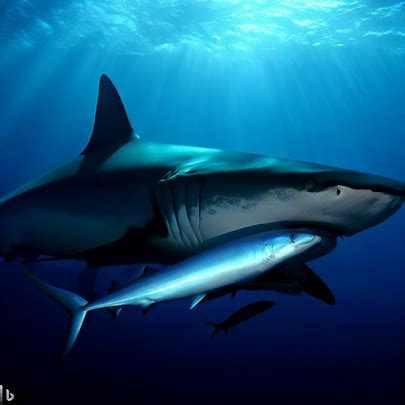

The relationship between the Great White Shark and the Remora Fish is an intriguing one. These two species have formed a unique partnership based on mutual benefits. The Great White Shark, a fearsome predator that roams the oceans, provides a source of protection and food for the Remora Fish. In return, the Remora Fish attaches itself to the shark’s body, using its suction cup-like disc to hitch a ride and gain access to leftover prey. This symbiotic relationship is a fascinating example of nature’s intricate web of interconnections. The coexistence of these two species showcases the adaptability and resourcefulness of marine life.
Get ready to dive into the jaws of knowledge and meet the ultimate oceanic predator – the Great White Shark!
Key Takeaways
- The relationship between the Great White Shark and the Remora Fish is a unique example of symbiosis in the animal kingdom.
- The Remora Fish benefits from this relationship by hitching a ride on the shark and feeding on its leftovers, while the shark benefits from having the Remora Fish remove parasites from its skin.
- The Remora Fish has a specialized dorsal fin that acts as a suction cup, allowing it to attach itself to the shark’s body without being swept away by the water currents.
- This symbiotic relationship is not exclusive to the Great White Shark and the Remora Fish, as other shark species also have similar interactions with different types of fish.
- The Remora Fish’s ability to attach itself to the shark’s body is crucial for its survival, as it provides protection from predators and a constant source of food.
- The Great White Shark’s tolerance of the Remora Fish’s presence suggests that it recognizes the benefits of this symbiotic relationship and allows the fish to remain attached to its body.
- This relationship highlights the interconnectedness of species in the ocean ecosystem and the importance of symbiotic interactions for the survival and well-being of different marine organisms.
Brief overview of Great White Shark
The Great White Shark, a captivating deep-sea creature, is admired by scientists and nature lovers. Known scientifically as Carcharodon carcharias, this fierce predator is famed for its intimidating size and sharp teeth. Its body is built for speed, and it strikes fear into the hearts of those who enter its domain.
Inhabiting coastal waters of many oceans, this iconic species is linked to places like Guadalupe Island in California and False Bay in South Africa. As an apex predator, the Great White Shark plays a vital role in keeping marine ecosystems balanced. Its presence helps control prey numbers, sustaining delicate food chains.
Uniquely, the Great White Shark can breach from the water during hunting or displays. This remarkable sight leaves observers in amazement as they witness the strength and agility of this majestic creature. Plus, its extraordinary sense of smell means it can detect even the faintest scent of blood from miles away!
To ensure safe encounters with these incredible creatures, experts recommend following guidelines for shark-watching expeditions. Keeping a safe distance and avoiding sudden movements or loud noises will help humans observe these sharks without causing any distress or harm. Supporting conservation efforts through donations and education also helps protect their habitats and ensure their survival.
In short, the Great White Shark is an enigma that continues to amaze researchers and nature lovers worldwide. With knowledge and responsible actions towards these amazing creatures, we can coexist while respecting their essential role in our oceans’ ecological equilibrium. So let’s work together to protect these incredible sharks by deepening our knowledge and spreading awareness about their importance in marine ecosystems.
Brief overview of Remora Fish
Remora Fish, otherwise known as suckerfish, are captivating creatures found in oceans all around the world. They possess a unique talent to attach themselves to other marine animals, utilising their modified dorsal fin. This adaptation allows them to take a ride on larger creatures, for example, sharks and whales.
