
Image Credits: Sloth, Wkimedia Commons, CC By 2.0
Sloths: mysterious and seemingly lethargic creatures that live in the rainforests of Central and South America. Are they primates? This article aims to uncover the truth!
Do sloths have opposable thumbs? No. Instead, they possess long, sharp claws for hanging onto tree branches. What about agility and dexterity? Nope. Sloths move at snail’s pace and spend most of their lives in trees.
So, what sets sloths apart from primates? Their closest relatives are anteaters and armadillos – all three form a unique branch within the mammal family tree known as Xenarthra. Sloths have forward-facing eyes and high developed brains, but their evolutionary history is distinct.
This evolutionary path has granted sloths an extraordinary adaptation – a slow metabolism that enables them to conserve energy efficiently while getting sustenance from leaves. So, while primates have lots in common, sloths are certainly a unique species.
Key Takeaways
- Sloths are not primates, but they are part of the order Pilosa, which also includes anteaters.
- Sloths are known for their slow movement and hanging upside down from trees.
- There are two main species of sloths: two-toed sloths and three-toed sloths.
- Sloths have a unique digestive system that allows them to survive on a low-energy diet.
- Despite their slow nature, sloths are excellent swimmers.
- Sloths have a symbiotic relationship with algae and moths, which live in their fur and provide camouflage and nutrients.
- Conservation efforts are important to protect sloth populations, as they are vulnerable to habitat loss and human activities.
Evolutionary History of Sloths

Sloths have an intriguing evolutionary history that has befuddled scientists for decades. These special creatures belong to the Xenarthra group of mammals, which also includes anteaters and armadillos. Sloths’ evolutionary path can be traced back millions of years, providing precious understanding into how they have developed and adapted over time.
The Paleocene epoch saw the first signs of sloth-like mammals in the fossil record. These ancient ancestors established the foundation of the different group we know today. In the Eocene epoch, ground-dwelling sloths developed and began to live on land.
The Oligocene epoch witnessed a major shift as tree-dwelling sloth species appeared. This made way for them to inhabit arboreal habitats and gain specialized adaptations for climbing and hanging from branches.
The Miocene epoch was a time of expansion and diversification for sloth populations. They spread across various regions and tailored to different ecological niches. This led to two distinct lineages: three-toed sloths (Bradypodidae) and two-toed sloths (Megalonychidae).
Finally, the Pliocene epoch saw the two lineages further differentiate into the species we know today.
Exploring the evolutionary history of sloths reveals their extraordinary journey through the ages. By knowing their past, scientists get precious insights into their unique adaptations and roles in the ecosystem.
To understand the captivating story of sloth evolution, one must go deep into the intricacies hidden in their old lineage. Let us uncover the secrets that time has concealed and discover the amazing tale of these slow-moving wonders. Dig further to unlock the mysteries of sloth evolution and appreciate them more.
Characteristics of Sloths As Primates
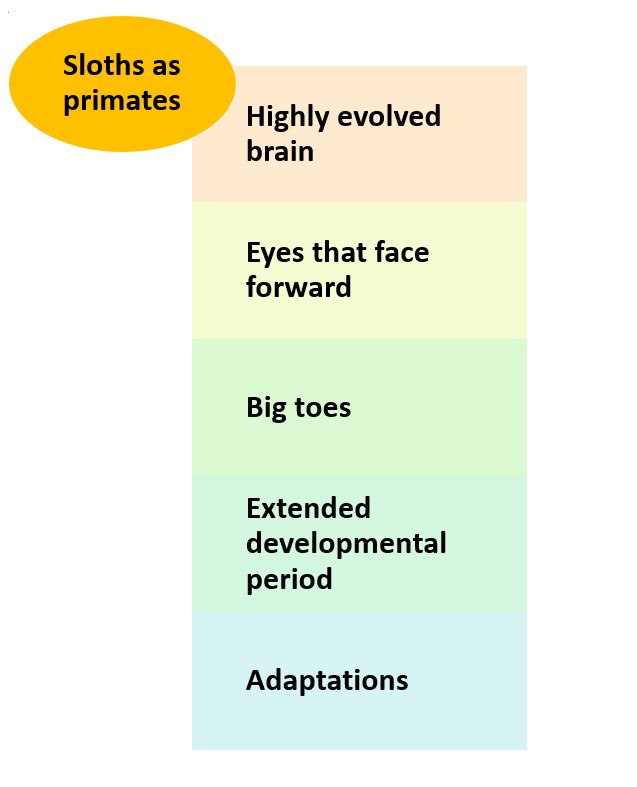
Primates are distinct from other animals, possessing special traits. These include a highly evolved brain, eyes that face forward with depth perception, hands and feet that can grasp, and flexible limbs. Plus, primates have opposable thumbs or big toes, enabling them to manipulate objects. They’re social creatures, living in complex groups, and have nails instead of claws. Vision is their navigational tool, not smell.
