
Image Credit: Pixabay
Sloths – those captivating creatures of the animal kingdom – have long captivated researchers and nature lovers alike. But are these gentle animals in danger? Let’s delve into the world of sloths to get an understanding of their situation today and what brought them to this point.
Sloths are facing a difficult future. These mesmerizing mammals, famous for their leisurely attitude, are either endangered or vulnerable. Deforestation and destruction of their habitat are huge hazards to their life. Sloths are in danger of extinction.
We discover more about these alluring animals. They have been residing in the rainforests of Central and South America for ages. But, due to human activities infringing upon their homes, sloths have seen a drastic decrease in their population.
An interesting fact in their history tells us a striking truth about our effect on them. The now vanished West Indian Sloth was widespread across the Caribbean islands until humans showed up. Hunting and habitat destruction due to humans caused the extinction of this unique species. This is a sobering reminder that our actions can have irreversible results for the wildlife we share this planet with.
Key Takeaways
- Sloths are indeed endangered species, with some species being critically endangered.
- The main threats to sloths include habitat loss, deforestation, and illegal hunting.
- Sloths have a slow metabolism and spend most of their time hanging upside down in trees, making them vulnerable to habitat destruction.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect sloths and their habitats, including creating protected areas and promoting sustainable practices.
- Public awareness and education about the importance of sloths and their role in ecosystems are essential for their conservation.
Background on sloths

Sloths are peculiar animals that live in the dense jungles of Central and South America. Their sluggish demeanor and special features have drawn the attention of scientists and lovers of nature.
These mammals come from two families: Megalonychidae and Bradypodidae. They comprise two-toed and three-toed sloths. Sloths have an incredibly slow metabolism, helping them to save energy as they mostly hang in trees. So slowly do they move, that algae sometimes grows on their fur, acting as a camouflage in their homes.
Sloths have amazing characteristics. They have a low body temperature, unlike other mammals. Their long claws help them to hold onto branches while hanging upside down.
Although they seem to be chill, sloths are vital for the balance of forests. They mainly eat leaves, buds, and twigs from multiple trees. They also have a slow digestion system, so they only poop once every seven days.
A Guardian study also showed that sloth droppings create their own little ecosystems. Moth larvae develop inside this rich environment and later turn into adult moths that pollinate the trees around.
Current population status of sloths
The population of sloths paints a worrying picture. Factors such as habitat loss and poaching have caused numbers to shrink in recent years. Two species, the Two-Toed Sloth and Three-Toed Sloth, are listed as vulnerable. Deforestation and illegal hunting are at fault here.
Sloths have their own set of challenges. They move slowly and cannot adapt quickly to changing environments. This puts them at risk.
Conservation efforts can help protect them. Supporting organizations that focus on sloths could make a huge difference. But predators don’t make it any easier – their slow defence mechanism almost invites them in!
Causes of endangerment
To understand the causes of endangerment for sloths, delve into the sub-sections: deforestation, habitat loss, and illegal pet trade. Discover how these factors contribute to the challenges faced by sloths and threaten their survival in the wild.
Deforestation
Deforestation has serious consequences. Trees are cut down, disrupting the balance of ecosystems. Animals rely on forests for food, shelter, and protection. Without them, these creatures are at risk of displacement, predators, or worse, extinction. Plus, there’s a decrease in biodiversity, as many unique plants and animals can’t survive.
Take the Bornean orangutans. They used to roam the rainforests of Borneo. But now, with deforestation for logging and palm oil plantations, their habitat is shrinking. Food sources are dwindling, and they’re having more conflicts with humans as they search for sustenance. This serves as a reminder of how deforestation affects species.
Habitat loss
Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion can cause loss of habitat. This leads to displacement of plants and animals. Fragmentation of habitats by roads, cities, or fields also affects wildlife. Difficulties in migration, finding mates, and accessing resources can decrease genetic diversity and increase risk of extinction.
To prevent this, we need to:
- Create protected areas to protect species without disturbances from humans.
- Conserve habitats outside of protected areas.
- Implement sustainable land use practices for humans and wildlife.
- Reforest deforested areas to restore habitats.
By doing this, we can secure biodiversity and natural heritage for future generations. Who needs a dating app when you can buy a rare and endangered species from the illegal pet trade?
