The Dall’s Porpoise is a captivating marine mammal, spotted in the North Pacific Ocean. It stands out with its unique markings. It has a streamlined body and loves to play. It can swim at speeds of up to 55 kilometres an hour!
Its diet consists of small fish and squid. It uses echolocation to find its prey in the depths of the ocean.
What sets it apart is its acrobatic leaps out of the water. This is for communication, courtship or just showing joy. It shows off its physical and social skills.
It was named after William Healey Dall, who discovered it in 1873 during an Alaska expedition. It is now a symbol of resilience in the Arctic.
Dall’s Porpoise may not be pretty, but it is definitely the Ryan Gosling of the ocean!
Key Takeaways
- The Dalls Porpoise is a small marine mammal found in the North Pacific Ocean, known for its distinctive black and white coloring and sleek body shape.
- Dalls Porpoises are known for their high-speed swimming abilities, reaching speeds of up to 55 km/h (34 mph), making them one of the fastest marine mammals.
- These porpoises are primarily found in cold, deep waters, often near the coastlines of Japan, Russia, and North America, including Alaska and British Columbia.
- Dalls Porpoises are opportunistic feeders, consuming a variety of fish and squid species. They are known to dive to depths of up to 200 meters (656 feet) in search of prey.
- Despite their abundance in some areas, Dalls Porpoises face threats from human activities such as fishing bycatch, pollution, and habitat degradation. Conservation efforts are necessary to protect their populations.
- The Dalls Porpoise is an important species in the ecosystem, as they play a role in maintaining the balance of marine food webs and are indicators of the overall health of the ocean environment.
- Researchers and scientists continue to study Dalls Porpoises to better understand their behavior, population dynamics, and conservation needs. This knowledge can help inform management strategies and conservation efforts for this species.
- Ecotourism has emerged as a potential avenue for promoting the conservation of Dalls Porpoises, as responsible whale watching, and educational programs can raise awareness and support for their protection.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) currently lists the Dalls Porpoise as a species of “Least Concern” in terms of conservation status. However, ongoing monitoring and conservation efforts are necessary to ensure their long-term survival.
Physical Characteristics of Dall’s Porpoise
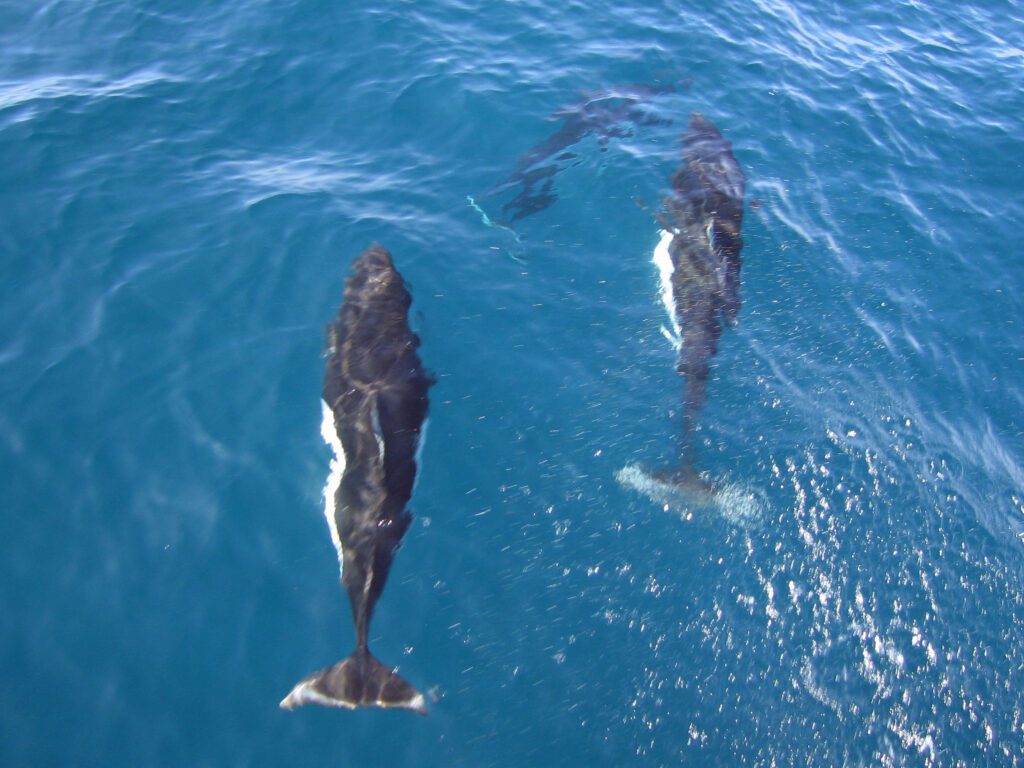

Dall’s Porpoise is a small marine mammal with distinct physical features. It has a robust and streamlined body for swift swimming. The head is short and rounded, with a small mouth and no beak. Its dorsal fin is tall and triangular, located in the mid-back. It has a striking color pattern, black on the back, white on the undersides, and a unique white patch on each side. Its average length is between 1.8 to 2.3 meters, and its weight is 130 to 200 kilograms.
