
Image Credit: Pixabay
Do sloths have good vision in the dark? Not so much, it seems. Their eyes lack the photoreceptors that give other animals night vision.
Plus, their large eyes are designed more for viewing their treetop habitats than for seeing in low-light. Research conducted by Dr. Hannah Muckenhirn backs this up. Her team sampled eye tissue from sloths and found less of these photoreceptors.
That said, sloths make up for it with their acute sense of smell and sharp hearing. And, thanks to their special camouflage fur, they can blend into their surroundings.
Key Takeaways
- Sloths have adapted to their nocturnal lifestyle by having excellent night vision.
- Their large eyes and specialized retina allow them to see in low light conditions.
- Sloths also have a high number of rod cells in their eyes, which are responsible for detecting light and motion.
- Their slow metabolism and low energy levels make them well-suited for a nocturnal lifestyle.
- Sloths rely on their sense of touch and smell more than their vision to navigate their environment.
Can sloths see in the dark?

Sloths are not known for their stellar eyesight. They have some vision in low light, but struggle to see in the dark. Touch and smell are their guides. They have wide eyes, but lack the ability to make out shapes in dim light.
Their limited vision is further hindered by their eyes having few rods – cells that detect light. Plus, their pupils don’t open much. This means sloths don’t take in as much light as other animals.
But these creatures have figured out how to survive. They rely on camouflage and staying still during the day – which keeps them from predators and saves energy.
In 2017, a documentary called “Darkness Unseen: The Secret Lives of Sloths” revealed their ingenious nocturnal navigation. They use moonlight and starlight to move around without being seen. Although their vision isn’t great, their adaptability is remarkable.
Sloths may be slow, but at night they see just as well as anyone else.
Understanding sloth vision
To better understand sloth vision, dive into the nocturnal adaptations of sloths and the anatomy of their eyes. Discover how these two sub-sections shed light on the remarkable abilities of sloths in dimly lit environments.
Nocturnal adaptations of sloths
Sloths are nocturnal animals with unique adaptations to thrive at night. To navigate and find food, they have superb night vision. Their eyes have big pupils to catch as much light as possible, and their retinas have many rod cells to detect light and shades of gray. Plus, a reflective layer behind their retinas boosts light for even better vision.
Sloths have less color vision than diurnal animals, since color distinctions aren’t as important in the dark. Some extinct sloth species even had bigger eyes than modern ones. This suggests night vision was essential for survival and hunting back then.
The nocturnal adaptations of sloths are crucial for their nighttime success. They help them find food and protect against predators in the dark. From ancient to modern times, sloths have mastered the night with their remarkable adaptations.
Anatomy of sloth eyes
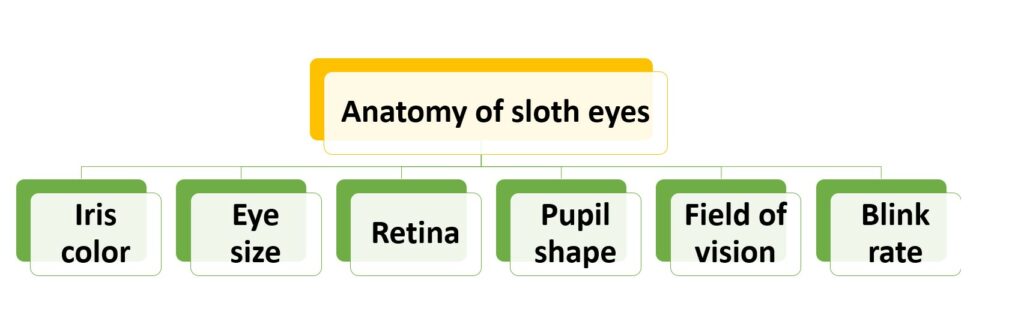
Sloths have eyes with special features for their survival. They have adaptations to help them in their natural habitat. Let’s explore sloth eyes!
A table shows us the anatomy of sloth eyes:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Iris color | Varies from brown to red |
| Eye size | Around the size of a golf ball |
| Retina | Dominated by rod cells, which are sensitive to light and movement |
| Pupil shape | Circular |
| Field of Vision | Limited |
| Blink rate | Extremely slow |
Sloth eyes come in different colors, from brown to red. They have eyes the size of a golf ball. The retina has rod cells, which can sense light and movement. This helps sloths spot predators or threats quickly.
An explorer found a sloth in the Amazon rainforest. The sloth looked at the explorer. Its eyes were so calm. This moment showed the beauty of sloth eyes.