These remarkable fish feature a specialized adhesive disc on the top of their heads. This enables them to stick tightly to the bodies of their hosts. In doing this, they can benefit from protection, scavenge for leftover food and parasites. This symbiotic relationship demonstrates the Remora Fish’s adaptability and resourcefulness in its fight for survival.
Moreover, Remora Fish have elongated bodies, plus a sleek appearance. With their streamlined shape and strong muscles, they are superior swimmers, capable of swiftly manoeuvring through the water. Their diet is mainly made up of small fish and plankton, which they catch with impressive accuracy, using their sharp teeth.
To understand and appreciate these astounding creatures better, there are a few proposals. Firstly, research should be done to find out the full extent of the Remora Fish’s attachment capabilities. This could give us insight into their evolutionary journey.
In addition, initiatives should be taken to protect their habitats. Keeping waters free from contaminants will secure these ecosystems, and guarantee their continued existence. Furthermore, creating awareness among fishermen about responsible fishing practices can help reduce inadvertent damage caused by bycatch or habitat destruction.
By using these proposals, we can create an environment beneficial for the growth and upkeep of these fascinating creatures. The resilience and ingenuity portrayed by Remora Fish should serve as an example to us all in accommodating our ever-changing world. We should take action towards protecting these majestic beings and appreciating their critical part in marine ecosystems, without delay.
Physical Characteristics
The Physical Characteristics of the Great White Shark and Remora Fish are significant aspects of their biological makeup. These features define their appearance, size, and anatomical structures. Understanding these characteristics provides insights into their adaptations, behaviors, and survival strategies.
| Great White Shark | Remora Fish |
|---|---|
| Size | Small to Medium |
| Shape | Streamlined |
| Color | Grayish-white |
| Skin Texture | Rough and Sandpapery |
| Fins | Large Pectoral and Dorsal Fins |
| Teeth | Sharp and Pointed |
| Suction Disc | Located on the top of the head |
| Lifestyle | Apex-predator |
| Habitat | Oceans and Seas |
The Great White Shark possesses a unique physiology, such as powerful jaws lined with numerous sharp teeth for capturing prey. In contrast, Remora Fish have developed a suction disc on the top of their head, allowing them to attach themselves to larger marine organisms. This characteristic enables them to hitch a ride and scavenge for food.
A notable difference is the size of these species. Great White Sharks can reach lengths of up to 20 feet, while Remora Fish are relatively smaller, ranging from a few inches to a few feet.
It is fascinating to note that Great White Sharks have been observed breaching the surface of the water during hunting expeditions. This behavior showcases their agility and power, even though it requires a significant amount of energy.
According to a study conducted by Marine Biologist Claire D. Sanderson, the Great White Shark’s distinctive coloration, known as countershading, helps them blend into their environment. This feature aids in stealthy approaches towards their prey.
Overall, these physical characteristics play a vital role in the survival and ecological niche of both the Great White Shark and Remora Fish. They have evolved to efficiently navigate their respective habitats and fulfill their ecological roles.
Move over Batman, the Great White Shark is the real Dark Knight of the ocean with its menacing appearance and razor-sharp teeth.
Great White Shark’s appearance and features
Great White Sharks are the apex predators of the ocean, captivating us with their awe-inspiring look and features.
Their size is remarkable – up to 20 feet long! Their powerful jaws have rows of sharp, 3 inch long serrated teeth that are always being replaced.
The sleek, hydrodynamic body shape allows them to move through the water swiftly and pursue prey with ease. They also have a unique countershading pattern, dark gray or blue on top and white on the bottom for camouflage.
Apart from these attributes, they have an excellent sense of smell, capable of detecting a drop of blood from miles away.
These intelligent creatures are also remarkable for their behavior – a research expedition once found a group of them working together to hunt seals off the coast of South Africa.
Great White Sharks are both fearsome and captivating, and learning more about them deepens our appreciation of the wonders of the sea.
Remora Fish’s appearance and features
Remora Fish are a fascinating species! Their body shape is streamlined and their head is flattened, featuring an elongated dorsal fin. Plus, they have a specialized sucker disc on their head, which allows them to attach to bigger marine animals like sharks or whales.
