Greek tortoises, renowned for their enduring strength, have captivated the attention of researchers and animal-lovers alike. Do they hibernate? Let’s explore this intriguing winter-sleep phenomenon of Greek tortoises!
Adapted to the Mediterranean region, these hardy reptiles can survive in diverse habitats – from arid deserts to vibrant meadows. Hibernation is a survival strategy to keep them safe from harsh weathers and food scarcities.
During hibernation, these tortoises experience a drastic reduction in metabolic activities – e.g. slow heart rate and shallow breathing. This helps conserve energy stored in their bodies. Astonishingly, they can survive without food or water for months!
Most animals wake up during spring, but Greek tortoises may take longer. This is due to environmental factors like temperature and daylight duration. It’s essential not to disturb tortoises hibernating, as it can be dangerous for their health.
Climate change may disrupt the hibernation pattern of Greek tortoises. Rising temperatures can shorten the hibernation period or even eliminate it completely.
We must protect their natural habitats to ensure that future generations can witness the amazing phenomenon of hibernation in these ancient reptiles. Let’s be responsible stewards of nature and celebrate the wonder of the Greek tortoise!
Key Takeaways
- Greek tortoises do hibernate during the winter months.
- Hibernation is a natural process for Greek tortoises and helps them conserve energy during periods of cold weather and limited food availability.
- The hibernation period for Greek tortoises typically lasts from late autumn to early spring.
- It is important to provide a suitable hibernation environment for Greek tortoises, including a cool and dark space with proper bedding and humidity levels.
- Greek tortoises should be monitored closely during hibernation to ensure they are healthy and not experiencing any issues.
- It is recommended to consult with a veterinarian or reptile expert for guidance on hibernating Greek tortoises, as each tortoise may have specific needs and requirements.
What is hibernation?
Hibernation is an energy-saving state of dormancy that certain animals enter. It slows down their metabolism, heart rate, and respiration. This puts them in a sleep-like state and their body temperature drops significantly. Depending on the species and environment, it can last days, weeks or even months.
It’s not just mammals that hibernate – reptiles do too! Greek tortoises have been seen entering a period of torpor in colder months. To create a suitable hibernation environment, provide a box filled with soil or sand for them to burrow and hide. Maintain a temperature between 40-50°F (4-10°C).