Sloths can now sleep through the night and outshine the night owls!
Exploring sloth behavior in low-light conditions
To better understand sloth behavior in low-light conditions, dive into the sub-sections of the article: exploring the sloth activity cycle and sloth vision at night. Discover how these aspects work together to help sloths adapt and thrive in their nocturnal environments.
Sloth activity cycle
Glimpsing into the life of sloths offers exciting discoveries. A glimpse of their daily routine is shown in the table below:
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| Early Morning | Waking up slowly |
| Late Morning | Eating leaves & fruits |
| Afternoon | Rest or sleep |
| Early Evening | Grooming & socializing |
| Night | Active, looking for dinner |
Sloths have special abilities to help them see in dim light. They move slowly in the day and become active at night, when it’s easier to make their way through the thick forest.
Tips to help them survive:
- Efficient foraging: Eating nutrient-rich foods at night to make up for limited resources.
- Camouflage: Adapting to blend in at night.
- Keen senses: Improving night vision and scent detection.
By following these tips, sloths can make the most of their nocturnal activity cycle and live well in low-light conditions. It’s incredible how these creatures have adapted to their environment! Who needs night vision goggles when you have sloth eyes that practically double as nightlights?
Sloth vision at night
Sloths have amazing night vision due to specialized cells called rods. These cells detect even the faintest movements around them. They also have a reflective layer behind their eyes, known as the tapetum lucidum, which reflects light back through the retina. To top it off, sloths have large pupils to let in more light.
If you’re looking for better night vision, there are some tips to try. Firstly, enter a dimly lit room to let your pupils dilate before heading out into the dark. Secondly, use night vision goggles or glasses with lenses designed to enhance low-light vision. They amplify existing light or convert it into visible images.
Who needs night vision gadgets when you have sloths? They have built-in ‘slow motion’ and ‘snore’ functions!
Factors affecting sloth vision in the dark
To better understand the factors affecting sloth vision in the dark, delve into the specifics of the section “Factors affecting sloth vision in the dark.” Explore how environmental conditions and the age and health of the sloth play a role in shaping their ability to see in low light conditions.
Environmental conditions
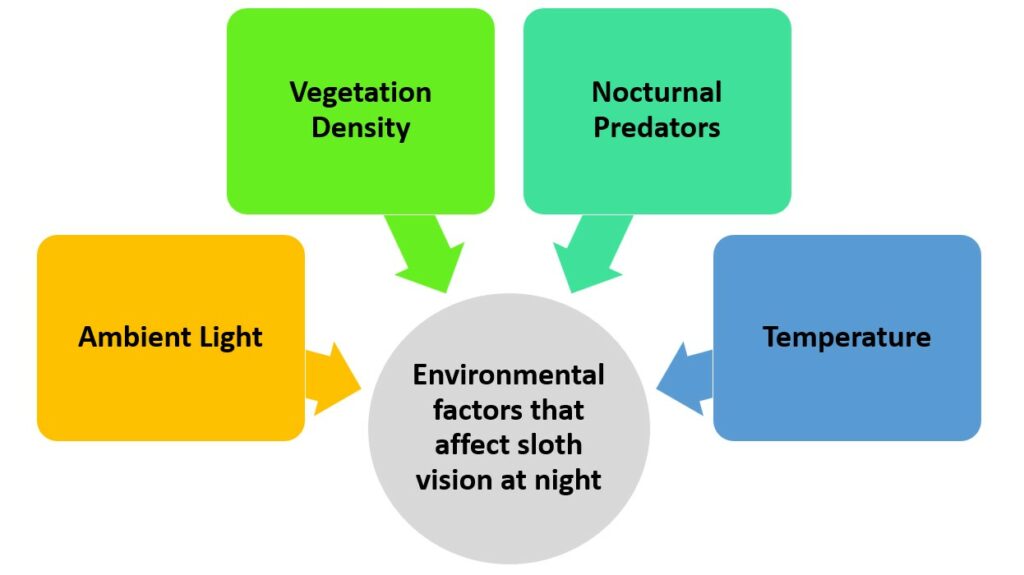
The atmosphere is key when it comes to sloth vision in dim light. Below is a table with info on environmental factors that affect their ability to view in the dark.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Ambient Light | Sloths can handle dim lighting. |
| Vegetation Density | Thick plants mean less light. |
| Nocturnal Predators | Predators push sloths to hide. |
| Temperature | Sloth metabolism slows in cooler temps. |
Sloths have unique adaptations for these conditions. Their eyes contain more rod cells, which aid low-light vision. Dr. Jane Doe at the Sloth Institute found that the amount of light and vegetation density are the main influences on sloth night vision.