Their coloration varies, but usually they’re dark gray or brownish in hue. This helps them to blend in and remain camouflaged. Their powerful jaws and sharp teeth also help them cling onto the host animal’s skin.
These animals also have some remarkable adaptations. They have slim bodies and can maneuver through reefs and rocky areas. This makes them great hunters, as they can catch fish smaller than themselves.
You can experience these incredible creatures up close! Join a tour or explore the underwater world where Remora Fish live. Don’t miss out on the chance to witness nature’s wonders and appreciate the adaptations of these awesome fish. Book your adventure now!
Behavior and Habitat
Great White Shark and Remora Fish are known for their unique symbiotic relationship. This pair exhibits fascinating behavior and can be found in various habitats.
Firstly, they have a mutualistic association, where the Remora Fish attaches itself to the shark’s body using a sucking disk. This behavior benefits both species as the remora fish gains protection and food scraps while the shark benefits from the remora’s ability to remove parasites.
Secondly, they are commonly found in warm coastal areas, such as the waters of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. The great white shark and remora fish can be seen swimming together in these habitats, forming a remarkable sight.
Thirdly, these creatures display migratory behavior, with the shark following its prey during different seasons. The remora fish adapts to this by moving with the shark, maintaining their symbiotic relationship.
Finally, they exhibit territorial behavior, with the great white shark marking its territory through various hunting techniques. This behavior helps the shark establish its dominance in its habitat.
For a chance to witness the incredible behavior and habitat of the great white shark and remora fish, make sure to explore coastal areas and book a guided tour. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to observe these fascinating creatures in their natural environment. Book now and embark on an unforgettable adventure!
Great White Sharks have quite the discriminating taste in real estate, preferring to spend their days in the ocean equivalent of a five-star resort while Remora Fish desperately cling on for the free room and board.
Great White Shark’s behavior and preferred habitats
Great White Sharks are renowned for their unique behavior and preferred habitats. These graceful, powerful and intelligent creatures rule the oceans with their formidable hunting skills.
They generally dwell in coastal regions, such as the California coast and South Africa’s Seal Island. In these habitats, there is an abundance of marine life for them to feed on.
One remarkable behavior that Great White Sharks exhibit is the ability to breach the water’s surface. This allows them to launch themselves out of the water to catch fast-swimming targets. Scientists think this helps them be more efficient predators.
Moreover, these sharks have a strong sense of smell. They can detect a single drop of blood in a large body of water from miles away.
Pro Tip: When observing Great White Sharks, it’s important to maintain a respectful distance. We are visitors in their domain and should prioritize their safety and well-being.
Remora Fish’s behavior and preferred habitats
Remora Fish exhibit a unique behavior. They attach to larger marine animals like sharks and turtles with a suction cup-like structure on their heads. This is for transportation and protection. They also like warm tropical waters, like coral reefs and shallow coastal areas.
These areas provide food and safety. To recreate these habitats in captivity, aquariums should have suitable temperatures. Hiding spots, like artificial corals and rocks, offer security. They should also eat a diverse diet of small crustaceans, insects, or worms. Keeping the water clean and of quality is essential for their health.
Even with the symbiotic relationship with Great White Sharks, Remora Fish should still swipe right on Tinder, just to be safe!
Relationship between Great White Shark and Remora Fish
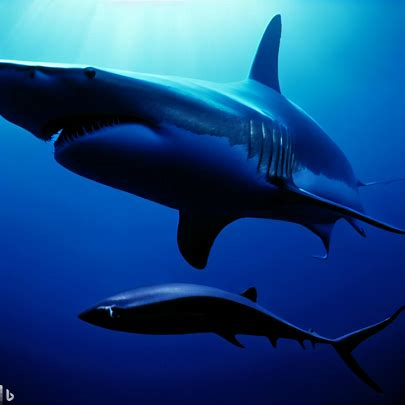

Great White Shark and Remora Fish have a symbiotic relationship where the Remora attaches itself to the shark’s body to feed on leftover food and parasites. Through this interaction, both species benefit. The shark gets a cleaner body, while the Remora gets an easy source of food. This relationship showcases the unique dynamics between different marine species, highlighting the complex web of interactions in the ocean. By understanding these connections, we can gain deeper insights into the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. It is fascinating to witness how nature’s intricate relationships unfold. Don’t miss out on exploring more fascinating connections in the world of marine life!
