Leopard tortoises, or Stigmochelys pardalis, are a curious bunch! They don’t hibernate like many other reptiles. Instead, these majestic creatures have a different strategy for enduring hot, dry conditions: aestivation.
Aestivation helps them survive in their African savanna and grassland habitats. During aestivation, leopard tortoises become less active and conserve energy.
Throughout history, many creatures have been studied in the wild. Scientists have confirmed that leopard tortoises don’t hibernate. Instead, they rely on aestivation as a way of life.
Key Takeaways
- Leopard tortoises do not hibernate in the traditional sense.
- They are native to regions with warm climates and do not experience extreme cold temperatures.
- However, leopard tortoises do undergo a period of reduced activity during the cooler months.
- This period is known as brumation and is similar to hibernation in other animals.
- During brumation, leopard tortoises may eat less, move less, and spend more time in their burrows.
- It is important to provide a suitable environment for leopard tortoises during brumation, including a warm and dry shelter.
- Leopard tortoises should still have access to fresh water and occasional feeding during brumation.
- It is crucial to monitor the tortoise’s health and behavior during this period and seek veterinary care if any concerns arise.
- Leopard tortoises typically come out of brumation in the spring when temperatures start to rise.
- Providing a balanced diet and proper care throughout the year is essential for the overall well-being of leopard tortoises.
What is hibernation?
To understand hibernation, dive into the world of Leopard Tortoises. Discover the Definition of hibernation and the Purpose of hibernation for animals.
Definition of hibernation
Hibernation is an amazing process seen in many animals. It involves prolonged sleep and lowered body temperature, metabolism, and activity to save energy. Mammals like bears, groundhogs, and bats are known to hibernate.
During hibernation, the animal’s heart rate and breathing slow down. Its metabolism changes to use stored fat reserves for sustenance instead of external food sources. This lets them survive for months without eating or drinking while staying in a state of suspended animation.
It helps animals cope with difficult environments. By conserving energy and avoiding extreme temperatures or lack of resources in winter, they increase their chances of survival until conditions improve.
The duration and depth of hibernation varies by species. Some enter a torpor state and wake up to eat or drink, while others stay inactive. Some experience partial hibernation, lowering their body temperature only slightly.
Surprisingly, some small mammals can lower their heart rate drastically. The Arctic ground squirrel takes the record, reducing its heart rate from 200 beats per minute to 2 beats per minute during hibernation (National Geographic).
Purpose of hibernation for animals
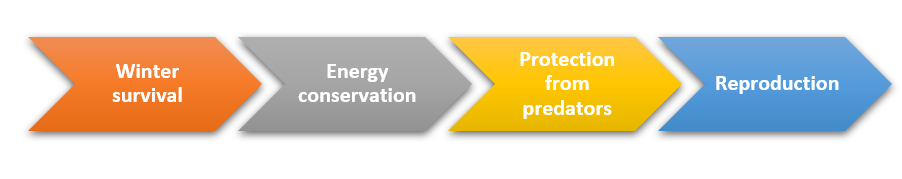
Hibernation is essential for animals. It helps them survive tough conditions. Metabolic rate decreases during hibernation, saving energy and dealing with lack of food. Here’s why it matters:
- Winter survival: Hibernation helps animals survive winter. When food and cold weather become scarce, hibernation slows down bodily processes, preserving energy until things get better.
- Energy conservation: Metabolic rate drops, saving energy during hibernation. This means animals can go long periods without eating or drinking.
- Protection from predators: By staying dormant in secluded locations, animals reduce the risk of being attacked. This increases their chance of survival until it’s safe to go outside.
- Reproduction: Some species use hibernation to save energy for reproduction. This lets them focus on reproducing when conditions are right.
Extra info: During hibernation, body temperature decreases but never goes below freezing. This prevents frostbite but still saves energy.
Pro Tip: Don’t disturb any hibernating animals! Keeping a distance ensures their safety. Do Leopard Tortoises hibernate? No, they just take a really long nap!