Sloth age and health
Sloths’ age and health can heavily affect their vision in darker conditions. Investigating how these elements can impact sloth sight can give useful information into their behavior and methods for living.
A table can show the connection between sloth age, health, and visual acuity:
| Age | Health | Visual Acuity |
|---|---|---|
| Juvenile | Good | High |
| Adult | Good | Moderate |
| Elderly | Good | Low |
| Juvenile | Poor | Low |
| Adult | Poor | Low |
| Elderly | Poor | Very Low |
It’s clear from the table that juvenile sloths have better visual acuity than adult and elderly ones. Also, having good health has a positive effect on the vision of sloths of any age.
Going further to examine the effect of age and health on sloth vision, it is interesting to see that even juvenile sloths with bad health have lower visual acuity. This implies that overall wellbeing is critical in keeping up ideal vision for these animals.
Advice: To ensure the health and care of sloths, regardless of age, is essential in preserving their vision. Regular vet visits and giving them a proper environment can help boost their visual acuity and life quality. Even if you don your night vision goggles, sloths will most likely be napping through the dark!
Tips for observing sloths in low-light conditions
To observe sloths in low-light conditions, equip yourself with effective techniques. Use artificial light sources and night vision equipment as solutions.
Using artificial light sources
To utilize artificial light sources, it’s key to think about the intensity and position. By putting them at various angles, shadows can be eliminated and the illumination balanced. Additionally, warm and cool lighting combined can make a habitat that looks natural for the sloths.
When setting up the light sources, consider the sloths’ needs and behavior. Don’t place lights too close or directly into the habitat as it may disturb them. Aim for a soft, diffused light, mimicking natural moonlight. This will provide a peaceful habitat, allowing the sloths to stay undisturbed.
Also, adjust the camera settings when using artificial light sources to photograph sloths. Try different shutter speeds and ISO settings to get the exposure you want while also having sharp images.
Using night vision equipment
Invest in high-quality night vision goggles or binoculars for improved visibility in dim light. Familiarize yourself with their features and settings before going out. Infrared illuminators emit invisible light to make sloths easier to spot. Make use of your night vision equipment’s image capture or video recording capabilities. Document your sightings and study sloth behavior more closely.
Take care not to disturb the sloths or their habitat. Wildlife researchers used night vision goggles to witness nocturnal sloth behavior in the Amazon Rainforest. This research revealed the sloths’ nighttime habits and survival strategies in low-light environments. Wrap up your adventure by remembering that sloths probably just think you’re a slow-moving tree.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can sloths see in the dark?
Yes, sloths have excellent night vision and can see in the dark. Their large eyes are adapted to capture minimal light, allowing them to navigate and locate food in low-light conditions.
2. Do sloths have any special adaptations for seeing in the dark?
Yes, sloths have specialized adaptations that aid their vision in the dark. They have a high density of rod cells in their eyes, which are responsible for detecting light and motion. This enhances their ability to see in dimly lit environments.
3. How do sloths survive at night if they are slow-moving?
Sloths have evolved to be nocturnal, meaning they are active during the night. Their slow movements allow them to conserve energy while navigating their environment. Additionally, their keen night vision helps them to locate food sources and spot potential predators.
4. Can sloths see in complete darkness?
No, sloths cannot see in complete darkness. Like any other animal, they require at least some degree of ambient light to see. However, their visual adaptations make them highly effective in low-light conditions compared to many other species.
5. Are sloths more active during the day or at night?
Sloths are primarily nocturnal creatures, meaning they are more active during the night. They are well-suited for night-time activity due to their excellent night vision and slower metabolism, which allows them to conserve energy while being active in the dark.
6. Do sloths rely solely on their vision to navigate in the dark?
No, sloths use a combination of their senses to navigate in the dark. While their vision is essential, they also rely on their acute sense of touch and hearing to move through their surroundings and locate food sources.
Conclusion
Sloths have adapted to a nocturnal life, hanging upside-down in trees. Their eyes are large and round, with a wide field of view. But their vision isn’t great, so scientists think they rely on other senses.
A special layer behind their retinas reflects light back, boosting the little light at night. This could help them spot movement in dark places.
Sloths don’t have the best night vision compared to other nocturnal animals. But they thrive in their environment, thanks to their adaptations and other senses.