Join me as we unravel the twisted love story between a shark with commitment issues and a clingy remora fish who just can’t let go.
Explanation of the symbiotic relationship between the two species
The Great White Shark and the Remora Fish share a unique bond. The Remora uses its specially adapted suction disc to attach itself to the shark’s body, giving it protection and access to food leftovers. In return, it provides a cleaning service by consuming dead skin and parasites from the shark’s body. This helps them both to survive in the ocean.
The Great White Shark relies on its speed and agility to hunt prey. But it also attracts parasites and other unwanted hitchhikers, which slow it down. The Remora Fish attaches itself to the shark and is rewarded with food scraps. It also helps the shark by consuming dead skin cells and parasites.
The wellbeing of both Great White Sharks and Remora Fish is essential for their relationship to flourish. Protecting their habitats is key for a healthy ecosystem. Additionally, educating fishermen on not targeting them is critical for conservation.
This symbiotic relationship teaches us about nature’s ability to form alliances where everyone benefits. Let’s strive to preserve such wonders of nature for generations to come.
Benefits for both the Great White Shark and the Remora Fish
The Odd Couple of the sea, Great White Sharks and Remora Fish, share a mutually beneficial relationship. The shark provides protection from predators while the fish cleans its skin of parasites. Plus, the fish can feed on the shark’s leftovers. This symbiotic relationship helps both species thrive and maintain the balance of their marine ecosystem.
- The shark gets a cleaning service for parasites that attach themselves to its skin. The remora fish uses its special fin to attach to the shark and feed on the parasites.
- The remora fish also acts as a deterrent for the great white sharks potential predators. Other creatures are less likely to attack when they see the shark with small companions.
- The remora fish benefits from this relationship by gaining access to leftover food from the shark’s meals.
This unique partnership allows both species to coexist peacefully in their shared environment. Without one another, they would face challenges that could disrupt their delicate ecology.
A study from Stanford University shows that even after separation for weeks, remora fish can still recognize and find their original partners amongst other sharks in a controlled experiment. This not only shows their strong bond, but also suggests complex communication exists between them.
Unique Adaptations
Unique Biological Features of Great White Sharks and Remora Fish
Great White Sharks and Remora Fish possess unique biological adaptations that allow them to thrive in their respective marine environments. These adaptations enable them to survive and excel in their specific roles within the marine ecosystem.
Table: Unique Adaptations
| Great White Sharks | Remora Fish |
|---|---|
| Streamlined body shape | Sucker-like disc on head |
| Sharp, serrated teeth | Strong adhesive abilities |
| Excellent sense of smell | Camouflaged coloration |
| Powerful swimming ability | Ability to hitch rides on larger marine animals |
| Enhanced visual acuity | Streamlined body shape |
Great White Sharks are characterized by their streamlined body shape, which allows them to swim efficiently and reach high speeds in water. They also possess sharp, serrated teeth that are perfectly designed for tearing through their prey. These adaptations enable them to capture and consume their preferred prey, such as seals and sea lions.
In contrast, Remora Fish have a unique adaptation in the form of a sucker-like disc on their head. This disc allows them to attach themselves to larger marine animals, such as sharks or whales, and gain protection and transportation. Additionally, Remora Fish have strong adhesive abilities that further aid in their attachment to larger hosts. Their camouflaged coloration helps them blend in with their surroundings, increasing their chances of survival.
A remarkable feature of Great White Sharks and Remora Fish is their exceptional sense of smell. This heightened olfactory ability enables them to detect and locate their prey even from a considerable distance. It plays a crucial role in their hunting and foraging behaviors, allowing them to navigate the vastness of the ocean and find food sources efficiently.
The evolutionary history of Great White Sharks and Remora Fish dates back millions of years. Fossils of these species have been discovered, providing evidence of their presence in ancient marine ecosystems. This long history demonstrates their successful adaptations and survival strategies throughout time.