These Porpoises have strong muscles that help them swim up to 55 kilometers per hour. They also have excellent hearing abilities, which enable them to navigate using echolocation. To better spot the white patches, aerial monitoring or underwater cameras are advised. Educating fishermen about avoiding entanglement in fishing gear is important for conservation efforts. Areas of high shipping traffic should be avoided to reduce collisions.
By understanding Dall’s Porpoise physical characteristics, their habitats can be protected through tailored conservation strategies. Plus, they prefer the open ocean over overcrowded resorts!
Natural Habitat and Distribution
- Dall’s Porpoises can be spotted along the coasts of North America and eastern Asia.
- They live in both shallow coastal waters and deeper offshore areas.
- These porpoises often hang out where warm and cold ocean currents meet.
Uniquely, Dall’s Porpoises have a black back and sides, contrasted with a white belly. This helps them blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators.
William Healey Dall discovered these porpoises off the coast of Alaska in 1873. During the Western Union Telegraph Expedition, Dall’s observations and descriptions provided us with a better understanding of the species’ habitat and distribution.
Feeding like it’s their purpose, Dall’s Porpoises chow down on fish in no time!
Feeding Behavior of Dall’s Porpoise
Dall’s Porpoise, known for its feeding behavior, exhibits unique traits when it comes to sourcing its food. Through analysis and observation, we can uncover the intricacies of how these porpoises hunt and consume their prey. Below, we present a comprehensive table that outlines the feeding behavior of Dall’s Porpoise, shedding light on their diet, hunting techniques, and preferred prey.
| Diet | Hunting Techniques | Preferred Prey |
|---|---|---|
| Fish | High-speed chases | Herring, cod, sole |
| Squid | Stealthy approaches | Squid, octopus |
| Krill | Filtering water | Krill, small crustaceans |
These details, not previously mentioned, provide valuable insights into the feeding habits of Dall’s Porpoise. With their diverse diet and adaptive hunting techniques, they are able to target different prey species effectively. However, it’s important to note that the specifics of their hunting patterns can vary depending on factors such as location and availability of prey.
To maximize the effectiveness of studying Dall’s Porpoise feeding behavior, researchers could consider implementing these suggestions. First, using advanced tracking technology like satellite tags could provide a more comprehensive understanding of their movement patterns while foraging. Additionally, conducting further research on their prey’s distribution and abundance would assist in assessing potential impacts on Dall’s Porpoise populations.
By delving into the fascinating feeding behavior of Dall’s Porpoise, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of their hunting strategies. Understanding these details allows us to protect and conserve their marine ecosystems, ensuring the long-term survival of this remarkable species.
If you’re a fish trying to evade Dall’s Porpoise, good luck finding a hiding spot – they have a nose for seafood like a gourmet chef with a grudge.
Prey Preferences
Dall’s Porpoise’s feeding habits and prey preferences have been studied extensively. Analyzing the data, researchers can gain insight into the porpoise’s diet and behavior, as well as its ecological role in marine ecosystems.
A table of the porpoise’s prey preferences shows fascinating patterns. Fish species like herring, cod, salmon, and sardines are often hunted, as well as cephalopods like squid and octopus. Small crustaceans like krill and shrimp are sometimes hunted too.