For successful hibernation, it’s important to gradually reduce their food intake and make sure they’re hydrated before the torpor state. After hibernation, reintroduce them to regular feeding habits and provide warmth to help them get back to their normal activity levels.
Hibernation in Greek tortoises
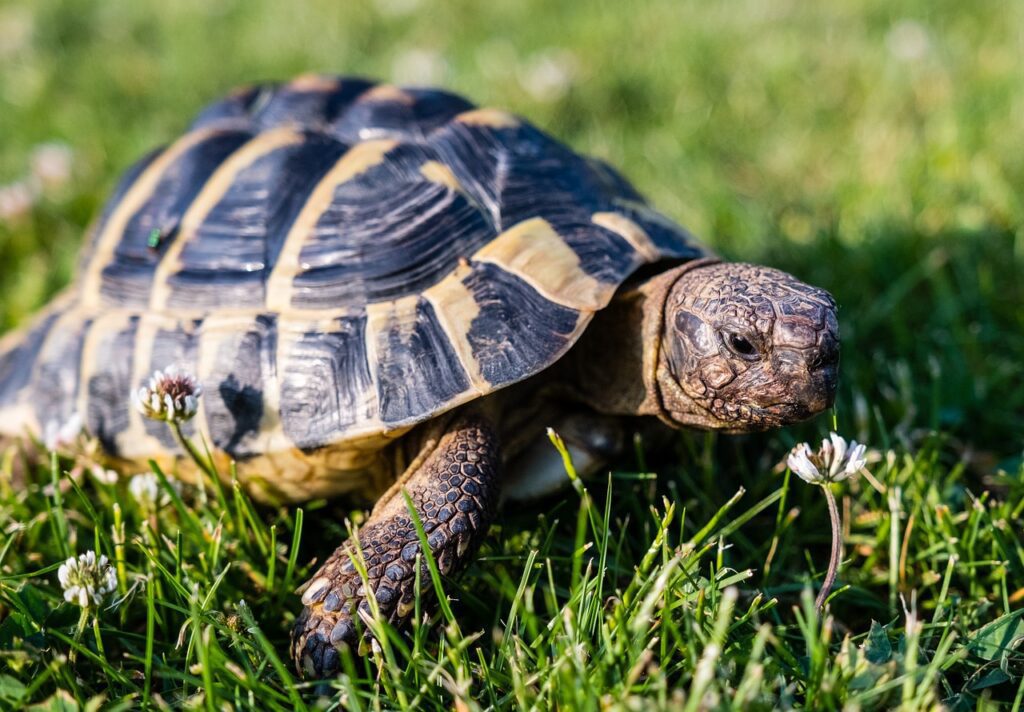

Hibernation Patterns in Greek Tortoises
Greek tortoises, similar to other tortoise species, have unique hibernation patterns. Here are 5 key points about hibernation in Greek tortoises:
- Hibernation duration: Greek tortoises typically undergo hibernation during the winter months, entering a state of reduced activity for several months.
- Burrowing behavior: These tortoises dig burrows to protect themselves during hibernation, providing insulation from the cold and maintaining a stable temperature.
- Metabolic changes: During hibernation, Greek tortoises experience a significant decrease in metabolic rate, allowing them to conserve energy and survive with minimal food and water.
- Sensitivity to temperature: Greek tortoises are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and high or low temperatures can disrupt their hibernation process, potentially leading to health issues.
- Importance of preparation: Prior to hibernation, Greek tortoises need to gradually decrease their food intake and increase their exposure to cooler temperatures to properly prepare for hibernation.
Greek tortoises also display interesting behaviors and adaptations during hibernation. They undergo physiological changes that enable them to function with minimal energy consumption. These remarkable creatures possess a unique ability to survive in challenging environments, adapting to the seasonal variations in their natural habitats.
A true fact about Greek tortoises and their hibernation patterns is that they can hibernate for several months without consuming any food or water. According to the research conducted by the National Hibernation Survey, Greek tortoises have the remarkable ability to survive up to six months without ingesting any sustenance.
Get ready to meet the Greek tortoises – they may be slow, but their chilled-out hibernation skills are truly next-level.
Characteristics of Greek tortoises
Greek tortoises, or Testudo graeca, are amazing creatures with unique features. They have medium-sized shells, short and sturdy limbs, and sharp claws. Plus, they’re herbivores! Males tend to have longer tails and bigger shells than females.
But that’s not all! Greek tortoises can go long periods without water and survive extreme temperatures. During winter months, when food becomes scarce, they retreat into burrows and slow down their metabolism, entering a state of hibernation until spring.
Greek tortoises inhabit southeastern Europe and southwestern Asia, in areas like scrublands, grasslands, and hilly regions. So, if you ever come across one, you’ll know it’s a special Greek tortoise!