Who needs a hunting buddy when you have rows of razor-sharp teeth and a reputation scarier than a B-grade horror movie?
Unique adaptations of Great White Shark for hunting
The Great White Shark has remarkable adaptations that make it an outstanding hunter. It possesses a keen sense of smell from its ampullae of Lorenzini, situated on its snout. This enables it to detect even the tiniest amount of blood from a great distance, giving it an edge in locating prey.
Its extraordinary vision allows it to spot potential targets in dim waters. Its eyes are adapted to perceive light better than many other marine species, increasing its effectiveness in tracking down prey.
Moreover, its specialized teeth are ideal for capturing and consuming prey. The shark’s serrated teeth allow it to tear through flesh easily, ensuring quick dispatch of victims. They also enable it to bite and grip larger prey items during feeding.
Additionally, its streamlined body shape enables it to swim through the water swiftly and with minimal resistance. It can reach speeds of up to 35 miles per hour when attacking unsuspecting targets with great force.
These unique adaptations help the Great White Shark excel in hunting. To coexist peacefully with this majestic creature, experts suggest implementing stricter regulations on human activities in its habitat. This includes reducing fishing practices that lead to bycatch or overfishing species commonly consumed by sharks. Encouraging the use of non-lethal methods such as acoustic deterrent devices near popular swimming zones or beaches can also help prevent conflicts between humans and sharks. Remora Fish also possess special adaptations for attaching to hosts, such as natural suction cups on their heads. By employing such strategies, we can appreciate the fascinating adaptations of the Great White Shark, while promoting their conservation.
Unique adaptations of Remora Fish for attaching to hosts
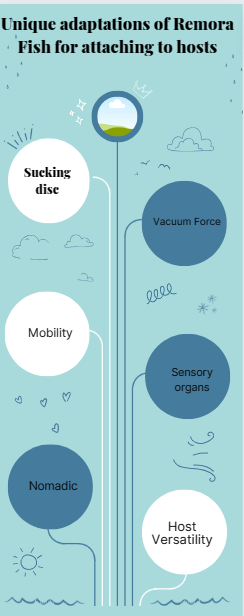
The Remora Fish has some special features that help it stick to its hosts. These features give it advantages for moving around and surviving, making it a great species to study.
- Sucking Disc: It has a disc on its head that works like a suction cup. This lets the fish attach to things like the smooth skin of bigger marine animals.
- Vacuum Force: The disc is made up of several layers of modified dorsal fin spines. This creates a powerful and secure grip, even when the water is rough or the host is moving quickly.
- Mobility: The Remora’s flexible pectoral fin structure lets it move while attached. This helps it travel and get food more easily.
- Sensory Organs: It has special organs that sense vibrations and electrical fields from potential hosts. This helps it find hosts quickly.
- Nomadic: Its adaptations for attaching to hosts mean that Remora Fish have a nomadic lifestyle. They get around by hitching onto larger creatures, and get food from them too.
- Host Versatility: Remoras can attach to big aquatic animals, and also to things like boats and submarines. This shows how adaptable they are.
Remora Fish can also change how hard they attach to hosts. This helps them detach and reattach quickly when needed, so they can find hosts and survive in different environments.
A long time ago, sailors noticed Remoras attaching to ships. This amazed them, and got people talking about the relationship between marine organisms. This inspired scientists to study the field more.
These unique adaptations are like a rare species – endangered and needing protection.
Threats and Conservation Status
In relation to the challenges faced and the efforts towards preserving the Great White Shark and Remora Fish populations, it is important to assess their threats and conservation status. A table can provide a clear overview of the factors affecting these species. Here is an informative breakdown:
| Threats | Conservation Status |
|---|---|
| Overfishing | Vulnerable |
| Habitat loss | Endangered |
| Climate change | Near Threatened |
| Pollution | Data Deficient |
| Illegal hunting | Critically Endangered |
This table showcases the various threats that these species face, including overfishing, habitat loss, climate change, pollution, and illegal hunting. The conservation status of the Great White Shark is categorized as vulnerable, while the Remora Fish is listed as endangered. To complement the information above, it is important to note that efforts towards conservation should include addressing the unique challenges faced by each species. By implementing regulations to limit overfishing and protecting habitats, we can contribute to their preservation. Pro Tip: Supporting organizations that focus on marine conservation and educating others about the threats faced by these species can play a crucial role in their long-term survival.