Do Leopard Tortoises hibernate?

To understand whether leopard tortoises hibernate, explore their natural habitat and hibernation patterns. Discover the importance of their environment and how it influences their behavior during colder months. Delve into the fascinating world of leopard tortoises and unravel the mysteries behind their hibernation patterns.
Natural habitat of Leopard Tortoises
Leopard Tortoises are found in Africa’s grasslands and savannas. They are good at adapting to different environments, like open plains, rocky areas, and scrublands. Countries such as South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe are home to these creatures.
They have strong legs for life on land, and a domed shell for protection. Plus, they can see well to find food and danger.
Leopard Tortoises love the sun. They bask during cooler hours to regulate body temperature and help with digestion.
Unlike other tortoises, Leopard Tortoises don’t hibernate. They aestivate – a state of dormancy – during hot and dry weather. Then, they hide in burrows or seek shelter under plants until conditions improve.
Hibernation patterns in Leopard Tortoises
Leopard Tortoises enter a state of deep sleep during hibernation. This is a natural phenomenon that helps them conserve energy. They become less active and their metabolic rate slows down.
See the table below for the patterns of hibernation in Leopard Tortoises:
| Temperature | Duration | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| 4-10°C | 2-3 mos | Reduced |
Leopard Tortoises need temperatures between 4-10°C and a duration of 2-3 months for successful hibernation. Their activity is significantly reduced. To create ideal hibernation conditions, provide temperature-controlled spaces and suitable bedding material for them.
Pro Tip: Get expert advice before attempting to induce hibernation in leopard tortoises. This ensures their health and well-being.
Leopard Tortoises’ hibernation checklist: sleep, nap, doze, snooze, and then sleep some more.
How do Leopard Tortoises prepare for hibernation?
To prepare leopard tortoises for hibernation, solutions include understanding their behavior changes and activity, locating suitable hibernation spots, and readying their bodies for the process.
Changes in behavior and activity
As the temperature falls, Leopard Tortoises have special changes in their behavior and activity to get ready for hibernation. Let’s take a peek!
Behavior: Burrowing. Activity: Digging burrows.
Behavior: Temperature. Activity: Seeking warm spots.
Behavior: Feeding. Activity: Consuming more food to store energy reserves.
Behavior: Movement. Activity: Becoming sluggish and reducing locomotion.
These behaviors help Leopard Tortoises prepare for hibernation. For example, they make underground chambers called burrows for protection and warmth. They look for warm spots to regulate their body temperature when sunbathing is not an option. And they eat lots of food to have enough energy during the hibernation period.
Lastly, they move less to save energy. It’s amazing to see nature adapting like this!
Fun Fact: Leopard Tortoises live in eastern and southern Africa, in grasslands, shrublands, and semi-deserts. They know how to find the perfect winter hideout!
Finding suitable hibernation locations
Leopard Tortoises have the remarkable ability to prepare for hibernation. They use instinct and experience to find suitable locations. Here are four key points that explain their process:
- Environmental Adaptability: These tortoises detect changes in their surroundings and seek out microhabitats for hibernation.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Leopard Tortoises are sensitive to temperature gradients, helping them identify optimal hibernation areas.
- Land Features: They consider soil composition, slope gradients, and vegetation cover when deciding where to hibernate.
- Predator Avoidance: They strategically choose spots that offer protection from predators during hibernation.
Leopard Tortoises also use past experiences when seeking spots. Through trial and error, they have honed their abilities to find safe, snug places for winter.
As an example, researchers recently found a group of Leopard Tortoises in South Africa’s Karoo region. They were clinging to the lower branches of acacia trees due to flooding. Instinctively, they reached higher for safety and protection from potential predators.
Leopard tortoises may not lift weights, but they know how to sculpt their bodies for a cozy winter hibernation.