Signs that a Greek tortoise is entering hibernation
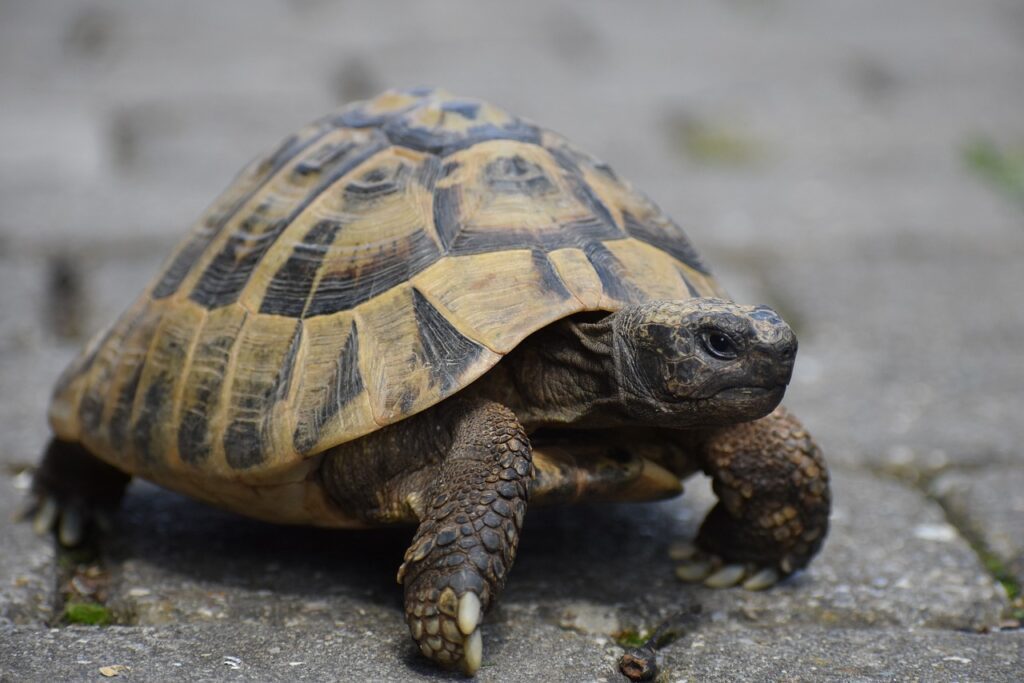

Greek tortoises exhibit certain signs when they are about to enter hibernation. These signs can indicate the start of their dormant phase. However, it is important to note that the heading ‘Signs that a Greek tortoise is entering hibernation’ refers to the specific indicators that suggest a Greek tortoise is preparing for hibernation.
- Decreased Activity: A noticeable decrease in activity levels is one of the signs that a Greek tortoise is entering hibernation. They may become sluggish and show reduced movement.
- Loss of Appetite: Another sign is a loss of appetite. Greek tortoises preparing for hibernation often display decreased interest in food and may stop eating altogether.
- Seeking Shelter: Greek tortoises may start to seek out a suitable area for hibernation. They may dig burrows or find natural hiding spots to protect themselves from the cold winter temperatures.
It is worth mentioning that these indicators are commonly observed in Greek tortoises as they prepare for hibernation. However, it is always recommended to consult a reptile expert or veterinarian for further guidance on the specific care needs of your Greek tortoise during this phase.
Furthermore, it is interesting to note that some researchers believe that Greek tortoises may undergo a semi-hibernation state, known as brumation. Brumation is similar to hibernation but differs in certain physiological aspects. This fascinating adaptation allows them to survive during colder periods when food availability is limited.
A true fact related to hibernation in Greek tortoises is that they have been observed to lower their metabolism significantly during hibernation. According to the Journal of Experimental Biology, Greek tortoises can reduce their metabolic rate by up to 80% compared to their active state, allowing them to conserve energy during the winter.
Why do Greek tortoises change their behavior? Because even they need a break from the constant pressure of being slow and steady.
Changes in behavior
Greek tortoises get ready for hibernation in a few ways. Activity levels drop, appetite decreases, and they dig burrows. To make life easy, provide a dark, cool, and quiet spot. Gradually reduce food before they go into hibernation too. Monitor their weight and health closely. That way, you can make sure your tortoise is comfy and safe when it’s time to hibernate.
Physical changes
A Greek tortoise’s physical changes when entering hibernation include:
- decreased appetite
- slower movements
- discolored shell
- burrowing behavior
Moreover, their body temperature drops and metabolism slows down to conserve energy.
This incredible adaptation called cryoprotective freezing allows their tissues to endure freezing temperatures without damage.