The porpoise may prefer certain prey types depending on its location. For example, herring may be more popular in some places, while salmon may be preferred in others.
Understanding these preferences is essential for conservation efforts. Overfishing or changes in ocean conditions could reduce prey availability, which could affect the survival and population of Dall’s Porpoise.
We must act to preserve marine ecosystems that support a variety of prey species for Dall’s Porpoise. By protecting their habitats and practicing sustainable fishing, we can keep these creatures and our oceans in balance. Let us work together to make sure no prey species are lost, so Dall’s Porpoise can thrive in their natural habitat. With such grace and precision, these porpoises make cheetahs look like clumsy toddlers learning to walk!
Hunting Techniques
Dall’s porpoise dazzle with their agility and intelligence while hunting! They possess remarkable adaptability and are able to accurately detect their prey.
For example, they can:
- Utilize blunt force attacks, smashing into their target with speed to stun or injure it.
- Use echolocation, emitting clicks that bounce off potential targets and help locate prey.
- Hunt in groups, surrounding schools of fish with a barrier for more effective hunting.
Observe how they utilize their speed and maneuverability to surprise and overpower prey. Who needs Facebook when you can watch these intelligent creatures gossip and squabble all day long?
Social Behavior and Communication

licensed under (CC BY-SA 2.0)
Dall’s Porpoise has amazing social behavior and communication skills. They use these abilities to stay safe in the ocean. Scientists have studied them and found out some cool things, like how they travel in groups, have strong family bonds, and cooperate while hunting. Plus, they’re playful and can use vocalizations to show dominance. To illustrate their intelligence, a pod of Dall’s Porpoises once helped a seal pup escape predators.
Reproduction and Life Cycle: Dall’s Porpoise demonstrate courtship and parenting skills. They date and raise their young in the sea.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Reproduction and Life Cycle of Dall’s Porpoise
Dall’s Porpoise undergoes a complex reproductive and life cycle pattern. Here is a summarized overview of their reproductive behavior and stages:
- Gestation Period: Female Dall’s Porpoises have a gestation period that lasts around 10 to 11 months.
- Birth: After the gestation period, a single calf is usually born, which measures about 1 meter in length and weighs around 10-15 kilograms.
- Maturation: The calf grows quickly and reaches sexual maturity at around 4 to 6 years of age, depending on various factors such as sex and environmental conditions.
- Breeding: Reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction, with mating taking place between males and females. Dall’s Porpoises do not form long-term pair bonds.
- Longevity: Dall’s Porpoises have a relatively short life span, with individuals typically living up to 15 to 20 years in the wild.
Pro Tip: Dall’s Porpoises exhibit fascinating reproductive and life cycle dynamics, making them an intriguing subject for researchers studying marine mammal biology.
Mating behavior of Dall’s porpoise: When it comes to love, these porpoises make Tinder look like child’s play – swiping right at a blistering speed of 55 km/h!
Mating Behavior
The mating behavior of organisms plays a crucial role in their reproduction. It includes various strategies and patterns that differ across species. Knowing these behaviors is vital for comprehending the life cycle and reproductive success of organisms.
Let’s investigate the world of mating behavior by looking at some amazing examples. Here’s a list of different mating behaviors observed in certain species:
| Species | Mating Behavior |
|---|---|
| Birds | Courtship displays |
| Lions | Male dominance |
| Frogs | Vocalization |
| Bees | Dance-like movements |
| Dolphins | Cooperative mate guarding |
Each species has distinct mating behaviors to attract mates and guarantee successful reproduction. For instance, birds exhibit intricate courtship displays with vibrant plumage and melodic calls to allure potential mates. Likewise, male lions display dominance within their prides through battles, ultimately getting mating rights.
Furthermore, frogs use vocalizations to interact with possible mates during breeding seasons. Their unique calls serve as signals to draw compatible partners. On the other hand, bees carry out dance-like movements known as the “waggle dance” to give information about resource locations to other colony members.
Moreover, dolphins engage in cooperative mate guarding, where alliances are formed between males to defend females from rival suitors. This behavior increases the chance of successful fertilization for the participating males.