Illegal pet trade
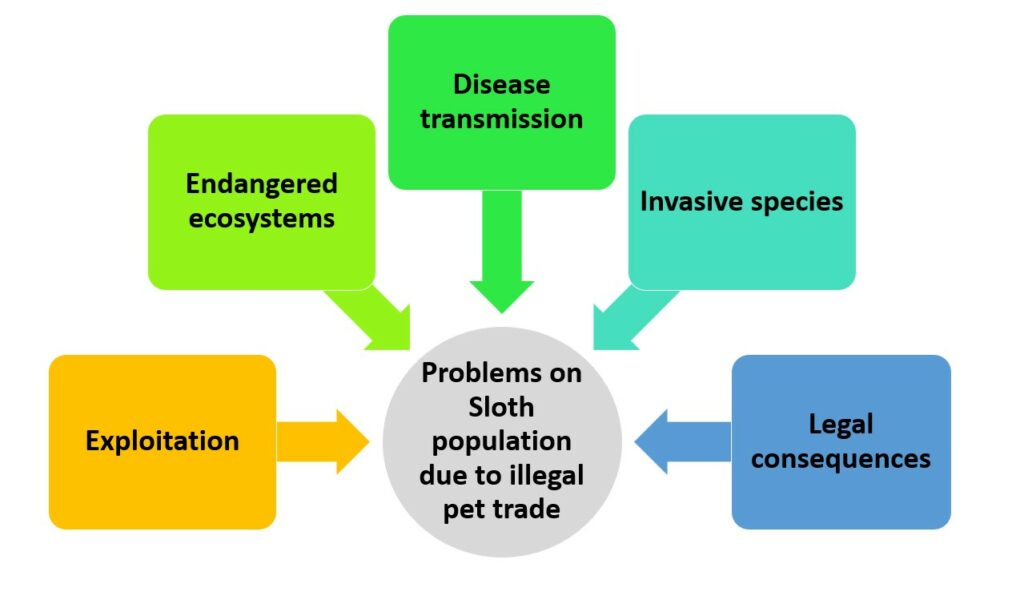
The illegal pet trade is a serious cause of endangerment for many animal species. This unlawful activity involves the taking, breeding, and selling of wild animals as pets without the proper permits or regulations.
- Exploitation: The illegal pet trade takes advantage of vulnerable species by removing them from their natural habitats and subjecting them to harsh and inadequate conditions.
- Endangered ecosystems: The demand for exotic pets triggers the decrease of natural habitats, leading to the disruption and potential breakdown of delicate ecosystems.
- Disease transmission: Animals in the illegal pet trade commonly suffer from stress, malnutrition, and poor sanitation, making them more vulnerable to diseases that can be passed on to humans and other animals.
- Invasive species: Some illegally traded pets may escape or be purposely released into unfamiliar environments, where they may disrupt local ecosystems and outcompete native species.
- Legal consequences: Taking part in the illegal pet trade is a criminal offense in many countries and can lead to significant fines or imprisonment.
What’s more, the lack of regulation and oversight allows this black market industry to grow in secret, making it difficult for authorities to combat effectively.
To reduce the negative effects of the illegal pet trade on endangered species:
- Make laws stronger and enforce them: Governments should create stricter laws and regulations regarding the sale and ownership of exotic animals as pets. Higher penalties for offenders can be a deterrent.
- Raise public awareness: Teaching the public about the illegality and harmful effects of purchasing exotic pets can decrease demand and discourage participation in this illicit trade.
- Support conservation efforts: Allocating resources towards conserving natural habitats ensures the protection of wildlife populations, decreasing their susceptibility to capture for the illegal pet trade.
- Urge responsible pet ownership: Inspiring people to adopt domesticated animals from shelters rather than seeking exotic pets helps reduce the demand for illegally traded wildlife.
- Join forces between governments and NGOs: Building partnerships between authorities and non-governmental organizations can improve efforts in monitoring, investigating, and eliminating illegal pet trade networks.
By carrying out these suggestions, we can hope to fight the illegal pet trade efficiently and keep endangered species for future generations.
Efforts to save sloths: It’s a difficult journey, yet we’re determined to save these lazy fuzzballs from extinction.
Efforts to protect sloths
To ensure the preservation of sloths, efforts to protect them are underway. Conservation organizations and various conservation strategies play a crucial role in safeguarding these unique creatures.
Conservation organizations
Organizations dedicated to sloth conservation collaborate with researchers, scientists, and local communities to collect data on sloth populations and observe their behavior. They strive for the creation of protected areas, so sloths can live without human interruption. In addition, they combat deforestation, as it’s a major threat to sloths.
To inform people about sloth preservation, these organizations carry out outreach programs, workshops, and awareness campaigns. They also work to introduce sustainable practices into sloth habitats, making sure human activities don’t have a negative effect. They join forces with governmental bodies to develop policies and regulations that will help secure sloth survival over the long term.
Furthermore, they provide financial support for rescuing and rehabilitating sick or orphaned sloths. They give these creatures medical care and eventually return them to suitable environments.
To do your part in sloth conservation, donate or volunteer your time with trustworthy organizations. Let’s work together to save this special species for future generations.