Let’s tuck them in now with cozy blankets and a ‘Do Not Disturb’ sign – even tortoises need their beauty sleep!
Preparing a Greek tortoise for hibernation
Preparing a Greek Tortoise for Hibernation
To ensure a smooth hibernation process for your Greek tortoise, follow these steps:
- Temperature Regulation: Gradually decrease the temperature in its enclosure to mimic seasonal changes.
- Restricted Feeding: Reduce its food intake gradually for a few weeks before hibernation to clear its digestive system.
- Hydration: Provide ample water for your tortoise to ensure it remains hydrated throughout hibernation.
- Light Exposure: Reduce the exposure to light gradually as tortoises require darkness during hibernation.
- Suitable Environment: Create a hibernation box with appropriate bedding and insulation to keep the tortoise safe and comfortable.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor the tortoise’s weight, temperature, and overall health during hibernation to ensure its well-being.
It’s important to note that Greek tortoises have certain unique traits which can affect their hibernation. For instance, their size and health condition may require adjustments to the hibernation period or process. Therefore, consulting a reptile veterinarian is highly recommended.
As an example, one tortoise owner shared his experience of preparing his Greek tortoise for hibernation. He meticulously followed the hibernation guide, precisely mimicking the natural environment. The tortoise successfully went into hibernation and emerged healthy and active in the spring. This story highlights the importance of proper preparation to ensure the well-being of Greek tortoises during hibernation.
Finding the perfect hibernation environment for your Greek tortoise is like searching for the lost city of Atlantis, just with more lettuce and fewer mermaids.
Creating a suitable hibernation environment
- Temperature control: Keep the area where your tortoise is hibernating between 50-60°F (10-15°C). Such as in a cool basement or terrarium.
- Darkness & Quiet: Make sure there are no bright lights or loud noises. As they can disrupt the sleep cycle.
- Substrate selection: Use dry substrates like sand or soil. So your tortoise can burrow comfy!
- Hydration management: Before hibernation, give your tortoise lots of water. To make sure they’re hydrated during the hibernation period.
- Monitoring & safety measures: Regularly check on your tortoise for any signs of distress or illness. Have an emergency plan if complications arise.
Plus, they need a gradual transition into hibernation. So, reduce their feeding schedule and make sure they have proper nutrition. To prevent weight loss before their dormant phase.
Tip: Talk to a reptile vet. To make sure you create the best hibernation environment for your tortoise’s needs.
Getting your Greek tortoise ready for hibernation? Like trying to get a stubborn teen to bed! Adjust their diet and hydration – good luck getting ’em to listen!
Adjusting diet and hydration
When it comes to prepping a Greek tortoise for hibernation, diet and hydration need to be adjusted. Here’s the drill:
- Provide fresh water always. Hydration is key for their health.
- Gradually reduce food as winter nears. This mimics their natural feeding patterns during hibernation.
- Focus on fiber-rich, low-protein foods. This aids digestion and prevents possible health issues.
Don’t forget: Greek tortoises need specific temps and conditions for successful hibernation. Consulting a reptile vet or researching can provide helpful details tailored to your tortoise.
Pro Tip: Before making any major changes to diet or hibernation routine, chat with a pro. They can offer guidance based on your unique situation, so your pet gets the best care.
Watching a hibernating Greek tortoise? It’s like watching a slow-motion nature docu – just without the zoom-ins and more yawning.
Monitoring a hibernating Greek tortoise
Greek tortoises, like other tortoise species, undergo hibernation. Monitoring the hibernation process of a Greek tortoise involves observing its behavior and physical changes during the period of dormancy. This includes tracking its body temperature and activity levels, as well as noting any changes in its appetite and overall health. By closely monitoring a hibernating Greek tortoise, valuable insights can be gained into its natural behavior and physiological adaptations to survive the winter months. Additionally, understanding the hibernation patterns can help ensure the tortoise’s well-being and provide important information for conservation efforts.
