bay. As picky eaters, porpoises make Gordon Ramsay look like a lenient chef!
Diet and Feeding Habits
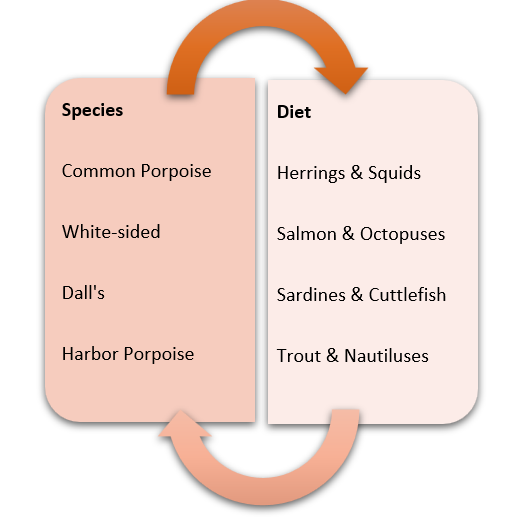
Carnivorous porpoises feed on small fish, such as herrings and sardines, as well as cephalopods like squids and octopuses. Let’s take a look at the diet of different species in a table:
These sea mammals also possess unique hunting tactics. Some species use echolocation to detect their prey, emitting clicks that bounce off anything nearby. When hunting, porpoises travel in small groups called pods that coordinate their attacks on schools of fish.
Humans have always been fascinated by these creatures due to their intelligence and sociability. Ancient civilizations even had stories of dolphins, relatives of porpoises, aiding sailors in danger. Porpoises continue to have a special status among seafaring societies. They may not have Facebook, but they know how to school!
Behavior and Social Structure
Porpoises are highly intelligent and social creatures. They display complex behaviors, living in pods of family members or individuals with similar characteristics. Porpoising around, they exhibit playful behavior like jumping out of the water and riding waves. Plus, their curious nature often leads them to approach boats and swimmers.
Echolocation helps them to find food and navigate their environment. Within the pod, they establish hierarchies based on age, size, or dominance. Their interactions are essential for learning from one another. Remarkably, they have been known to display altruistic behavior towards injured or sick individuals.
A study by Marine Mammal Science Society discovered that porpoise communication involves vocalizations and synchronized swimming patterns. This helps them coordinate group activities while sustaining a cohesive social structure.
Reproduction and Lifecycle is where love and biology come together to create the next generation of porpoises.
Reproduction and Lifecycle
Porpoises have a unique lifecycle and reproductive process. It’s essential to understand them to appreciate the animals and their role in the environment.
- Gestation: 10-11 months – like other cetaceans.
- Birth: Calves come out 3 feet long, and need milk and guidance.
- Lifespan: 20-30 years, or even 40.
- Reproduction: Males compete for mating.
- Parental Care: Females give milk full of nutrients.
- Social Structure: Form small pods for migration and feeding.
Unique Details:
- Males use vocalizations to attract females, which can differ between species and even individuals.
- Females display preferences when picking mates.
Tip:
Keep distance from porpoises in their habitats. This helps preserve their life cycle and the marine ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Threats
The conservation status of porpoise mammals and the threats they face are key to preserving their future.
- Vulnerable, endangered, or critically endangered classification depends on the species.
- Habitat loss from human activities, such as coastal development and pollution, is a major danger.
- Entanglement in fishing gear can lead to drowning.
- Noise pollution from maritime activities can disrupt communication and behavior.
- Climate change can alter habitats and affect prey availability.
Regulations and strategies exist to protect them, yet global efforts are needed to face the threats. The Vaquita porpoise, ‘panda of the sea,’ is the most endangered. Only 10 remain in Mexico’s Gulf of California. Porpoise puns are now at your service!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a porpoise mammal?
A: A porpoise is a type of marine mammal that belongs to the family Phocoenidae. They are closely related to dolphins but are smaller in size and have a distinct body shape.
Q: How do porpoises differ from dolphins?
A: Porpoises and dolphins differ in several ways. Porpoises have shorter snouts, spade-shaped teeth, and a more robust body compared to dolphins. They also tend to have a less playful behavior and are less acrobatic than dolphins.
Q: What do porpoises eat?
A: Porpoises are carnivorous and primarily feed on small fish and squid. They use echolocation to locate their prey and consume a significant amount of food to sustain their energy needs.
Q: Where do porpoises live?
A: Porpoises can be found in oceans and seas around the world, preferring temperate and colder waters. They are highly adaptable and can live in both coastal and offshore environments.
Q: Are porpoises endangered?
A: Some species of porpoises are endangered due to various threats such as habitat degradation, pollution, fishing nets, and noise pollution. It is essential to protect their habitats and implement conservation measures to ensure their survival.
Q: Can porpoises communicate with each other?
A: Yes, porpoises are highly social animals and communicate with each other using a combination of clicks, whistles, and body language. They have a complex vocal repertoire that helps them coordinate group activities and establish social bonds.
Conclusion
Our journey into the realm of porpoises has come to an end. These interesting creatures are an important part of our seas. A few of their features and behaviours make them a subject of curiosity. Their sleek bodies and intelligence fascinate researchers for years.
One unique trait is their communication. They make clicks and whistles to talk. This is essential for their social life and to find their way. Scientists are still discovering how these complex signals work. But, they are important for them to survive.
They eat mostly fish and squid. It seems they pick certain species depending on where they are. This shows their resourcefulness in different conditions.
References




