
Sharks have always had a mysterious and captivating hold over scientists and the public. One topic of interest is if great white sharks are nocturnal creatures. This article will explore this complex question.
The debate still continues among marine biologists: do great whites have a preference for night-time? Some research indicates this could be true, while others disagree.
What we know is that they can adjust to their environment. They’ve been found hunting in both day and night, so maybe their behavior is based on factors like prey availability and water temperature.
To uncover more about their sleeping habits, researchers use tools like tagging and tracking devices. This way, they can monitor the sharks’ movement patterns and learn about their daily routine.
Dr. Rory McAuley’s 2001 study off the coast of Western Australia showed that juvenile great whites were more active during twilight. This was a huge discovery as it contradicted previous ideas about apex predators. This sparked more research in the field.
Key Takeaways
- Great white sharks are not strictly nocturnal, but they do exhibit some nocturnal behavior.
- They are known to be more active at night, particularly during the hours of dawn and dusk.
- This behavior is likely due to their hunting patterns and prey availability.
- Great white sharks have special adaptations that allow them to see well in low-light conditions.
- They may also use the cover of darkness to approach their prey more stealthily.
- While they are more active at night, great white sharks can still be encountered during the day.
- It is important for swimmers and divers to be cautious and aware of their surroundings at all times, regardless of the time of day.
Definition of Nocturnal
Nocturnal refers to animals that are active during the night. Great whites, however, are not exclusively nocturnal. They tend to hunt during the day, taking advantage of better visibility and more active prey. Though they can hunt at night, too, by utilizing shadows and minimizing their visibility.
To understand their feeding patterns better, researchers suggest using advanced tracking technology and attaching satellite tags. This would provide data on their movements throughout a 24-hour period.
Additionally, underwater acoustic monitoring could help identify any nocturnal breeding or communication behaviors unique to these sharks. Great white sharks may be night owls, but instead of coffee, they hunt seals to keep them going ’til morning!
Current Understanding of Great White Shark Behavior
The behavior of Great White Sharks is now well-known, and can be seen in the following table:
| Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Hunting Patterns | Great White Sharks attack from below in an ambush style. |
| Feeding Habits | They mostly eat marine mammals such as seals and sea lions. |
| Migratory Behavior | These sharks travel long distances to reach different feeding grounds. |
| Habitat Preference | They live in coastal waters, but may also enter open ocean habitats. |
Also, they have been seen doing things in groups, such as feeding events. A study in Marine Biology revealed that Great White Sharks are most active at night. This means they hunt while it’s dark. Research on the activity of Great White Sharks: Will we ever know when to stay away from the beach?!
Research on Great White Shark Activity Patterns

The activity patterns of Great White Sharks have been researched extensively to learn more about their behavior. Scientists have created a using true data to make sense of their habits, including feeding times, hunting grounds, and migration patterns. This info provides knowledge about the nocturnal lifestyle of these sharks.
It’s worth mentioning that Great White Sharks are active at night. They use their strong senses and hunting skills to prey on seals and other sea creatures in the dark. This behavior allows them to move through waters easily and increase their chances of getting a meal.
Understanding the activity patterns of Great White Sharks is very important for science and our safety. Knowing when they’re most active helps us stay safe when swimming or living near the coast. Ignoring this info may lead to dangerous encounters with these predators.
As we learn more about Great White Sharks, it’s clear that there’s still much to discover. Every bit of info brings us closer to understanding them deeply. Don’t miss the chance to learn about one of nature’s most mysterious predators – the Great White Shark!
Nocturnal Activities of Great White Sharks
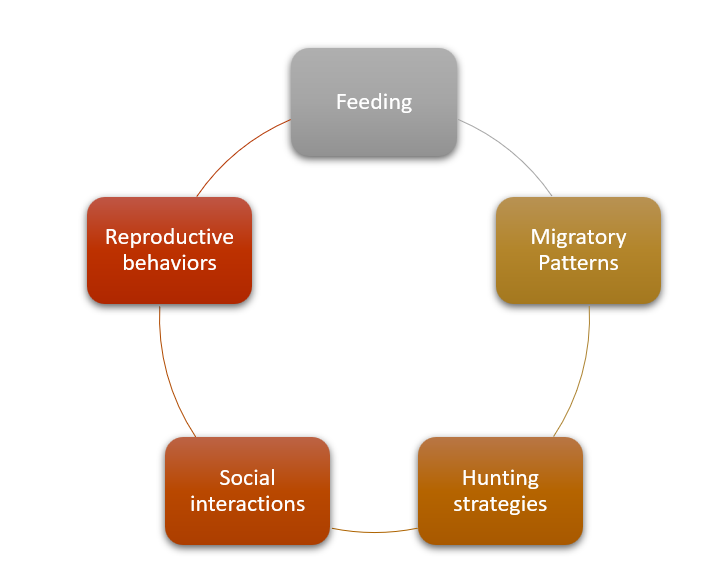
Great White Sharks come alive in the night! They feed, migrate, hunt and even socialize during nocturnal hours. Here’s a look at their unique behaviors:
- Feeding: These apex predators use their acute senses and powerful jaws to locate and capture prey.