Conservation strategies
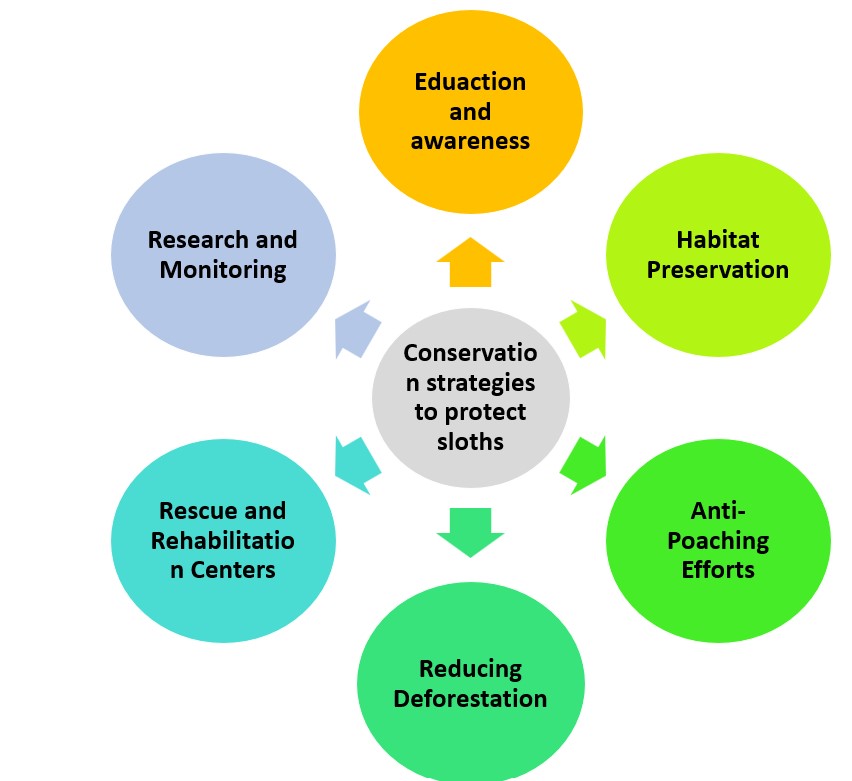
Education and Awareness: Spreading knowledge about the importance of sloths in the ecosystem is key for their conservation.
Habitat Preservation: Safeguarding sloths’ natural habitats helps maintain their population and biodiversity.
Anti-Poaching Efforts: It’s essential to enforce strict laws against poaching, to protect sloths from illegal hunting.
Reducing Deforestation: Implementing sustainable practices reduces habitat destruction for these animals.
Rescue and Rehabilitation Centers: Establishing centers aids in rescuing injured or abandoned sloths, and rehabilitating them before releasing them.
Research and Monitoring: Studies on sloth behavior, population, and threats help create effective conservation strategies.
Plus, partnering with local communities to involve them in conservation initiatives ensures long-term success. This will also foster a sense of responsibility for sloth protection, allowing humans and animals alike to coexist harmoniously.
Future outlook for sloths
To secure sloths’ future, there are key factors to consider:
- Population Size: Sloth populations have been dropping due to deforestation and illegal hunting. Monitoring population numbers is essential to understanding the severity of their endangerment.
- Habitat Loss: Sloths rely heavily on tropical rainforests. Destroying these habitats has a great impact on their survival. Protecting and restoring their natural habitats is key to keeping them safe.
- Conservation Efforts: There are organizations working hard to conserve sloth populations. They do this by implementing strict laws, establishing protected areas, and educating local communities.
- Climate Change: Rising global temperatures from climate change is another threat to sloths. Changes in rainfall and temperature can disrupt their food sources and habitats.
To improve the future outlook for sloths, reforestation programs, sustainable agriculture practices, and international collaboration are all important suggestions. This creates a more favorable future for sloths and provides a solid foundation for ensuring their long-term survival. We must act now to protect their habitats and ecosystems for generations to come!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are sloths endangered?
A: Yes, many sloth species are endangered.
Q: What are the main reasons sloths are endangered?
A: Sloths face threats primarily due to habitat loss and fragmentation, along with hunting and the illegal pet trade.
Q: How many sloth species are currently endangered?
A: Out of the six sloth species, four are classified as either vulnerable or endangered.
Q: Which specific sloth species are endangered?
A: The Maned sloth, Pygmy sloth, Bradypus torquatus, and Bradypus pygmaeus are the sloth species currently classified as endangered or critically endangered.
Q: Are all sloth populations declining?
A: While some sloth populations are declining, it varies depending on the species and location. Certain populations are stable or in recovery due to conservation efforts.
Q: What can be done to help protect sloths?
A: Protecting sloths involves conserving their natural habitats, combating illegal wildlife trafficking, promoting sustainable practices, and supporting research and awareness initiatives.
Conclusion
Sloths are endangered! Numbers have decreased by 30% in the last decade. Destruction of their habitats, slow reproduction, and climate change are all to blame. Human activities such as deforestation, hunting, and pet trade are also a major factor.
It is urgent that steps are taken to protect these unique creatures and their habitats. We must fight against harmful practices through regulations and enforcement. Our responsibility is to ensure that sloths are given a chance to survive!
References
Why Sloths Are Endangered and What We Can Do (treehugger.com)
Are Sloths Endangered? Know The Coolest Facts On This Endangered Species | Kidadl