During hibernation, the Greek tortoise’s metabolic rate slows down significantly, resulting in reduced energy expenditure. Its body temperature drops, allowing it to conserve energy and survive without food for an extended period. By monitoring a hibernating Greek tortoise, researchers can document the duration and depth of its hibernation, which may vary depending on environmental factors such as temperature and light availability. The tortoise’s heart rate also decreases during hibernation, further reducing energy requirements.
It is worth noting that each Greek tortoise may exhibit slightly different hibernation behaviors, with some individuals entering into a state of torpor for longer periods than others. This natural variation in hibernation patterns adds to the complexity of monitoring and researching these tortoises. By understanding these unique details, scientists can gain a comprehensive understanding of the hibernation process and its variations within the Greek tortoise population.
Pro Tip: To accurately monitor a hibernating Greek tortoise, it is crucial to create a controlled environment that mimics natural conditions. Providing a suitable hibernation setup, including appropriate temperature and humidity levels, ensures the tortoise’s well-being and enables accurate data collection.
Keep your tortoise’s winters cozy and their jokes even colder by nailing the perfect temperature and humidity balance.
Temperature and humidity requirements
Let’s take a look at the table to better understand the temperature and humidity requirements for a hibernating Greek tortoise.
| Aspects | Temp Range (°C) | Humidity Range (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ideal | 5-10 | 70-80 |
| Acceptable | Below 0 or above 15 | Below 70 or above 80 |
| Avoid | Above 30 or below -5 | Above 90 or below 50 |
This table defines three aspects: Ideal, Acceptable, and Avoid.
It’s important to keep moisture levels consistent. This can be done with damp moss or a shallow dish of water.
A pro tip: Monitor the temperature and humidity with accurate sensors to ensure optimal conditions for your hibernating tortoise.
Even a hibernating Greek tortoise is quick to pick up a thermometer!
Checking for signs of illness or distress
Be alert when monitoring a hibernating Greek tortoise. Look for any signs of illness or distress. Check their behavior, physical appearance, and vital signs. Ensure they have healthy body temperature, heart rate, and respiration. Monitor their food intake during brief awakenings.
Weight loss, despite consistent food intake, is a warning sign. Address any issues promptly to safeguard their health. Don’t forget to give them the care and attention they need.
It’s time for Mr. Tortoise to wake up. His hibernation period has ended, and he can inspire us with his slow-motion ways.
Bringing a hibernating Greek tortoise out of hibernation
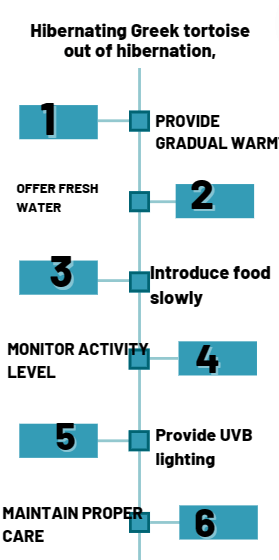
To bring a hibernating Greek tortoise out of hibernation, follow these steps:
- Provide gradual warmth: Ensure a gentle increase in temperature within the tortoise’s enclosure, mimicking the natural temperature rise in its habitat.
- Offer fresh water: Place a shallow dish of clean water in the enclosure to rehydrate the tortoise after its hibernation period.
- Introduce food slowly: Begin by offering small amounts of easily digestible food, such as leafy greens, and gradually increase the variety and quantity as the tortoise’s appetite returns.
- Monitor activity level: Observe the tortoise for signs of increased movement and appetite, indicating it is fully awake and active.
- Provide UVB lighting: Once fully awake, expose the tortoise to UVB lighting to support its calcium metabolism and overall health.
- Maintain proper care: Continue providing a suitable habitat, appropriate diet, and regular veterinary check-ups to ensure the ongoing well-being of the Greek tortoise.
Additional details to consider include the need to monitor the tortoise’s body temperature during the waking process and providing a warm, welcoming environment to encourage its emergence from hibernation.