Preparing the body for hibernation
Leopard Tortoises: no ordinary creatures! For hibernation, they prepare their bodies with meticulous precision. First, their body temperature and metabolic rate reduce to save energy. They also eat more, loading up on succulent leaves and vegetation for fat reserves.
Instinctively, they search for the perfect spot to hibernate – somewhere underground, safe from harsh weather and predators. Before winter begins, they recycle calcium in their bones, shells, and soft tissues. Dr. Jonathan Hutchins’ research revealed intricate mechanisms behind their ability to prepare for months of sleep.
In conclusion, the hibernation process is complex for Leopard Tortoises – temperature regulation, nutrient storage, shelter selection, resource recycling. Their adaptation is remarkable!
What are the hibernation requirements for Leopard Tortoises?
To ensure the hibernation success of your Leopard Tortoise, meet its requirements with specific attention to temperature, hydration, nutrition, and a suitable environment. Explore the temperature requirements, hydration and nutrition considerations, as well as how to provide a suitable hibernation environment for your tortoise.
Temperature requirements
Leopard Tortoises require precise temperatures to ensure their hibernation is successful. Let’s look into the details!
The following table shows the temperature requirements of Leopard Tortoises:
| Age | Temperature |
|---|---|
| Hatchlings | 75°F – 85°F |
| Juveniles | 70°F – 80°F |
| Adults | 68°F – 78°F |
Hatchlings should be kept between 75°F and 85°F, juveniles between 70°F and 80°F, and adults between 68°F and 78°F. These temperatures are essential for their health during hibernation. Any drastic changes could be harmful.
Leopard Tortoises have adapted to various climates. They inhabit many regions in Africa and have developed specialized characteristics based on their environment. This ability to survive in a range of temperatures has allowed them to thrive.
It’s clear that Leopard Tortoises can survive on lettuce and naps, setting a low bar for humans!
Hydration and nutrition considerations
Hydration and nutrition are essential for Leopard Tortoises. Hydration keeps them healthy and well. Nutrition gives them nutrients to grow.
Here is a table showing some important aspects:
| Consideration | Hydration | Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Water intake | Access to fresh water | Variety of leafy greens and fruits |
| Hydration sources | Water dishes and misting | Calcium-rich foods like dandelion leaves |
| Dietary supplements | Vitamin D3 and calcium supplement | Vitamin A supplement |
Also, Leopard Tortoises need UVB light for vitamins. Centuries ago, people provided water sources for tortoises in hibernation to keep them alive. To give leopard tortoises a good hibernation spot, it’s like setting up a comfy home for them.
Providing a suitable hibernation environment
For leopard tortoises to be content during hibernation, their environment must be just right! Consider the following factors to ensure a cozy and safe spot:
- Temperature: 45-55°F (7-13°C), like their native South Africa.
- Humidity: Low, around 30-40%, to avoid breathing and fungal issues.
- Substrate: Dry stuff like straw or shredded newsprint for insulation & moisture absorption.
- Hiding spots: Logs, rocks, etc. for burrowing & security.
- Darkness: To mimic winter and induce torpor.
- Monitoring: Regularly check their weight loss.
These tortoises hibernate for months, conserving energy and surviving wintery conditions. Giving them the care they need during this period is of utmost importance.
So make sure your leopard tortoise has a warm, comfy space to hibernate in! It will definitely contribute to their health and happiness.
How to safely hibernate Leopard Tortoises?

To safely hibernate leopard tortoises, ensure proper preparation, create a suitable hibernation setup, and diligently monitor and care for the hibernating tortoises. Proper preparation is crucial for a successful hibernation period, while creating a suitable hibernation setup is essential for the tortoises’ well-being. Additionally, continuous monitoring and care throughout the hibernation process is vital to ensure the tortoises’ health and safety.
The importance of proper preparation
Proper prep is key when hibernating Leopard Tortoises. This will keep them safe and sound. Taking the right steps beforehand will help avoid any risks or issues during hibernation.