These mammals have an extended developmental period compared to many other animals. Their diet is varied, consisting of fruits, leaves, insects, and sometimes even small animals. Some primates use tools, such as for gathering food or defending against predators.
The study of primate evolution reveals they descended from a common ancestor millions of years ago, adapting to different environments and producing various species with different traits and behaviors. This knowledge allows us to appreciate the complexity and diversity of primates.
Skeletal and Genetic Evidence
Let us uncover the secrets of sloths and primates! We can explore this captivating topic by looking at their traits. Below is a table that shows similarities and differences between sloths and primates:
| Criteria | Sloths | Primates |
|---|---|---|
| Skeleton | Modified for arboreal lifestyle | Adapted to quadrupedal or bipedal locomotion |
| Diet | Mainly herbivorous | Omnivorous |
| Vision | Poor | Excellent |
We can observe that sloths have a modified skeleton which enables them to live in trees. Additionally, they mainly eat plants, whereas primates are omnivorous. Plus, sloths have poor vision compared to primates.
These findings lead to further research. We can look at their genetic makeup to understand their shared ancestry. Also, we can research how environment influences genetic expression and skeletal development. This could help explain why sloths possess distinct characteristics from other primates.
Debate and Alternative Views Of Sloths As Primates
Debate rages on about if sloths should be classed as primates. Let’s explore the different views on this.
| Criteria | For Sloths Being Primates | Against Sloths Being Primates |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Similar skeleton to others | Low metabolism rate |
| 2 | Forward-facing eyes | No opposable thumbs |
| 3 | Can hang from trees | Not much social behavior |
Still, sloths have characteristics of primates, for example their skeleton and forward-facing eyes. But, they also have traits that set them apart, such as a slow metabolic rate and no opposable thumbs.
Taxonomy and classification are complex. When considering how to classify sloths, it’s vital to have an open mind. Often, there is disagreement in the scientific world about where to place certain species.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are sloths primates?
A: Yes, sloths are indeed primates. They belong to the order Primates, which encompasses a wide range of mammals including humans, monkeys, and apes.
Q: What characteristics make sloths primates?
A: Sloths possess several key characteristics that classify them as primates. These include grasping hands and feet with long, curved claws, forward-facing eyes for binocular vision, and a highly adapted arboreal lifestyle.
Q: Do sloths share any similarities with other primates?
A: Yes, sloths share certain similarities with other primates. For instance, they have a similar skeletal structure and teeth arrangement. However, sloths have evolved unique adaptations to their arboreal habitat that set them apart from other primates.
Q: Are sloths closely related to monkeys and apes?
A: While sloths fall under the same order Primates as monkeys and apes, they are not closely related in terms of evolutionary lineage. Sloths belong to the suborder Folivora, whereas monkeys and apes belong to the suborder Haplorhini.
Q: Are sloths considered intelligent like other primates?
A: Sloths have a different type of intelligence compared to other primates. While they may not demonstrate complex problem-solving skills like monkeys or apes, they possess unique adaptations for survival in their habitat, such as slow movements and camouflage.
Q: Can sloths be found in the wild?
A: Yes, sloths are native to the rainforests of Central and South America and can be found in the wild. However, due to habitat destruction and other factors, some sloth species are endangered or threatened.
Conclusion
Sloths are primates! They are from the Pilosa order and belong to the family Bradypodidae. Though their movements are slow, sloths have adapted to life in trees and found an exclusive place in the primate family tree.
These mammals live in Central and South American rainforests. They may not be as agile or swift as other primates, but the sloth’s special lifestyle helps it survive in the treetops. Its long claws enable movement on branches, while its low metabolism helps it subsist on a diet of leaves.
Sloths possess features that are typical of primates. They have eyes that face forward, giving them binocular vision. Plus, they have an opposable thumb (or toe) on each limb – this helps with gripping and hanging onto branches.
If you’re lucky enough to spot a sloth in the wild, take a moment to observe it. You’ll be able to appreciate the unique adaptations that let these creatures thrive in their natural home.