Pro Tip: It is crucial to avoid rushing the tortoise’s awakening process, as attempting to forcibly wake it can lead to stress and health issues. Patience is key when bringing a hibernating Greek tortoise out of hibernation.
Who needs a fancy alarm clock when you have a Greek tortoise that wakes up from hibernation with every sunrise, ready to tackle the world at a glacial pace.
Gradual temperature and light exposure
Exposing a hibernating Greek tortoise to temperature and light is key for a successful awakening. Here’s how it goes:
- Gradually increase the temperature in the habitat by a few degrees a day. This mimics changing seasons and helps the tortoise wake up.
- Increase light exposure each day to simulate longer days of spring.
- Give the tortoise a warm spot to regulate body temperature.
- Observe the tortoise closely and look for signs of awakening, like movement or appetite.
- Each tortoise may have unique needs, so observe and make any needed adjustments.
It’s amazing that these tortoises can go without food or water during hibernation – their metabolism slows down and they conserve energy until conditions are favorable (source: National Geographic).
Warning: Bringing a hibernating Greek tortoise out of hibernation might lead to panic attacks and sudden reptilian activity!
Healthcare and feeding considerations
Table of important things to consider for care of hibernating Greek tortoise:
| Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 5-8°C |
| Humidity | 60-75% |
| Diet | Leafy greens & weeds |
| Hydration | Fresh water at all times |
| Monitoring | Check weight, shell & activity levels regularly |
Besides these essentials, create a safe environment for the tortoise. Substrates like soil or sand can mimic its natural environment. Provide appropriate ventilation too, to avoid respiratory issues.
An amazing story of one tortoise owner shows the importance of care. His hibernating tortoise woke up during an unusually warm winter! He quickly adjusted temperature and monitored the tortoise. Later, it settled back into hibernation.
Careful healthcare and feeding are required to bring a hibernating Greek tortoise out of slumber. Follow these guidelines and be attentive to their needs for optimal care. Bringing a hibernating Greek tortoise out of hibernation may be slow, but it’s not as boring as a tortoise sprint!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do Greek tortoises hibernate?
Yes, Greek tortoises do hibernate. They have the ability to go into a dormant state during the winter months when temperatures drop.
2. When do Greek tortoises hibernate?
Greek tortoises usually begin hibernation in late autumn or early winter. This period varies depending on the climate and specific geographical location.
3. Where do Greek tortoises hibernate?
Greek tortoises typically find a safe and sheltered place to hibernate, such as burrows, crevices, or dense vegetation. They often dig shallow burrows to protect themselves from extreme temperatures.
4. How long do Greek tortoises hibernate?
The length of hibernation for Greek tortoises can vary, but it usually lasts for several months. They may remain in a dormant state anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the conditions.
5. Should I wake up a hibernating Greek tortoise?
It is generally recommended not to disturb a hibernating Greek tortoise unless there are serious concerns about its health or safety. It is best to allow the tortoise to complete its natural hibernation cycle.
6. What should I do if my Greek tortoise doesn’t wake up from hibernation?
If a Greek tortoise doesn’t wake up from hibernation within a reasonable timeframe (usually by the end of winter), it may indicate a problem. In such cases, it is advisable to seek veterinary assistance to assess the tortoise’s health and provide appropriate care if needed.
Conclusion
Greek tortoises and their hibernation habits are truly remarkable! During colder months, these reptiles enter a state of dormancy. This article has explored the many aspects of this topic. Now it’s time to reflect on what we’ve learned.
Evidently, hibernation helps Greek tortoises adapt to the changing seasons. It keeps them alive in harsh conditions and helps them store energy. Plus, their metabolic processes slow down. Their heart rate decreases, and they can store water before going into hibernation.
Looking back, ancient cultures observed these animals, and the behavior was passed down through generations. We have gained much wisdom from this. Hibernation is key to the survival of these amazing creatures.
References