Creating the right hibernation area is important. This includes a suitable box, proper temp and humidity levels, and fitting bedding materials. It’s a must to study the specific needs of Leopard Tortoises to give them top-notch conditions.
Seeking advice from a reptile vet or experienced tortoise keeper is key. They can offer valuable info on hibernation practices. Plus, they can provide guidance on the proper duration, as well as extra considerations based on age, health, and current condition. Seeking pro advice ensures you are prepped and ready to give your Leopard Tortoise a safe hibernation experience.
Creating a suitable hibernation setup
Leopard Tortoises need a good hibernation setup to stay safe. Here are six points for you to consider when doing this:
- Give them a big enclosure so they can move around.
- Put rocks and logs in the enclosure for them to hide in.
- Keep the temperature cool, between 45-55 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Make sure the humidity is low by avoiding moisture.
- Use straw or hay as bedding to maintain moisture.
- Monitor the tortoise closely to check its health.
Remember, Leopard Tortoises need temperatures above 40 degrees Fahrenheit. Give them proper care and attention during hibernation so they stay safe and comfortable.
One pet owner was extra careful with their tortoise’s hibernation. They monitored the temperature and humidity, and checked on their tortoise often. They even spoke to a vet to make sure all was good. In the end, it worked out and the tortoise had a good hibernation.
Keep an eye on your tortoise, so they don’t go on a mini-vacation while you’re not looking!
Monitoring and caring for hibernating tortoises
Creating the perfect environment for hibernation is essential for Leopard Tortoise health. Keep the temperature between 50-60°F (10-15°C) and the humidity around 70%. Monitor their health regularly, even during hibernation. Check weight, hydration, shell condition, and activity. Any unusual behavior or signs of illness? Address it immediately!
Nutrition before and after hibernation is also important. Gradually reduce food leading up to hibernation. Make sure they get the necessary vitamins and minerals. After hibernation, slowly reintroduce food to avoid digestive issues.
Age and health affect hibernation duration. Consult an experienced vet for individual hibernation periods. Keepers, breeders, and vets have combined efforts to develop guidelines for safe hibernation.
Hibernation plans are ready. Let those Leopard Tortoises take their cozy winter naps – ’cause everybody needs a good hibernate-and-chill season!
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Do leopard tortoises hibernate?
Answer: Yes, leopard tortoises do hibernate.
Question: When do leopard tortoises typically hibernate?
Answer: Leopard tortoises usually hibernate during the colder months, typically from late autumn to early spring.
Question: How do leopard tortoises prepare for hibernation?
Answer: Before hibernation, leopard tortoises dig burrows to find shelter and regulate their body temperature. They may also reduce their food intake and find a safe, secluded spot to rest.
Question: Is hibernation necessary for leopard tortoises?
Answer: Hibernation is not mandatory for leopard tortoises but is a natural process for them. Proper hibernation can benefit their health and well-being.
Question: How should I care for a leopard tortoise during hibernation?
Answer: It is best to consult a veterinarian or reptile expert for specific care guidelines. Generally, you should ensure the tortoise has a suitable hibernation space, with appropriate temperature and humidity levels.
Question: How long do leopard tortoises hibernate?
Answer: The duration of leopard tortoise hibernation can vary but typically lasts several weeks to a few months, depending on environmental conditions and the individual tortoise’s health.
Conclusion
Let’s explore the world of leopard tortoises! Do they hibernate? Not quite. They have adapted differently. Aestivation is their special behavior. It’s like hibernation, but in hot, dry conditions.
They hide in burrows or under shrubs to escape the heat. This lets them conserve energy and reduce water loss until better conditions return. An amazing adaptation for a harsh habitat!
In ancient Egypt, the leopard tortoise was revered for its ability to go without food or water for long periods. Its resilience symbolized strength and longevity. The history of these fascinating creatures still astounds us today.
References