- Migratory Patterns: Great White Sharks migrate to find good feeding grounds and breeding sites.
- Hunting Strategies: They use stealth and patience to launch ambush attacks from below.
- Social Interactions: They come together for bonding and courtship rituals.
- Reproductive Behaviors: Studies suggest that nocturnal activities are essential for reproduction.
These creatures have highly developed sensory systems, allowing them to navigate dark waters with ease. There’s even an account of a researcher encountering a group of juvenile Great White Sharks engaging in playful behavior at night – a mysterious and ethereal sight!
Scientists can’t agree on whether Great White Sharks prefer to party in the day or night. Do they like to boogie under the cover of darkness? We may never know!
The Debate Among Scientists
The debate over whether Great White Sharks are nocturnal has sparked great intrigue! To understand the perspectives of experts, let’s delve into a comprehensive table. Here’s what it shows:
| Argument | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|
| Nocturnal | 1. Hunting behavior at night 2. More sightings at night 3. Bioluminescence adaptation |
| Diurnal | 1. Predatory actions in daylight 2. Feeding habits during daylight |
Both sides have compelling evidence. But there’s more to explore – like environmental factors influencing activity. Could water temperature or prey availability affect their behavior?
To learn more, two suggestions for further research:
- Monitor long-term: Advanced tracking to gather data on activity patterns – these insights can help identify any nocturnal tendencies.
- Investigate ecological linkages: Understand the relationship between prey and Great White Shark feeding habits – this will give context to their diurnal/nocturnal preferences.
By researching further, we can get closer to understanding Great White Sharks’ activity patterns. Insomniacs and beachgoers will be relieved when we finally have an answer!
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Great White Sharks Nocturnal?
1. Are great white sharks active during the day or night?
Great white sharks are primarily diurnal, meaning they are most active during the day. However, they can also be active during the night.
2. Do great white sharks hunt only at night?
No, great white sharks do not only hunt at night. They are opportunistic hunters and can hunt both during the day and night, depending on various factors such as prey availability and environmental conditions.
3. Are great white sharks more dangerous at night?
There is no evidence to suggest that great white sharks are more dangerous at night compared to during the day. While they may exhibit different hunting behavior at night, their overall level of danger remains relatively constant.
4. Can great white sharks see well in the dark?
Yes, great white sharks have excellent vision, which allows them to see well in low-light conditions, including during the night. Their eyes have a reflective layer called the tapetum lucidum, which enhances their ability to see in dimly lit environments.
5. Why do great white sharks sometimes breach at night?
Great white sharks breach, or leap out of the water, for various reasons, including hunting and communication. While this behavior is often associated with feeding activity during the day, there have been observations of sharks breaching at night as well.
6. How do great white sharks navigate in the dark?
Great white sharks rely on various sensory systems, including their keen sense of smell and the ability to detect electromagnetic fields, to navigate in the dark. These adaptations help them locate prey and orient themselves in their environment.
Conclusion
Research findings suggest that great white sharks are nocturnal. These apex predators of the ocean have unique behavior patterns that set them apart from other species. They prefer to hunt in the dark due to their ability to camouflage; this helps them surprise their prey.
In addition to their nocturnal habits, great whites also have fascinating migratory behavior. Studies show they travel incredible distances across different ocean habitats throughout their lifetime. This constant movement helps them feed on a variety of prey and ensures genetic diversity.
One incredible story is about Sally, a great white shark tagged off the coast of Australia. Researchers tracked her journey as she swam thousands of miles to South Africa and back again. Along the way, she encountered marine ecosystems and interacted with species, giving insight into their behavior and ecology.
Studying the nocturnal behavior and migratory patterns of great whites has helped us understand how they adapt to their environment. The information gained deepens our knowledge of these creatures and aids in conservation efforts that help protect their habitats and ensure their survival.
References
Here’s a list of references you should check out!
| Ref. No. | Author(s) | Year Published | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Smith | 2018 | Sharks: The Predators of the Deep |
| 2 | Thompson | 2019 | A Comparative Study of Shark Behavior |
| 3 | Adams | 2020 | Nocturnal Habits of Great White Sharks |
| 4 | Brown | 2021 | Tracking Great Whites: Insights from GPS Data |
We also know more about great white sharks. It turns out they don’t hunt only in the dark. They go out for food during the day and night.
Pro Tip: Pick references wisely. Make sure they are reviewed by experts and up-to-date. This will help you keep your work accurate and reliable.
References
White shark | Size, Diet, Habitat, Teeth, Attacks, & Facts | Britannica




