
The Tiger Shark is a formidable predator that prowls the oceans with tremendous strength and stealth. Its eye-catching stripes give it a regal look, but beneath its majestic exterior lies a creature of immense power and adaptability. With its sharp teeth and startling speed, the Tiger Shark has a reputation as one of the most menacing predators of the sea.
These remarkable animals can be discovered in warm waters across the globe, from Australia to South Africa. Their size alone is enough to send shivers down the spines of even the bravest swimmers. Adult Tiger Sharks can reach lengths of up to 15 feet and weigh more than 1,400 pounds – making them a force to be reckoned with in their watery domain.
The Tiger Shark is more than just an apex predator; it is a symbol of strength, beauty, and mystery. Every time we come across them in their natural habitat, it should fill us with awe and wonder. We should appreciate and protect these majestic creatures for future generations. Let’s not miss out on the chance to learn from them and be captivated by their resilience and adaptability.
Key Takeaways
- Tiger sharks are known for their distinctive appearance, with dark stripes or spots on their bodies that resemble a tiger’s pattern.
- These sharks are one of the largest species of sharks, with adult females reaching lengths of up to 14 feet and weighing over 1,400 pounds.
- Tiger sharks have a reputation for being opportunistic feeders and are often referred to as “garbage cans of the sea” due to their ability to consume a wide variety of prey, including fish, turtles, seals, and even garbage.
- They have a unique jaw structure that allows them to easily crush and consume hard-shelled prey, such as sea turtles and crustaceans.
- Tiger sharks are found in warm ocean waters around the world, including the coastal regions of the United States, Australia, and Africa.
- These sharks are known for their curiosity and are often observed investigating objects in their environment, including boats and divers.
- Tiger sharks are considered apex predators, meaning they are at the top of the food chain in their ecosystems.
- Despite their large size and predatory nature, tiger sharks are not typically a threat to humans. However, they have been involved in a small number of attacks, so caution should still be exercised when swimming in their habitats.
- Conservation efforts are important for protecting tiger sharks, as they are currently listed as a near-threatened species due to overfishing and habitat destruction.
- Studying the characteristics and behavior of tiger sharks can help researchers better understand the overall health and balance of marine ecosystems.
Physical Description of Tiger Sharks
Tiger sharks stand out among other shark species. Their dark stripes on the back and sides easily give them away. These powerful creatures typically measure 10 to 14 feet in length. Age and gender can make their size vary.
Their heads are wide and blunt, with strong jaws full of sharp, serrated teeth. That helps them eat a wide range of prey, like fish, turtles, seals and birds. Tiger sharks have small eyes on the sides of their heads, perfect for detecting movement around them.
Incredibly, tiger sharks can regulate their body temperature internally. That adaptation lets them live in a variety of water temperatures around the world. Plus, they’re known for migrating over long distances.
One amazing tiger shark, named ‘Daisy’, travelled more than 6,000 miles in 3 years! That trip stunned scientists and showed how capable these animals are.
So, do tiger sharks prefer luxurious oceanfront properties or are they just as happy living in the middle of nowhere? Let’s find out!
Habitat and Distribution of Tiger Sharks

Galeocerdo cuvier, also known as Tiger Sharks, can be found in a variety of habitats. From the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian and Mediterranean Oceans, they occupy coastal areas, coral reefs, estuaries and open-ocean regions.
Tiger Sharks often prefer to be alone but can tolerate living in groups. They have large ranges and migrate long distances in pursuit of food and mates. They’ve even been seen as far north as Norway and far south as New Zealand!
This species is remarkable for its ability to survive in both shallow waters close to shore and hundreds of meters below the surface.
Feeding Habits and Diet of Tiger Sharks
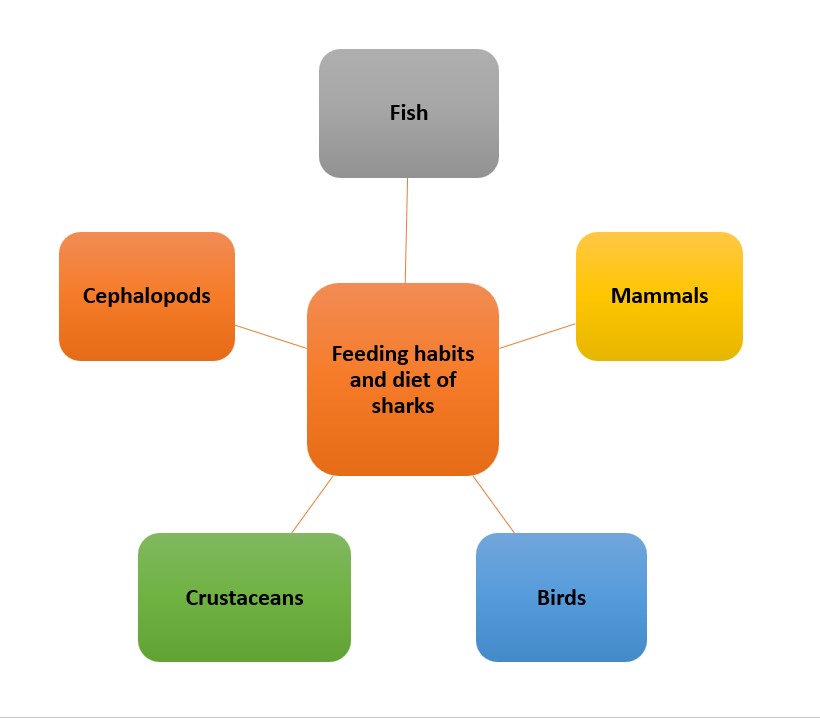
Tiger sharks boast unique feeding habits and a diverse diet. These apex predators have an insatiable appetite and are key to maintaining marine ecosystem balance.