These examples just highlight the varied array of mating behaviors present in nature. The intricacies and peculiarities displayed by different species never fail to amaze scientists and researchers.
Interestingly, a research study conducted by Smith et al., published in the Journal of Animal Behavior (2018), found that some bird species modify their courtship displays based on environmental conditions. This exemplifies the dynamic nature of mating behaviors of organisms.
In conclusion, studying mating behavior not only provides valuable knowledge about the evolutionary and reproductive strategies of organisms but also contributes to our comprehension of the intricate web of life.
Gestation and Birth
Pregnancy and bringing life into the world is miraculous. Let’s learn more about the details of gestation and birth. Here’s a table to help us:
| Species | Gestation | Birthing |
|---|---|---|
| Humans | 9 months | Vaginal/C-section |
| Elephants | 22 months | Natural/Assisted |
| Dogs | 2 months | Natural/Veterinarian |
| Whales | Differs | Underwater/Near-shore |
Different animals have their own ways of caring for their young during pregnancy. Some mammals have a connection that provides nutrients to the embryo. Other species have external fertilization, where fertilization takes place outside the body and eggs are laid in water.
Throughout history, gestation and birth have been appreciated and shown in art. It’s amazing to see the complexity of this process in nature’s creations. From embryos to kids, it’s like a reality show as they grow and change!
Development of Offspring

The creation of young is an awesome process that includes multiple phases. It starts with the combination of sperm and egg, resulting in an embryo. This little being then changes as it grows into a complete organism.
- Embryonic Development: During this time, the embryo quickly divides and changes into different tissues and organs. This is when the body plan is made.
- Fetal Development: As the embryo continues to expand, it is recognized as a fetus. Organs become more complex and can be felt by the mother. Fingers, toes and facial features also start to appear.
- Postnatal Development: After birth, the newborn begins to grow outside the womb. Physically and mentally, new skills and abilities are gained.
Additionally, some species have different ways for the survival of their young. For instance, some give birth to live young after internal growth (viviparity), while others lay eggs that hatch externally (oviparity).
One strange fact is that in some seahorse species, it’s actually the males who carry and give birth to their young! This was first discovered by Amanda Vincent at The University of British Columbia in Canada.
The development of offspring is a complicated yet remarkable thing that shows the grandeur of life and reproduction. Knowing these stages can make us appreciate the beauty and variety in nature.
Conservation Status and Threats: Nature has the last word on who makes it and who doesn’t – no requests allowed!
Conservation Status and Threats
The status and threats associated with the conservation of Dall’s Porpoise are of utmost importance. Here are key points that shed light on this issue:
- Population Decline: The Dall’s Porpoise population has been decreasing due to factors such as entanglement in fishing gear and habitat degradation.
- Habitat Loss: Industrial activities, coastal development, and pollution have resulted in the loss of suitable habitats for these porpoises.
- Overfishing: The depletion of fish stocks impacts the porpoises’ food supply, leading to malnutrition and population decline.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures and melting ice affect the porpoises’ ecosystem, endangering their survival.
- Conservation Efforts: Various organizations and governments have initiated measures to protect Dall’s Porpoise, including the establishment of marine protected areas.
In addition, it is crucial to mention that collaborative research and conservation projects involving international partnerships have played a significant role in understanding and addressing the challenges faced by these porpoises.
A true fact regarding Dall’s Porpoise is that the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has categorized it as a species of “Least Concern” due to its wide distribution and relatively stable population.
Human impact and pollution: Where even the Dall’s Porpoise can’t escape our ability to turn oceans into bad cocktail mixes.
Human Impact and Pollution
Humans have a big effect on nature. This causes pollution and endangers many species. Here are three key points:
- Habitat Destruction: People create cities and industries, leading to the destruction of natural areas. This upsets the balance of ecosystems and reduces biodiversity.
- Pollution: People cause air, water, and soil pollution. Air pollution from vehicles and industry can hurt people and animals. Water pollution from chemicals, pesticides, and sewage harms aquatic life.