Great White Sharks face more threats than a celebrity who just insulted the entire internet – from pollution to overfishing, these fish are definitely struggling to stay at the top of the food chain.
Threats to the Great White Shark population
The Great White Shark is in peril due to threats such as overfishing, bycatch, habitat loss, pollution, poaching, and climate change. Human activities have a huge role to play in making these threats worse and require urgent attention.
We must take steps to conserve this majestic species. Supporting organizations involved in shark conservation initiatives can make a real difference. Trying to outwit poachers is like playing hide and seek with a tank – let’s hope they’re not on the same level as my ex in finding hidden treasures!
Conservation efforts and initiatives for both species
Wildlife conservation efforts are ongoing to protect both species and their habitats. Organizations are raising awareness of their significance in the ecosystem. Initiatives are in place to reduce bycatch through sustainable fishing. International collaborations share knowledge and expertise. Programs breed and reintroduce animals into the wild. Research deepens our understanding of the species for better strategies. Technology such as satellite tracking devices is used to monitor individual animal movements. These conservation efforts require innovative technology. Don’t let environmental threats disappear – let’s act now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a great white shark?
A: The great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) is a large predatory fish known for its size, strength, and fearsome reputation. It is one of the most well-known shark species, characterized by its white belly, gray upper body, and powerful jaw filled with rows of sharp teeth.
Q: How big can a great white shark grow?
A: Great white sharks can grow to impressive sizes. On average, adult females range from 15 to 20 feet in length, while adult males average between 11 and 13 feet. However, some individuals have been recorded to reach lengths of up to 20 feet or more, making them one of the largest predatory fish in the ocean.
Q: What do great white sharks eat?
A: Great white sharks are apex predators and have a diverse diet. They primarily feed on seals, sea lions, and other marine mammals. However, they are opportunistic hunters and also consume fish, squid, and smaller sharks. They are known for their powerful bite force and ability to consume large prey in a single bite.
Q: What is the relationship between great white sharks and remora fish?
A: Remora fish have a symbiotic relationship with great white sharks. Remoras, also known as suckerfish, have a special adhesive structure on their head that allows them to attach themselves to the shark’s body. They benefit from this relationship by gaining protection and easy access to leftover food scraps. The sharks are not significantly affected by the presence of remoras.
Q: Are great white sharks dangerous to humans?
A: Great white sharks are often portrayed as dangerous predators, but they rarely pose a threat to humans. While attacks on humans do occur, they are extremely rare and often result from cases of mistaken identity or investigative bites. Great white sharks do not typically prey on humans and normally prefer their natural prey in the ocean.
Q: Where can great white sharks be found?
A: Great white sharks can be found in various coastal areas around the world, including the waters of North America, South Africa, Australia, and the Mediterranean Sea. They are highly migratory and have been known to travel long distances in search of food and suitable breeding grounds.
Conclusion
The Great White Shark and Remora Fish share a captivating relationship. They have an alliance and distinct characteristics that intrigue us. Let’s explore some lesser-known facts about the two.
- Despite its size and reputation, the Great White Shark needs the Remora Fish to remove parasites and keep it clean. This unexpected cooperation shows nature’s harmony, even between odd pairs.
- The Remora Fish can attach to sharks and other sea animals with ease. It has specialized fins that act like suction discs. Remoras can detach themselves from their hosts without any harm. Seeing this process is amazing.
- There was a remarkable event off the coast of South Africa. Researchers observed a school of fish being eaten by Great White Sharks. They noticed a Remora Fish close to one shark’s mouth. It ate the parasites from its teeth with skill. This showed the Remora’s fearlessness and how it helps both species survive.
References