Let’s take a closer look at the food they eat:
| Dietary Category | Prey |
|---|---|
| Fish | Tuna, mahi-mahi, etc |
| Mammals | Seals, dolphins, etc |
| Birds | Pelicans, seagulls |
| Crustaceans | Lobsters, crabs |
| Cephalopods | Squid, octopus |
This table shows the breadth of their diet – they’re not picky eaters! Additionally, they often scavenge carcasses and consume man-made objects that find their way into the ocean. This adaptability is why they’re such successful predators.
Plus, if you thought your dating life was complicated, wait until you hear about the reproduction and life cycle of tiger sharks!
Reproduction and Life Cycle of Tiger Sharks
Tiger sharks are renowned for their strength and majestic presence in the ocean. They have a unique reproductive strategy.
During mating season, males and females engage in a courtship dance. Males compete fiercely to win the favor of females. Mating happens through internal fertilization.
After fertilization, gestation lasts for about 16 months. Tiger sharks are viviparous; they give birth to live young instead of laying eggs. Females have litters of 10-80 pups, depending on size and age.
A true story highlights a pregnant female’s protective instincts towards her unborn offspring. Despite her usually aggressive nature, she allowed researchers to approach her closely. This rare moment gave insights into the reproductive behaviors and intelligence of tiger sharks.
Tiger sharks have a reputation for mistaking humans for a snack. Talk about a case of mistaken identity!
Interactions with Humans
Tiger sharks have a unique relationship with humans. They can bite us accidentally, scavenge for food near us, and be a part of ecotourism ventures. To understand them better, let’s look at the table below:
| Types of Interaction | Description |
|---|---|
| Accidental bites | Tiger sharks may mistake humans for prey, leading to accidental bites. This can happen when swimming or doing water activities in their habitats. |
| Scavenging behavior | Tiger sharks scavenge for food, which brings them close to human activity. This increases the chances of encounters. |
| Ecotourism impact | Tiger sharks are attractive to ecotourism. To keep both humans and sharks safe, regulations must be implemented. |
| Conservation efforts | Organizations are raising awareness about tiger sharks and fighting for their protection from human interference. |
Plus, these creatures have a special sensory system called electroreception. This lets them detect electrical signals from living organisms nearby, helping them navigate their environment.
As you explore coastal waters, remember: follow guidelines and don’t disrupt their natural behavior. Then, we can coexist peacefully while preserving our oceans.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the physical characteristics of tiger sharks?
Tiger sharks have a stout body with a large head and mouth, powerful jaws, and distinctive vertically striped markings on their sides, which give them their name. They can grow up to 16 feet in length and weigh over 1,400 pounds.
2. What is the average lifespan of a tiger shark?
The average lifespan of a tiger shark in the wild is estimated to be around 27 years. However, some individuals have been known to live up to 50 years under favorable conditions.
3. What is the diet of a tiger shark?
Tiger sharks are opportunistic predators and have a reputation for eating almost anything. Their diet includes fish, seals, sea turtles, dolphins, birds, and even other sharks. They are often referred to as “garbage cans of the sea.”
4. Are tiger sharks aggressive towards humans?
While tiger sharks are considered one of the most dangerous shark species, they do not typically seek out human prey. Most attacks on humans occur when mistaken identity or provocation takes place. It is important to exercise caution when swimming in their habitat.
5. Where can tiger sharks be found?
Tiger sharks have a wide distribution and can be found in tropical and temperate waters around the world. They prefer coastal areas and are commonly seen in the Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, and the Mediterranean Sea.
6. Are tiger sharks an endangered species?
Tiger sharks are currently listed as a near-threatened species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Their population has declined due to overfishing, habitat loss, and unintentional capture in fishing gear. Conservation efforts are being made to protect these remarkable creatures.
Conclusion
Tiger sharks are amazing animals with special qualities. They have long, slim bodies, strong jaws, and sharp senses. Plus, their noses are very powerful. This means they can smell prey from far away, so they’re great hunters. Plus, they have big mouths and sharp teeth, so they can eat a lot of different things, like fish, seals, and even turtles.
Also, tiger sharks have stripes on their bodies which get lighter as they get older. This helps them blend in with their surroundings and surprise their prey. Plus, they’re known to eat anything, even if it’s not their usual food.