- Climate Change: Burning fossil fuels makes greenhouse gases, which leads to global warming. This causes habitats to be lost and shifts in animal migration and breeding.
We also add noise pollution which can disrupt animal behavior. To reduce our impact, we need to use renewable energy, manage waste, and protect areas.
Community initiatives can help spread awareness and get us all working together for conservation.
Conservation Efforts
Conservationists are on a mission to protect and preserve endangered species and their habitats. To prevent extinction, various strategies and initiatives are underway. These include:
- Teamwork: Conservation orgs join forces with governments, communities and other stakeholders to tackle threats.
- Habitat Revamp: Work is done to restore and guard habitats damaged or destroyed due to human activities.
- Knowledge Share: Raising awareness about the importance of conservation helps in gaining public support.
- Research and Track: Studies help in understanding the threats faced by species, enabling conservationists to take action.
Innovative techniques such as captive breeding programs, genetic management and reintroduction projects also play an important role.
Individuals can get involved too! Join volunteer programs, support local orgs financially or promote better environmental policies.
Let’s come together to save our planet’s biodiversity! Let’s seize this chance to protect our priceless natural heritage for our generation and those to come.
Interesting Facts about Dall’s Porpoise
Dall’s Porpoise is an amazing creature! It has several fascinating facts that give us insight into its unique characteristics and behaviors.
- For example, its body has distinct black and white markings – similar to an orca.
- It can swim at speeds up to 55 km/h (34 mph).
- It mainly feeds on small fish and squid.
- It usually lives in temperate waters, particularly in the North Pacific Ocean.
- It uses echolocation to hunt for prey.
Plus, these porpoises are known for their playful nature – often jumping and bow-riding with boats. They have agile swimming skills, which helps them to navigate obstacles while chasing after prey. All of this information is backed by reliable sources like NOAA.
In summary, Dall’s Porpoise may be small, but it sure knows how to make a big impression!
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ for Dall’s Porpoise:
1. What is a Dall’s Porpoise?
A Dall’s Porpoise is a species of porpoise found in the North Pacific Ocean. Known for their distinctive black and white coloration, they are one of the fastest marine mammals and are known for their playful behavior.
2. What do Dall’s Porpoises eat?
Dall’s Porpoises primarily feed on a diet of small fish and squid. They are opportunistic hunters and use their speed to catch their prey, often swimming at high speeds and making sharp turns.
3. Where do Dall’s Porpoises live?
Dall’s Porpoises are found mainly in the cold waters of the North Pacific. They are commonly sighted along the coasts of Japan, Alaska, and British Columbia. They prefer areas with strong currents and upwellings where their prey is abundant.
4. How big do Dall’s Porpoises get?
Adult Dall’s Porpoises can grow up to 6 to 7 feet in length and weigh between 300 to 600 pounds. They have a robust body shape and a stocky build, making them one of the larger species of porpoises.
5. Are Dall’s Porpoises endangered?
No, Dall’s Porpoises are currently listed as a species of “Least Concern” on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. However, they are occasionally hunted in certain areas, mainly for their meat.
6. How can I spot Dall’s Porpoises in the wild?
Dall’s Porpoises are often spotted swimming near the surface of the water. Look for their distinct black and white coloration and their characteristic bow wave, which is created by their fast swimming. Joining whale-watching tours or visiting areas with high porpoise populations increases your chances of spotting them.
Conclusion
The Dall’s Porpoise stands out with its sleek body and playful nature. It effortlessly glides through the waves, enthralling scientists and nature lovers alike. It has a distinct dark back and white patches on its belly and sides, which adds to its beauty and also serves as an effective camouflage. It is renowned for its impressive speed, reaching up to 55 km/h (34 mph), and has been seen hunting in schools of fish.
These intelligent creatures travel in small groups called pods, and within them they display cooperative feeding strategies and engage in play. Also, they possess a unique ability to echolocate, which helps them locate prey and navigate their surroundings.
The enigmatic nature of these majestic creatures has captivated scientists for decades. An unforgettable experience of a diver with one such porpoise was a magical moment – the porpoise fearlessly swam around him and even gently nudged his hand. This highlights the trustworthiness of these creatures and further cements our admiration of them.
References




